Treating Bladder Cancer That Progresses Or Recurs
If cancer continues to grow during treatment or comes back after treatment , treatment options will depend on where and how much the cancer has spread, what treatments have already been used, and the patient’s overall health and desire for more treatment. Its important to understand the goal of any further treatment if its to try to cure the cancer, to slow its growth, or to help relieve symptoms as well as the likely benefits and risks.
For instance, non-invasive bladder cancer often comes back in the bladder. The new cancer may be found either in the same place as the original cancer or in other parts of the bladder. These tumors are often treated the same way as the first tumor. But if the cancer keeps coming back, a cystectomy may be needed. For some non-invasive tumors that keep growing even with BCG treatment, and where a cystectomy is not an option, immunotherapy with pembrolizumab might be recommended.
Cancers that recur in distant parts of the body can be harder to remove with surgery, so other treatments, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, or radiation therapy, might be needed. For more on dealing with a recurrence, see Understanding Recurrence.
What Are The Symptoms Of A Bladder Infection Vs A Uti
Symptoms can offer clues about whether youve got a bladder infection specifically or a UTI somewhere else in your system. Regardless of which type you have, youre likely to have some or all of the most common UTI symptoms, which MedlinePlus says includes:
- Pain or burning when you urinate
- Fever, tiredness, or shakiness
- An urge to urinate often
- Pressure in your lower abdomen
- Urine that smells bad or looks cloudy or reddish
- Pain in your back or side, below the ribs
If youre dealing with a bladder infection specifically, the CDC says you may experience the following symptoms:
- Pain or burning when you urinate
- Frequent urination
- Feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder
- Pressure or cramping in the groin or lower abdomen
Left untreated, a lower UTI or bladder infection can turn into a kidney infection, which the NIDDK says can lead to serious health issues like sepsis, kidney failure, or renal scarring in rare cases. According to the CDC, some common symptoms associated with kidney infections include:
- Lower back pain or pain in the side of your back
- Nausea or vomiting
The symptoms you experience with a UTI of any kind are importantthey can help clue your doctor into where the UTI is located, and which type of treatment will work best for your specific case. If you have any of the above symptoms, its important to seek medical care right away, to help treat whats going on and prevent any complications.
Who Has The Greatest Risk
- Individuals over 60 years of age
- Cigarette smokers
- Individuals who were exposed to certain industrial chemicals
Leiomyosarcoma is a rare type of cancer that affects smooth muscle tissue. These tumors are most common in the abdomen, but can occur anywhere in the body, including the uterus.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare type of cancer that forms in soft tissue specifically skeletal muscle tissue or sometimes hollow organs such as the bladder or uterus.
A medical doctor who specializes in the management and surgery of diseases of the genitourinary tract.
A colorless crystalline solid which readily forms water-soluble polymers.
A mucous membrane
The removal and microscopic examination of a tissue sample.
Visual examination of the inside of the bladder by means of a cystoscope .
Epithelium that lines the bladder mucosa, the renal pelvis, ureters and urethra
An imaging technique that uses beams of radiation to take an image of the body.
Medical subspecialty that studies tissue abnormalities caused by diseases. Biopsies and resection specimens are read and informed by surgical pathologists
The removal of tissue through the use of a cystoscope, without a surgical incision on the skin
Tubular structure that transports urine from the renal pelvis with the bladder
Vessels, connective tissue and cells providing support to epithelial cells
Carcinoma that resembles cancer originating in the skin
The process by which DNA is copied to make RNA
Cancer arising from stroma cells
Also Check: Bladder Cancer Mets To Bone
Other Types Of Bladder Cancer
Approximately 2% of bladder cancers are adenocarcinomas. Nonurothelial primary bladder tumors are extremely rare and may include small cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, primary lymphoma, and sarcoma . Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder accounts for only 0.3-0.7% of all bladder tumors. High-grade urothelial carcinomas can also show divergent histologic differentiation, such as squamous, glandular, neuroendocrine, and sarcomatous features.
