Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
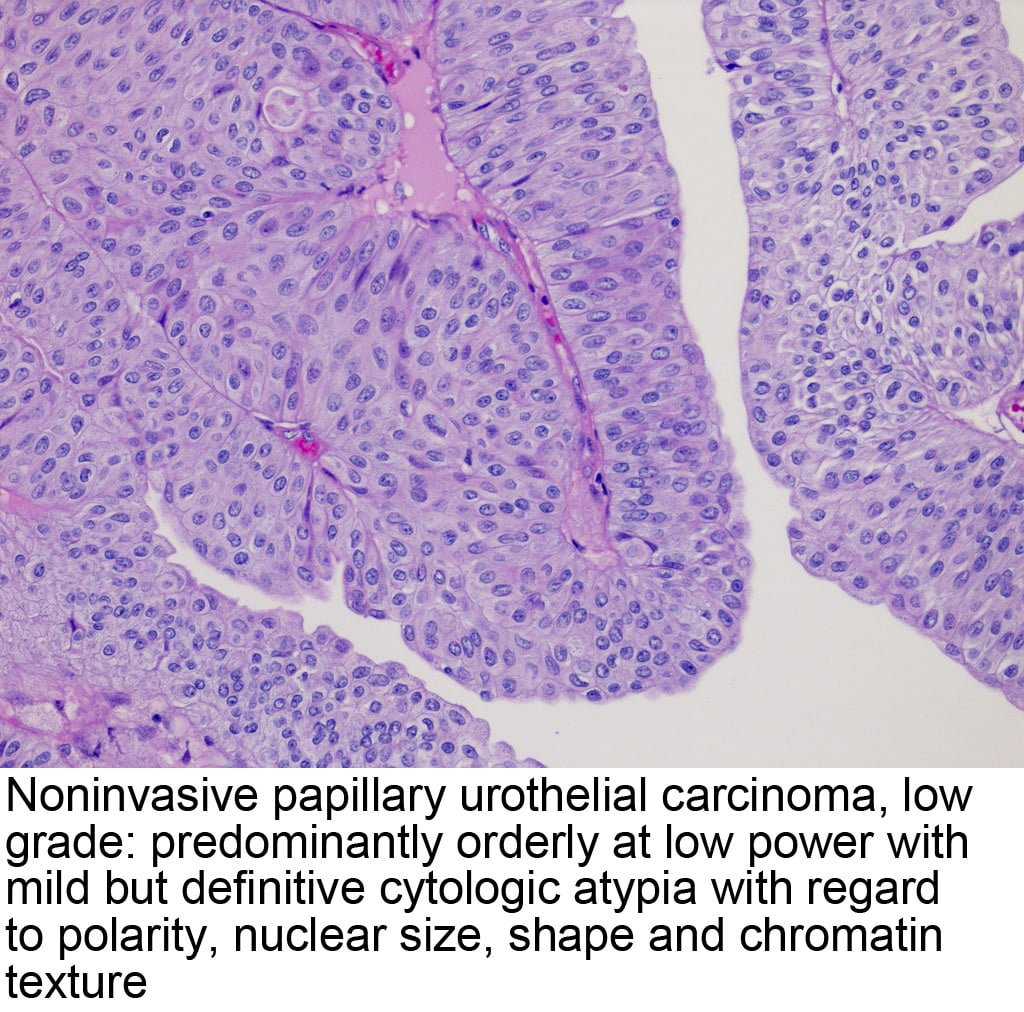
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
Urothelial Cis Without Ihc
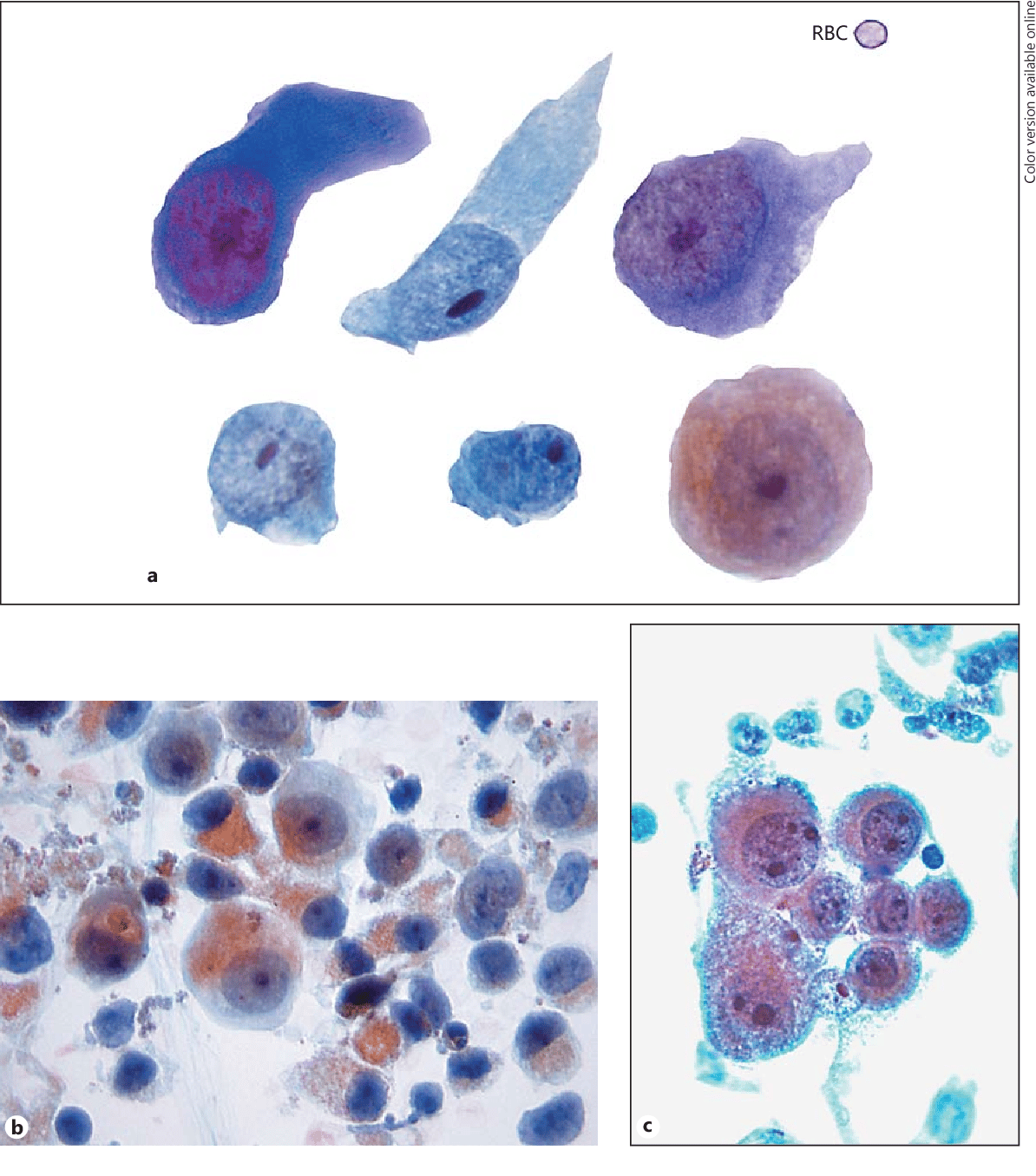
All cases of urothelial CIS without IHC were positive for AMACR with a mean intensity of 2.1. The percentage of cases with positive or partially positive AMACR expression was significantly greater for urothelial CIS without IHC compared to urothelial CIS with IHC . The mean intensity was greater in the group urothelial CIS with IHC compared to without IHC, but the difference was not significant . The rate of positivity of AMACR was significantly lower for non-neoplastic urothelium with IHC compared to urothelial CIS without IHC and urothelial CIS with IHC .
