Small Cell Carcinoma Of The Bladder
- Other Names:
Poorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma of the bladder SCCB Small cell bladder cancer Small cell bladder carcinoma Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladderPoorly differentiated neuroendocrine carcinoma of the bladder SCCB Small cell bladder cancer Small cell bladder carcinoma Small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder Read More
How Bladder Cancer Is Treated
Different people with bladder cancer have different needs that have to treated. The treatments that your doctor recommends in the treatment plan are chosen based on the characteristics of your diagnosis and your overall health, as well as other factors.
Take time to learn about all of your treatment options and be sure to ask questions about things that are unclear. Also, talk about the goals of each treatment with your doctor and what you can expect while receiving the treatment. These types of talks are called shared decision-making. Shared decision-making is when you and your doctors work together to choose treatments that fit the goals of your care. Shared decision-making is particularly important for bladder cancer because there are different treatment options. Learn more about making treatment decisions.
To read an overview of treatment options based on the extent of the bladder cancer, read the next section in this guide, Treatments by Stage.
The most common types of treatments used for bladder cancer are described below. Your care plan also includes treatment for symptoms and side effects, an important part of cancer care.
If Treatment Does Not Work
Full recovery from bladder cancer is not always possible. If the cancer cannot be cured or controlled, the disease may be called advanced or metastatic.
This diagnosis is stressful, and for some people, advanced cancer is difficult to discuss. However, it is important to have open and honest conversations with your health care team to express your feelings, preferences, and concerns. The health care team has special skills, experience, expertise, and knowledge to support patients and their families and is there to help. Making sure a person is physically comfortable, free from pain, and emotionally supported is extremely important.
People who have advanced cancer and who are expected to live less than 6 months may want to consider hospice care. Hospice care is a specific type of palliative care designed to provide the best possible quality of life for people who are near the end of life. You and your family are encouraged to talk with the health care team about hospice care options, which include hospice care at home, a special hospice center, or other health care locations. Nursing care and special equipment can make staying at home a workable option for many families. Learn more about advanced cancer care planning.
After the death of a loved one, many people need support to help them cope with the loss. Learn more about grief and loss.
Don’t Miss: How To Relieve Bladder Infection
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
Cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after an advanced cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Learn more about the importance of tracking side effects in another part of this guide. Learn more about palliative care in a separate section of this website.
Primary Small Cell Carcinoma In Urinary Bladder: A Rare Case
Ahmet Çamtosun
Abstract
Small cell carcinoma of bladder, which does not have a common and accepted treatment protocol, is a rare and highly aggressive tumor. It is mostly pulmonary originated however, it can rarely be seen in extrapulmonary sites. We presented an interesting and uncommon case, in which the transitional cell tumor was found in the transurethral resection specimen, but the small cell carcinoma was detected in the final radical cystectomy material.
1. Introduction
Small cell carcinoma is less than 1% in urinary bladder tumors and is very aggressive and refractory to treatment due to its higher metastatic capability compared to other common bladder tumors . When it is diagnosed, the disease is mostly in the metastatic stage, so the patients generally have a poor prognosis. To improve the cure chance or life expectancy, a multidisciplinary approach including radical cystectomy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy should be initiated as soon as possible .
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
Small cell carcinoma of bladder was firstly reported in 1981 by Cremer et al. . There were 600 cases reported till now. This is a very aggressive tumor and generally has a poor prognosis. More than 60% of the reported patients were metastatic at diagnosis .
4. Conclusion
Conflict of Interests
Don’t Miss: How To Test For Bladder Infection At Home
Catheterizable Continent Diversion Pouch
This is a reservoir of bowel with a stoma that is catheterizable for emptying the bladder. The urine is siphoned out of the urinary reservoir with a small catheter every four to six hours. The catheterizable pouch may require surgical repair at some point after surgery due to the wear and tear of frequent catheterization. This type of reconstruction is not performed on patients with a history of bowel disease.
About The Bladder Renal Pelvis And Ureter
The bladder is a hollow organ in the pelvis that stores urine before it leaves the body during urination. This function makes the bladder an important part of the urinary tract. The urinary tract is also made up of the kidneys, ureters, and urethra. The renal pelvis is a funnel-like part of the kidney that collects urine and sends it into the ureter. The ureter is a tube that runs from each kidney into the bladder. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body. The prostate gland is also part of the urinary tract.
The bladder, like other parts of the urinary tract, is lined with a layer of cells called the urothelium. This layer of cells is separated from the bladder wall muscles, called the muscularis propria, by a thin, fibrous band called the lamina propria.