What Is The Urinary Tract
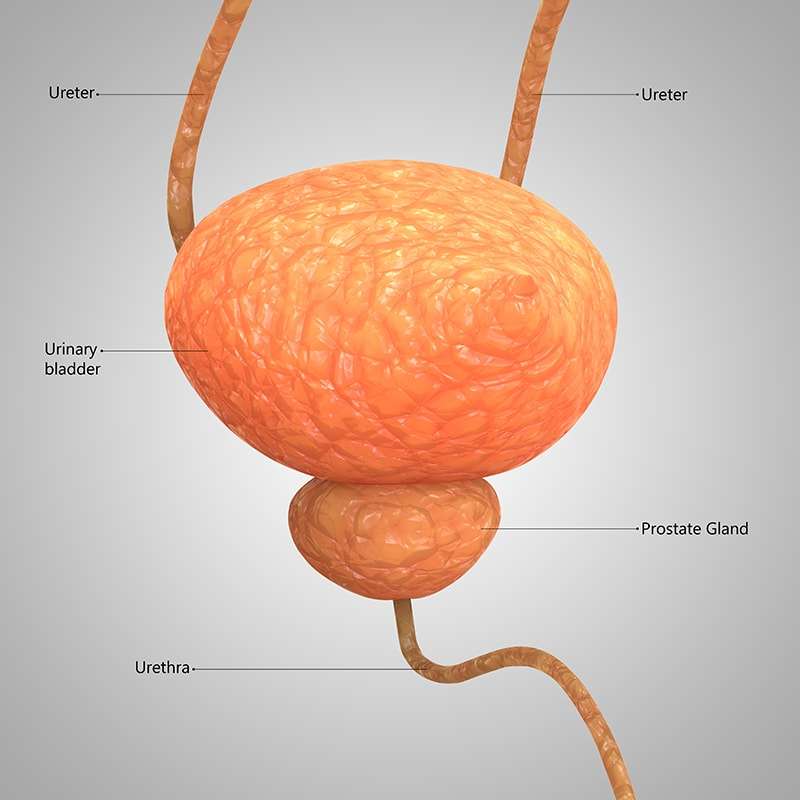
The urinary tract makes and stores urine, one of the bodys liquid waste products. The urinary tract includes the following parts:
- Kidneys: These small organs are located on back of your body, just above the hips. They are the filters of your body removing waste and water from your blood. This waste becomes urine.
- Ureters: The ureters are thin tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: A sac-like container, the bladder stores your urine before it leaves the body.
- Urethra: This tube carries the urine from your bladder to the outside of the body.
You May Like: Bladder Infection Bleeding Like Period
What Will Happen After Treatment
You’ll be glad when treatment is over. But its hard not to worry about cancer coming back. Even when cancer never comes back, people still worry about this. For years after treatment ends, you will see your cancer doctor. Be sure to go to all of your follow-up visits. People who have had bladder cancer are at high risk of having a second bladder cancer.
If you have no signs of cancer, most experts advise seeing with your doctor every 3 to 6 months. These visits might include urine tests, blood work, and other tests. If you still have your bladder, you will need regular exams of your bladder, too. The time between doctor visits may be longer after a few years if no new cancers are seen.
Having cancer and dealing with treatment can be hard, but it can also be a time to look at your life in new ways. You might be thinking about how to improve your health. Call us or talk to your doctor to find out what you can do to feel better.
You cant change the fact that you have cancer. What you can change is how you live the rest of your life making healthy choices and feeling as well as you can.
Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This is a medicine which affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- erectile dysfunction
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although there’s a chance they’ll be permanent.
Having radiation directed at your pelvis usually means you’ll be infertile for the rest of your life. However, most people treated for bladder cancer are too old to have children, so this isn’t usually a problem.
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
You may also be offered CT scans of your abdomen, pelvis and chest after 6 months, 1 year and 2 years. A CT scan of your urinary tract may be offered every year for 5 years.
Read Also: Will Bladder Infections Go Away By Themselves
Treatment For Stage 4 Bladder Cancer
Treatment for stage 4 bladder cancer may include:
- chemotherapy without surgery to relieve symptoms and extend life
- radical cystectomy and removal of the surrounding lymph nodes, followed by a surgery to create a new way for urine to exit the body
- chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and immunotherapy after surgery to kill remaining cancer cells or to relieve symptoms and extend life
- clinical trial drugs
, the five-year survival rates by stage are the following:
- The five-year survival rate for people with stage 0 bladder cancer is around 98 percent.
- The five-year survival rate for people with stage 1 bladder cancer is around 88 percent.
- The five-year survival rate for people with stage 2 bladder cancer is around 63 percent.
- The five-year survival rate for people with stage 3 bladder cancer is around 46 percent.
- The five-year survival rate for people with stage 4 bladder cancer is around 15 percent.
There are treatments available for all stages. Also, survival rates dont always tell the whole story and cant predict your future. Speak with your doctor about any questions or concerns you may have regarding your diagnosis and treatment.
Because doctors dont yet know what causes bladder cancer, it may not be preventable in all cases. The following factors and behaviors can reduce your risk of getting bladder cancer:
Permission To Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as NCIs PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: .
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Bladder Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated < MM/DD/YYYY> . Available at: . Accessed < MM/DD/YYYY> .
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author, artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Read Also: Can Endometriosis Affect Your Bladder
Legendary Nfl Quarterback Terry Bradshaw Reveals Serious Health News
- Publish date: Oct 2, 2022
BLOOMINGTON, MN – FEBRUARY 01: Former NFL player and NFL Hall of Fame player Terry Bradshaw attends SiriusXM at Super Bowl LII Radio Row at the Mall of America on February 1, 2018 in Bloomington, Minnesota.
Legendary NFL quarterback Terry Bradshaw shared some major health news on Sunday afternoon.
Bradshaw, a Hall of Fame quarterback for the Pittsburgh Steelers, revealed he’s overcome two different cancers over the past year.
Thankfully, Bradshaw is doing well now.