Donât Miss: What Is The Prognosis For Skin Cancer
What Causes Bladder Cancer And Am I At Risk
Each year, about 83,730 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States. It affects more men than women and the average age at diagnosis is 73.
Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor for bladder cancer. About half of all bladder cancers are caused by cigarette smoking. Other risk factors for developing bladder cancer include: family history, occupational exposure to chemicals , previous cancer treatment with cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, or pelvic radiation, the medication pioglitazone, exposure to arsenic , aristolochic , bladder infections caused by schistosoma haematobium, not drinking enough fluids, a genetic condition called Lynch Syndrome, a mutation of the retinoblastoma gene or the PTEN gene. and neurogenic bladder and the overuse of indwelling catheters.
Also Check: Antibiotics Given For Bladder Infection
You May Like: Bladder Infection Back Pain Right Side
Start And Spread Of Bladder Cancer
The wall of the bladder has many several layers. Each layer is made up of different kinds of cells .
Most bladder cancers start in the innermost lining of the bladder, which is called the urothelium or transitional epithelium. As the cancer grows into or through the other layers in the bladder wall, it has a higher stage, becomes more advanced, and can be harder to treat.
Over time, the cancer might grow outside the bladder and into nearby structures. It might spread to nearby lymph nodes, or to other parts of the body.
Metastatic Bladder Cancer Treatment
Without a professional evaluation, it can be difficult to know if the symptoms youre experiencing are the result of bladder cancer or something else. While its important not to panic most of these issues can be caused by other, less serious conditions its also important to talk with an expert if you notice something out of the ordinary. The earlier that bladder cancer is detected, the more treatment options youre likely to have.
You May Like: Bladder Infection In Toddler Girl Symptoms
Recommended Reading: Does Alcohol Cause Bladder Infections
Health Literacy To Empower Patients
With the right information, patients can make the best decisions about their care. By partnering with patients, healthcare providers, and hospitals, we hope to provide all patients with the tools and knowledge to understand their pathology report.
For more information about this site, contact us at .
Disclaimer: MyPathologyReport.ca is a registered not-for-profit charity . The articles on MyPathologyReport are intended for general informational purposes only and they do not address individual circumstances. The articles on this site are not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment and should not be relied on to make decisions about your health. Never ignore professional medical advice in seeking treatment because of something you have read on the MyPathologyReport site. MyPathologyReport is independently owned and operated and is not affiliated with any hospital or patient portal.
Copyright © 2021. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
Our work is generously supported by:
What Are The Pathological Outcomes Of Second Tur
Pathological outcomes from second TURs in patients with high-grade T1 are associated with prognosis. Herr et al. conducted a study in a cohort of 352 patients with T1 on initial TUR, and compared progression according to pathological outcome on second TUR. Of the 92 patients with residual T1 cancer, 82% progressed to muscle invasion within 5 years compared to 19% of those who had no or non-T1 tumor detected on restaging TUR. Dalbagni et al. performed a retrospective review of pathological outcomes from second TURs in 523 patients with T1 on initial TUR, and suggested that patients with T1 disease on restaging had a higher risk of progression thus early cystectomy should be considered.
Read Also: Small Cell Bladder Cancer Survival Rate
Cancer May Spread From Where It Began To Other Parts Of The Body
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if bladder cancer spreads to the bone, the cancer cells in the bone are actually bladder cancer cells. The disease is metastatic bladder cancer, not bone cancer.
Also Check: Why Is My Bladder So Weak All Of A Sudden
What Is The Best Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Most bladder cancers are initially treated with TUR , and high-grade T1 disease is diagnosed from clinical specimens. Therefore, the role of urologists and pathologists is important for accurate diagnosis of high-grade T1. The outcome of TUR is highly variable depending on the skills of urologists thus an educational program is recommended for effective TUR. The extended TUR technique, which obtains additional specimens from the bottom of the tumor and grossly normal-appearing margin sites could improve the outcomes of TUR . Bipolar equipment is an advantage of TUR because it appears to cause little tissue distortion and has the potential to facilitate the staging and grading of bladder tumors, although clinical outcomes are not different from those obtained with monopolar equipment . Photodynamic diagnosis or narrow-band imaging increases the sensitivity of cystoscopy, but whether it lowers the tumor recurrence rate is under debate .
