What Is Painful Bladder Syndrome/ Interstitial Cystitis
Painful Bladder Syndrome, also known as Interstitial Cystitis , refers to a persistent feeling of discomfort or pressure in the bladder region lasting for more than six weeks. You may often feel that you need to urinate, even without a bladder infection.
Symptoms of PBS/IC include urinary urgency and urinary frequency during the day as well as at night. Symptoms can be intermittent or constant and are often associated with irritable bowel syndrome and fibromyalgia. In addition, symptoms can fluctuate, flaring up in intensity and then subsiding or resolving.
Upon testing, the bladder may show signs of inflammation, areas of bleeding called glomerulations and/or cracks in the lining.
- The cause of PBS/IC is unknown. Several factors can contribute, including:
- Genetics such as having a family member with the condition
- Previous infection
- A defect in the bladder tissue that allows toxins to weaken the bladder wall or cause ulcers
- Changes to the nerves that allow normal bladder sensation
What Are The Symptoms Of Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome
Symptoms include:
- Urinary urgency.
- Only peeing a small amount.
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome symptoms vary among people. They may be mild or severe. They also may be constant or only appear occasionally.
If youre a woman or person AFAB, your symptoms often get worse when youre menstruating.
How Do Doctors Treat Ic
Researchers have not found one treatment for interstitial cystitis that works for everyone. Doctors aim current treatments at relieving symptoms in each person on an individual basis.
A health care professional will work with you to find a treatment plan that meets your needs. Your plan may include
- lifestyle changes
- bladder procedures
Some treatments may work better for you than others. You also may need to use a combination of these treatments to relieve your symptoms.
A health care professional may ask you to fill out a form, called a symptom scale, with questions about how you feel. The symptom scale may allow a health care professional to better understand how you are responding to treatment.
You may have to try several different treatments before you find one that works for you. Your symptoms may disappear with treatment, a change in what you eat, or without a clear reason. Even when your symptoms go away, they may return after days, weeks, months, or even years. Researchers do not know why. With time, you and your doctor should be able to find a treatment that gives you some relief and helps you cope with IC.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have A Bladder Infection Without Uti
Treatments That Should Not Be Offered
The treatments below appear to lack efficacy and/or appear to be accompanied by unacceptable adverse event profiles. See body of guideline for study details and rationales.
What Causes Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome
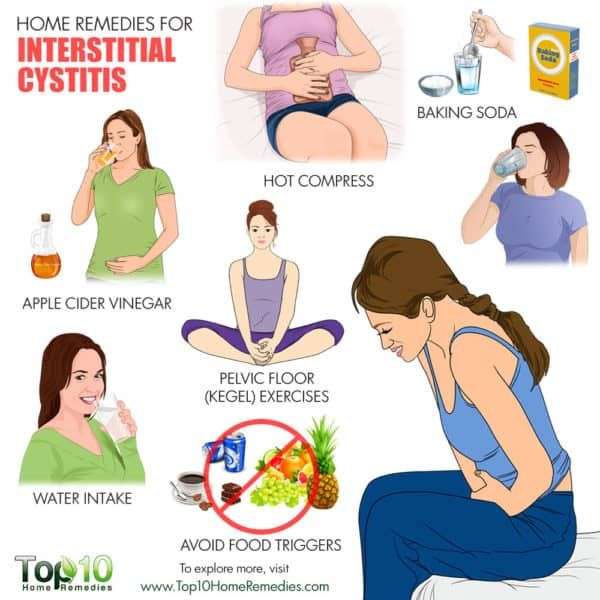
The cause of IC/BPS is still unknown and patients do not respond to antibiotic medication. Researchers are investigating many theories to understand the causes of IC and to determine appropriate treatments. Most people with IC find that certain foods make their symptoms worse, including most commonly: citrus fruits, tomatoes, chocolate, and coffee, and potassium-rich foods. Other foods that bother many patients are alcoholic beverages, caffeinated beverages, spicy foods, and some carbonated beverages.
Don’t Miss: What Medication Is Good For Bladder Infection
Where Can I Get More Information About Interstitial Cystitis
The support of family, friends, and other people with interstitial cystitis is very important to help you cope with this problem. People who learn about interstitial cystitis and participate in their own care do better than people who dont. To find information on IC/BPS support groups in your area, visit the International Painful Bladder Foundation website at www.painfulbladder.org.
What Is The Treatment For Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome
Specific treatment for IC will be determined by your doctor based on:
- Your age, overall health, and medical history
- Extent of the disease
- The presence of an ulcer in the bladder
- Your tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies
- Expectations for the course of the disease
- Your opinion or preference
Often times more than one treatment is necessary to optimally treat IC/BPS. In general your doctor will usually recommend the simplest treatments first. Treatments are primarily focused on relieving symptoms, and may include:
Consult your doctor with any questions of concerns you may have regarding this condition.