“Terry Bradshaw revealed on FOXs pregame show he is recovering from bladder cancer and skin cancer surgeries this year. He said he is cancer-free, but still getting back to normal,” Brad Galli tweeted.
It’s great to hear that Bradshaw is now cancer free.
Our thoughts are with Bradshaw and his friends and family as he overcomes these serious health issues.
Certain Factors Affect Prognosis And Treatment Options
The prognosis depends on the following:
- The stage of the cancer . Bladder cancer in the early stages can often be cured.
- The type of bladder cancer cells and how they look under a microscope.
- Whether there is carcinoma in situ in other parts of the bladder.
- The patients age and general health.
If the cancer is superficial, prognosis also depends on the following:
- How many tumors there are.
- The size of the tumors.
- Whether the tumor has recurred after treatment.
Treatment options depend on the stage of bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: How To Diagnose Bladder Infection
Treating Stage Ii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have invaded the muscle layer of the bladder wall , but no farther. Transurethral resection is typically the first treatment for these cancers, but it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it.
When the cancer has invaded the muscle, radical cystectomy is the standard treatment. Lymph nodes near the bladder are often removed as well. If cancer is in only one part of the bladder, a partial cystectomy may be done instead. But this is possible in only a small number of patients.
Radical cystectomy may be the only treatment for people who are not well enough to get chemo. But most doctors prefer to give chemo before surgery because it’s been shown to help patients live longer than surgery alone. When chemo is given first, surgery is delayed. This is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the bladder cancer, but it might be harmful if the tumor continues to grow during chemo.
If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
For people who have had surgery, but the features of the tumor show it is at high risk of coming back, the immunotherapy drug, nivolumab, might be offered. When given after surgery, nivolumab is given for up to one year.
For patients who cant have surgery because of other serious health problems, TURBT, radiation, chemotherapy, or some combination of these may be options.
Transurethral Resection Of A Bladder Tumour
If abnormalities are found in your bladder during a cystoscopy, you should be offered an operation known as TURBT. This is so any abnormal areas of tissue can be removed and tested for cancer .
TURBT is carried out under general anaesthetic.
Sometimes, a sample of the muscle wall of your bladder is also taken to check whether the cancer has spread, but this may be a separate operation within 6 weeks of the first biopsy.
You should also be offered a dose of chemotherapy after the operation. This may help to prevent the bladder cancer returning if the removed cells are found to be cancerous.
See treating bladder cancer for more information about the TURBT procedure
Don’t Miss: Reasons For Lack Of Bladder Control
Prognosis And Survival For Bladder Cancer
If you have bladder cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for bladder cancer.
Bladder Reconstructions And Stomas
If you have had your bladder removed, the way you pass urine will change. There are several options that your treatment team will talk to you about:
- Urostomy is where doctors create a new hole in your abdomen called a stoma. Urine drains from the stoma to the outside of your abdomen into a special bag.
- Neobladder is where a new bladder made from your small bowel forms a pouch inside your body to store urine. You will pass urine by squeezing your abdominal muscles. You will also pass a small tube into the neobladder each day to help drain the urine.
- Continent urinary diversion is a pouch made from your small bowel inside your body to store urine. The urine empties through a hole called a stoma to the outside of your abdomen into a special bag.
A bladder reconstruction is a big change in your life. You can speak with a continence or stomal therapy nurse for help, support and information. You can also call Cancer Council . You may be able to speak with a trained Cancer Council volunteer who has had cancer for tips and support.
If you find it difficult to adjust after your bladder reconstruction, it may help to be referred to a psychologist or counsellor.
Note: If you have a stoma, you can join a stoma association for support and free supplies. For more information about stoma associations, visit the Australian Council of Stoma Associations.
Recommended Reading: What Medication Is Good For A Bladder Infection
About Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections are common infections that can affect the bladder, the kidneys and the tubes connected to them.
Anyone can get them, but theyre particularly common in women. Some women experience them regularly .
UTIs can be painful and uncomfortable, but usually pass within a few days and can be easily treated with antibiotics.
This page is about UTIs in adults. There is a separate article about UTIs in children.
This page covers:
Whats Usually The First Symptom Of Bladder Cancer
Blood in your pee is the most common bladder cancer symptom. That said, simply having blood in your pee isnt a sure sign of bladder cancer. Other conditions cause this issue, too. But you should contact a healthcare provider whenever you spot blood in your pee. Other bladder cancer symptoms include:
- Visible blood in your pee : Healthcare providers can also spot microscopic amounts of blood in pee when they do a urinalysis.
- Pain when you pee : This is a burning or stinging sensation that you may feel when you start to pee or after you pee. Men and DMAB may have pain in their penises before or after peeing.
- Needing to pee a lot: Frequent urination means youre peeing many times during a 24-hour period.
- Having trouble peeing: The flow of your pee may start and stop or the flow may not be as strong as usual.
- Persistent bladder infections: Bladder infections and bladder cancer symptoms have common symptoms. Contact your healthcare provider if you have a bladder infection that doesnt go away after treatment with antibiotics.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Control Products By Mail