Don’t Miss: Icd 10 Code For Bladder Cancer
Cellular Classification Of Bladder Cancer
More than 90% of bladder cancers are transitional cell carcinomas derived from the uroepithelium. About 2% to 7% are squamous cell carcinomas, and 2% are adenocarcinomas. Adenocarcinomas may be of urachal origin or nonurachal origin the latter type is generally thought to arise from metaplasia of chronically irritated transitional epithelium. Small cell carcinomas also may develop in the bladder. Sarcomas of the bladder are very rare.
Pathologic grade of transitional cell carcinomas, which is based on cellular atypia, nuclear abnormalities, and the number of mitotic figures, is of great prognostic importance.
References
You May Like: Body Cancer Symptoms
Treatment For Hg Pt1 Bladder Cancer With Pt2 Or More Histology At Second Tur
There is no doubt about the need to perform radical cystectomy for patients with muscle-invasive disease at the second TUR. Most of these tumors are understaged at the initial TURBT due to technical problems, and may not be large or bulky like muscle-invasive tumors that are diagnosed at the initial TURBT and/or with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. The discussion on the treatment strategies for these tumors does not include whether cystectomy should be performed but whether neoadjuvant chemotherapy and/or extended lymph node dissection should be performed.
Several randomized Phase III trials and meta-analyses demonstrated the survival benefit of cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with MIBC. However, whether neoadjuvant chemotherapy prolongs the survival of patients with T1 cancer at the initial TURBT and with muscle-invasive disease detected by a second TUR is unclear. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy offers potential advantages in tumor downstaging and eradication of micrometastases, so this therapy should be indicated for patients who have risk factors for locally advanced disease or nodal metastasis.
Also Check: Why Does My Bladder Feel Irritated
Treating Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the pelvic or abdominal wall , may have spread to nearby lymph nodes , and/or have spread to distant parts of the body . Stage IV cancers are very hard to get rid of completely.
Chemotherapy is usually the first treatment if the cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body . The tumor is then rechecked. If it appears to be gone, chemo with or without radiation or cystectomy are options. If there are still signs of cancer in the bladder, chemo with or without radiation, changing to another kind of chemo, trying an immunotherapy drug, or cystectomy may be recommended.
Chemo is typically the first treatment when bladder cancer has spread to distant parts of the body . After this treatment the cancer is rechecked. If it looks like itâs gone, a boost of radiation to the bladder may be given or cystectomy might be done. If there are still signs of cancer, options might include chemo, radiation, both at the same time, or immunotherapy.
In most cases surgery cant remove all of the cancer, so treatment is usually aimed at slowing the cancers growth and spread to help people live longer and feel better. If surgery is a treatment option, itâs important to understand the goal of the operation whether itâs to try to cure the cancer, to help a person live longer, or to help prevent or relieve symptoms from the cancer.
Because treatment is unlikely to cure these cancers, many experts recommend taking part in a clinical trial.
Evaluation Of Upper Urinary Tract
Additional workup for all patients with bladder cancer includes evaluation of the upper urinary tract with intravenous urography , renal ultrasonography, computed tomography urography, or magnetic resonance urography.21,22 Renal ultrasonography alone is insufficient to complete the evaluation of hematuria in a patient with bladder cancer because it cannot delineate details of the urinary collecting system. Traditional IVU has been largely replaced by CT urography because of increased detail and data combined in the CT .