Don’t Miss: Best Thing For Bladder Infection
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome
To cite this guideline:
- Clemens JQ, Erickson DR, Varela NP et al: Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J Urol 2022 .
The purpose of this clinical guideline is to provide a clinical framework for the diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome , including discussion of treatments that should and should not be offered.
How Is Pbs/ic Diagnosed
To evaluate your condition, you will be asked questions regarding your symptoms. You may be asked to fill out a bladder diary which tracks voiding patterns and fluid intake. A physical examination will be performed to test your abdomen and the organs in your pelvis. See the chart that follows for additional tests that may be performed to assess your condition.
You May Like: How To Check Bladder Cancer
Association With Other Conditions
Some people with IC/BPS have been diagnosed with other conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome , fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, allergies, Sjögren syndrome, which raises the possibility that interstitial cystitis may be caused by mechanisms that cause these other conditions. There is also some evidence of an association between urologic pain syndromes, such as IC/BPS and CP/CPPS, with non-celiac gluten sensitivity in some people.
In addition, men with IC/PBS are frequently diagnosed as having chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, and there is an extensive overlap of symptoms and treatment between the two conditions, leading researchers to posit that the conditions may share the same cause and pathology.
What Happens When You See A Gp
BPS can have similar symptoms to long-term or frequent UTIs, so the GP may give you a urine test to check for a UTI.
Standard urine tests used in GP surgeries and hospitals may not pick up all infections of the bladder. You may be prescribed antibiotics to see if they help.
A GP may also suggest simple treatments such as:
- keeping a food diary and avoiding foods and drinks that make your symptoms worse
- stopping smoking chemicals in tobacco can irritate your bladder
You May Like: Whats The Difference Between A Uti And A Bladder Infection
Diagnosing Painful Bladder Syndrome
A definitive test to diagnose painful bladder syndrome has not yet been developed. Because many symptoms are similar to those of other urinary disorders, its often necessary to rule out other conditions through a variety of tests. Therefore, a doctor may order:
- A urinalysis to look for any organisms, signs of infection, red or white blood cells or excessive proteins
- A bladder wall biopsy to rule out bladder cancer and other conditions
- A cystoscopy, in which a small instrument is passed through the urethra and into the bladder so the doctor can examine it more closely
What Are The Symptoms Of Interstitial Cystitis/painful Bladder Syndrome
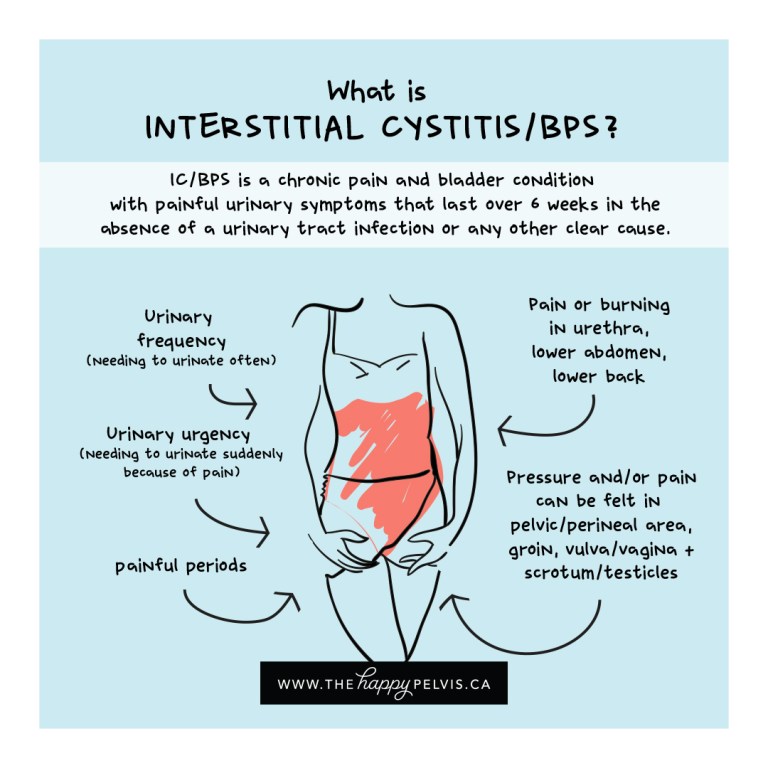
It is common to experience mild discomfort, pressure, tenderness or intense pain in your bladder and pelvic area. These symptoms often persist for many weeks. The intensity of your symptoms can often fluctuate and so be different on different days. Some days your symptoms are likely to be more severe than on other days.