For patients unable to undergo contrast injection , magnetic resonance urography may be used to evaluate the upper urinary tract. These tests are useful for disease staging and excluding other causes of hematuria. Pelvic imaging should be performed before transurethral resection to improve staging accuracy because postoperative inflammation mimics the appearance of tumor infiltration.21 Pelvic imaging also may detect synchronous upper tract urothelial cancer, which can occur in 5 percent of patients with bladder cancer.22
Recommended Reading: Tuberculosis Virus To Treat Bladder Cancer
Types Of Bladder Cancer
The type of bladder cancer depends on how the tumors cells look under the microscope. The 3 main types of bladder cancer are:
-
Urothelial carcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma accounts for about 90% of all bladder cancers. It also accounts for 10% to 15% of kidney cancers diagnosed in adults. It begins in the urothelial cells found in the urinary tract. Urothelial carcinoma is sometimes also called transitional cell carcinoma or TCC.
-
Squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cells develop in the bladder lining in response to irritation and inflammation. Over time, these cells may become cancerous. Squamous cell carcinoma accounts for about 4% of all bladder cancers.
-
Adenocarcinoma. This type accounts for about 2% of all bladder cancers and develops from glandular cells.
There are other, less common types of bladder cancer, including sarcoma of the bladder and small cell bladder cancer, among others. Sarcomas of the bladder often begin in the fat or muscle layers of the bladder. Small cell bladder cancer is a rare type of bladder cancer that is likely to spread to other parts of the body.
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
Read Also: Bladder Cancer In Dogs Treatment
Other Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk Factors
Having bladder diverticula may increase an individuals chance of developing SCC. Rarely, bacillus Calmette-Guerin treatment for CIS has been reported to lead to development of SCC. Development of bladder cancer at a younger age has been associated with bladder exstrophy. SCC has also been described in urachal remnants.
Coffee consumption does not increase the risk of developing bladder cancer. Early studies of rodents and a minority of human studies suggested a weak connection between artificial sweeteners and bladder cancer however, most recent studies show no significant correlation.
Donât Miss: Stage 3 Melanoma Survival Rate
Summary Of Evidence And Guidelines Forstratification Of Non
|
Summary of evidence |
|
|
The EAU NMIBC 2021 scoring model and risk tablespredict the short- and long-term risks of disease progression in individualpatients with primary NMIBC using either the WHO 1973 or the WHO 2004/2016classification system . |
|
|
The 2006 EORTC scoring model and risk tables predictthe short- and long-term risks of disease recurrence and progression inindividual patients with NMIBC using the WHO 1973 classification system . |
|
|
Patients with TaG1/G2 tumours receiving chemotherapyhave been further stratified into three risk groups for recurrence, taking intoaccount the history of recurrences, history of intravesical treatment, tumourgrade , number of tumours and adjuvant chemotherapy . |
2a-b |
|
In patients treated with 5 to 6 months of BCG, theCUETO scoring model predicts the short- and long-term risks of diseaserecurrence and progression using the WHO 1973 classification system . |
|
|
In patients receiving at least 1 year of BCGmaintenance prior recurrence rate and number of tumours are the most importantprognostic factors for disease recurrence. Stage and grade are the mostimportant prognostic factors for disease progression and disease-specificsurvival patient age and grade are the most important prognosticfactors for overall survival . |
Donât Miss: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 3 Life Expectancy
Don’t Miss: Where Does Bladder Cancer Metastasis To
What Is High Grade Urothelial Carcinoma
What Is High-Grade Urothelial Carcinoma? High-grade urothelial carcinoma is a type of bladder cancer that has a high risk of becoming aggressive and progressing, as stated by the John Hopkins University Department of Pathology. It is more likely to recur in the bladder, invade the muscle wall or spread to other parts of
Catheterizable Continent Diversion Pouch
This is a reservoir of bowel with a stoma that is catheterizable for emptying the bladder. The urine is siphoned out of the urinary reservoir with a small catheter every four to six hours. The catheterizable pouch may require surgical repair at some point after surgery due to the wear and tear of frequent catheterization. This type of reconstruction is not performed on patients with a history of bowel disease.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Management In Spinal Cord Injury
Irocker Blackfin Paddle Board Xl
Functionality, swiftness, and stableness make this set of our most preferred boards. If you like paddling at speed, with add-ons to entertain, then this board is created you.