In addition to this pain, you are likely to have symptoms such as needing to pass urine more frequently and/or pain on passing urine. You may also find that you are not able to hold on to urine for as long as you used to. Such symptoms will have lasted for more than six weeks and not have been found to be due to another cause such as infection.
You may feel pain when having sexual intercourse. IC/PBS can affect the way you exercise and sleep and can cause a great deal of distress. Without treatment, IC/PBS symptoms make it hard to get through your day or even to be able to work. This can really affect not only your life but also your relationship with your partner.
Some people with IC/PBS have other conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome and other pain syndromes.
You May Like: I Feel A Bladder Infection Coming On
Should I Limit The Amount Of Fluids I Drink
No. Many people with bladder pain syndrome think they should drink less to relieve pain and reduce the number of times they go to the bathroom. But you need fluids, especially water, for good health. Getting enough fluids helps keep your kidneys and bladder healthy, prevent urinary tract infections, and prevent constipation, which may make your symptoms worse.9
What Is Interstitial Cystitis/painful Bladder Syndrome
Interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome is a common condition that usually affects women in their 40s. It is a condition that results in recurring discomfort or pain in your bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. The symptoms can vary from person to person and even in the same individual.
This condition is thought to occur in around one in fifty women. Around a quarter of people with this condition will have actually had some symptoms since they were children.
You May Like: What Causes Losing Bladder Control
How Do You Fix Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Syndrome
You cant fix or cure IC/BPS. However, there are many ways to treat it. The goal of IC/BPS treatments is to relieve your symptoms. Your healthcare provider will work with you to decide the most appropriate treatment. In some cases, they may even combine treatments.
Healthcare providers cant predict how your body will respond to each treatment. Youll go through a process of trial and error with various treatments to see how your body responds. Your symptoms may go away or they may become more severe. Even if your symptoms disappear, they may return later.
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome treatments may include the following:
Diet changes
Some people who have IC/BPS report that certain foods and drinks worsen their symptoms . Keep a diary of what and how much you eat and drink each day. Noting what you eat and drink before the onset of symptoms and/or a flare-up can help you learn what foods and drinks to avoid.
If you notice that acidic foods or drinks citrus fruits, peppers, carbonated beverages, tomatoes cause flare-ups, your provider may recommend taking an antacid with meals. Antacids reduce the amount of acid that gets into your pee.
Common foods and drinks that may cause IC/BPS symptoms include:
Your provider may also refer you to a dietitian to help you create the best diet to reduce symptoms.
Physical activity
Exercise and physical activity may help relieve your IC/BPS symptoms. Examples of exercises include:
- Gentle stretching or yoga.
Surgery
Causes And Risk Factors For Interstitial Cystitis
The specific cause of IC is still not clearly known, but scientists have pinpointed several factors that may contribute to developing this condition:
- Trauma to the bladder, such as from pelvic surgery
- Pelvic floor muscle dysfunction
- Bladder overdistention if you repeatedly go long periods without urinating
- Autoimmune disorder
- Inflammation or hypersensitivity of the pelvic nerves
- Damage to the spinal cord
Many scientists believe that a trigger, such as one or more of these factors, may damage the bladder or its lining. This damage allows particles in the urine to leak into the lining, leading to further damage to the bladder and causing chronic pain.
Normally, the bladder repairs itself, but in people with IC it doesnt. Research shows that this might be because of a protein called APF that is produced by the cells of people with IC .
Read Also: Tb Virus To Treat Bladder Cancer
Supportive Therapies And Treatments
Some people may also find the following therapies and supportive treatments helpful:
- physiotherapy a specialist pelvic floor physiotherapist can help you relax your muscles to ease pain.
- acupuncture may help with pain relief
- talking therapies and counselling to help you cope with your symptoms and their impact on your life
- transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation where a small battery-operated device is used to relieve pain by sending electrical impulses into your body
- pain management ask the GP to refer you to a pain specialist
A Painful Bladder Syndrome
Interstitial cystitis, a painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic bladder condition in which a person feels pain or discomfort in the pelvic region. The bladder walls may be inflamed or irritated, and may be thickened or scarred. Interstitial cystitis can affect women and men, but is more common in women. Symptoms can range from mild to severe, and can seriously affect your quality of life.
Female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery specialists andpain management specialists can help you address pain or discomfort in the bladder or pelvic region, and manage symptom flare-ups.
Don’t Miss: What To Expect After Bladder Sling Surgery
How Can Pbs/ic Be Treated
Most patients benefit from a combination of treatments to manage their symptoms.