For taller riders over 5 8 the Blackfin XL iSUP maneuvers completely through any type of water environment and is great for natural buffs who intend to fish as well as bring camping gear along for the tripexpedition}.
It has an array of attributes, transforming to a dual kayak and integrated fishing installs. Adventure applicants and adventure enthusiasts, its time to enhance the means you paddle.
You May Like: Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Grade 1 Survival Rate
Morphologic Variants Of Urothelial Carcinoma
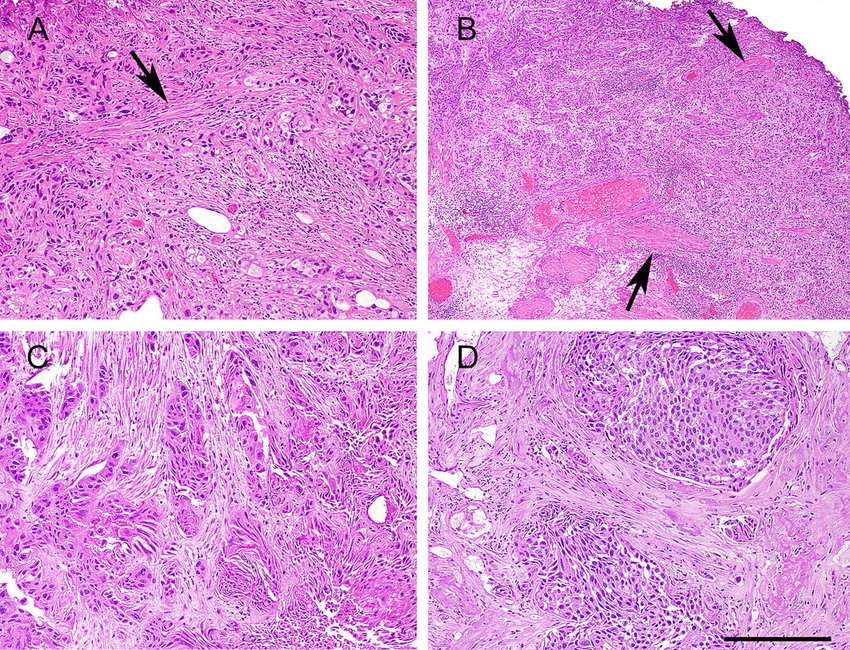
Some cases of urothelial carcinoma show morphologic patterns that are recognized as variants morphology. Those include nested variant, micropapillary, lymphoepithelioma-like, sarcomatoid, small cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma. These are frequently under-recognized in bladder biopsies and could have therapeutic implications with different criteria for surgery and different chemotherapy regimens.
You May Like: Blood In Urine Female Bladder Infection
Grade And Risk Category
The biopsy results will show the grade of the cancer. This is a score that describes how quickly a cancer might grow. Knowing the grade helps your urologist predict how likely the cancer is to come back and if you will need further treatment after surgery.
| Low grade | The cancer cells look similar to normal bladder cells, are usually slow-growing and are less likely to invade and spread. Most bladder tumours are low grade. |
| High grade | The cancer cells look very abnormal and grow quickly. They are more likely to spread both into the bladder muscle and outside the bladder.
In non-muscle-invasive tumours, the grade may be low or high, while almost all muscle-invasive cancers are high grade. Carcinoma in situ is a high-grade tumour that needs prompt treatment to prevent it invading the muscle layer. |
| Risk category | Based on the stage, grade and other features, a non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer will also be classified as having a low, medium or high risk of returning after treatment. This will help your doctors work out which treatments to recommend. |
You May Like: Skin Cancer 1st Stage