Diet:
Certain foods and fluids may make symptoms worse. Finding out which foods or fluids cause symptoms to flare can help you manage bladder pressure or pain.
Foods and drinks that seem to irritate the bladder may include:
- Carbonated drinks
- Lemon and grapefruit juice
- Artificial sweeteners
Not all of these items bother everyone. You need to determine which fluids and foods bother you.
Stress management:
Emotional and mental stress can play a role in your symptoms. Having strategies to decrease stress such as yoga, meditation and speaking with a mental health practitioner can help.
Pelvic floor physical therapy:
As with other areas of the body, the pelvic floor muscles can get tight when responding to pain and/or pressure. Strengthening these muscles is NOT recommended for patients with PBS/IC. A physical therapist specializing in pelvic health can teach you techniques for decreasing your symptoms through breathing, stretching and biofeedback.
Medication:
There are several medications that may help ease your symptoms but pentosan polysulfate sodium is the only one approved by the FDA for PBS/IC. Others, such as amitriptyline, heparin, hydroxyzine and cimetidine, may help with bladder pain.
Bladder installations:
A combination of medications can be inserted directly into your bladder in the doctors office to ease your symptoms.
Neuromodulation:
Botulinum Toxin :
Presentation Of Male Ic Patients
Historically, IC/BPS in men has been considered relatively unusual with a female to male ratio of 10:1.3, 59 However, uncontrolled clinical series over the past two decades have suggested the incidence of male IC/BPS may be higher than previously observed.5, 60 IC/BPS in men is diagnosed by identifying the same symptom complex that makes the diagnosis in women. That is, if the man fulfills the criteria established by the definition of IC/BPS , he can be assumed to have the disorder. In the MAPP Study which enrolled men and women with IC/BPS and/or CP/CPPS, about 3 out of 4 men had symptoms of painful bladder filling and/or painful urgency, consistent with IC/BPS. The data suggested that the overlap between IC/BPS and CP/CPPS in men is under-appreciated and that many men with CP/CPPS-like symptoms may in fact have IC/BPS if the bladder pain/storage symptoms are inquired. Men with IC/BPS is less likely to report perineal pain as their most bothersome symptom. Instead, men with IC/BPS are more likely to have suprapubic tenderness.58 Early clinical symptoms may begin with mild dysuria or urinary urgency. Mild symptoms may progress to severe voiding frequency, nocturia, and suprapubic pain.
You May Like: How Many Radiation Treatments For Bladder Cancer
Changes To Your Lifestyle
It is likely that you will be recommended to make some changes to your lifestyle, especially your diet. Certain foods and drinks can irritate the lining of your bladder and make your symptoms worse. These may include alcohol, tomatoes, spices, chocolate, caffeinated and citrus drinks and acidic foods. It may be worthwhile making a food diary to try to assess which foods aggravate and worsen your symptoms.
The simplest way to find out whether any foods bother your bladder is to try an elimination diet for one to two weeks. On an elimination diet, you stop eating all foods that could irritate your bladder. If your bladder symptoms improve while you are on the elimination diet, this means that at least one of the foods was irritating your bladder. The next step is to find out exactly which foods cause bladder problems for you. You should then try eating one food from the list of foods you stopped eating. If this food does not bother your bladder within 24 hours, this food is likely safe and can be added back into your regular diet. The next day, try eating a second food from the list, and so on. In this way, you will add the foods back into your diet one at a time and your bladder symptoms will tell you if any food causes problems for you.
Some people look at ways to reduce their stress levels, as this can actually improve their symptoms.
Treatment Categories For Ic/bps
The Panel assessed the available data for each treatment to determine whether a specific intervention demonstrated sufficient efficacy to be included as a treatment alternative. The types of studies available , quality of individual studies, consistency of outcome across studies, and generalizability of samples, settings, and interventions were examined, and overall evidence strength determined. The quality of individual studies is conceptually distinct from the categorization of overall evidence strength. For example, individual studies may be of high quality but if findings are contradictory or samples do not generalize well to the patient population addressed by the guideline, then evidence strength may be downgraded.
Given the lack of understanding regarding pathophysiological causal factors in IC/BPS and the consequence that treatment goals are to control symptoms to optimize QoL, the Panel judged that the most appropriate course was to preserve treatments as clinical choices as long as some efficacy for some patients was demonstrated and the risk of serious harms was low. In contrast, fulguration of Hunner lesions was designated a Recommendation because little to no uncertainty existed regarding the fact that benefits clearly outweighed risks/burdens. The same rationale led to the designation of manual physical therapy as a Standard if appropriately trained clinicians are available.
Read Also: Medication For Bladder Infection Over The Counter