Also Check: How To Prevent Bladder Infections In The Elderly
Arsenic In Drinking Water
Drinking water containing arsenic is associated with a greater risk of bladder cancer. However, this is not a large concern in the U.S. Where you live, as well as if you drink well water, or public system water will determine your risk. Most public water systems meet standards for low arsenic content.
Treatment Of Stage Iv Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has not spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Treatment of stage IV bladder cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lung, bone, or liver, may include the following:
- External radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Urinary diversion or cystectomy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of new anticancer drugs.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Don’t Miss: Va Decision On Agent Orange And Bladder Cancer
For An Active Bladder Cancer You Need The Knock Out The Cancer Protocol Below
The most important supplements for fighting bladder cancer are the following. These supplements will have a synergy with chemotherapies, helping the chemo produce better results while also reducing side effects. Of course, you can use these to fight cancer without being on chemo, or use them with other treatments you may be doing.
When cancer is in the bladder, you may see, when you are using some of these suggestions, and especially the Zeolite Enhanced with DHQ, bits of tumors, dead cancer cells, small amounts of blood, coming out in the urine. This can happen fast, within a week, or take a month or two. But at some point you will see it, and it is a sign the cancer is being killed.
Be sure and continue with a prevention protocol to correct the issues that caused the cancer in the first place.
The majority of these suggestions are frequency enhanced energy which work by stimulating the body to safely and successfully heal itself. These elixirs do not suppress the symptoms of cancer, but rather stimulate the body’s own healing mechanism to deal with cancer and to reverse it.
These elixirs are a safe, natural therapy using a base of purified structured spring water with a very small amount of organic Orange and Rosemary essential oils. This base holds and transmits the various energetic frequencies that trigger the body’s healing response.
Treatment Of Recurrent Bladder Cancer
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrentbladder cancer depends on previous treatmentand where the cancer has recurred. Treatment for recurrent bladder cancer mayinclude the following:
- Radiation therapy as palliative therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
- A clinical trial of a new treatment.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: Bladder Cancer In Dogs Treatment
Low Grade And High Grade Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer starts in the lining of the bladder in about 90 percent of people diagnosed with this cancer. Bladder cancer is called low grade or high grade.
- Low-grade bladder cancer means the cancer has not invaded the muscles around the bladder . People rarely die from this type of bladder cancer, it often recurs after treatment.
- High-grade bladder cancer also often recurs and has a higher chance of spreading to other parts of the body. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer result this type so it is treated more aggressively.
Genetics And Family History
If you have family members who have bladder cancer, you have a higher risk of developing it yourself. This could also be that family members share exposure to the same chemicals that cause cancer or they share the same changes in certain genes , making it harder for their bodies to break specific toxins down, increasing their risk of bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: Bowel And Bladder Cancer Prognosis
Recalcitrant Cancer Research Act
In 2013, the US Congress passed the Recalcitrant Cancer Research Act, which mandated increased attention to certain recalcitrant cancers, including small cell lung cancer. That led to the National Cancer Institute supporting small cellspecific research through a consortium.
As a result, new experimental drugs for small cell lung cancer are currently being tested, including Iadademstat and Keytruda .
Also Check: Essential Oils For Bladder And Kidney Health
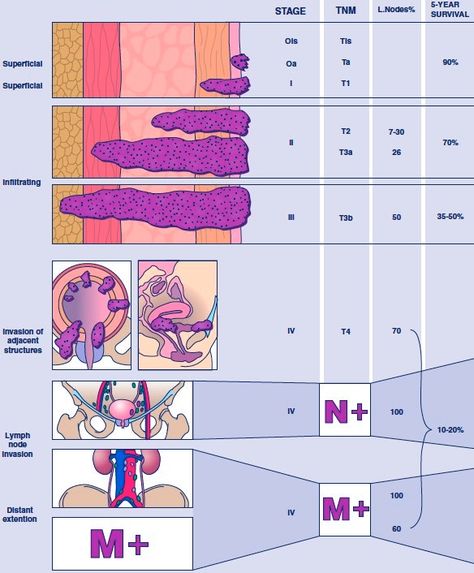
Primary Stages Of Bladder Cancer
The treatment used for bladder cancer depends on many factors, including the diagnosis stage, whether it has spread beyond the bladder, how old the patient is, and the patients wishes. The stages of bladder cancer include:
-
Superficial bladder cancer: Bladder cancer limited to the lining of the bladder.
-
Invasive bladder cancer: Bladder cancer that has spread through the lining of the bladder and invaded the muscle wall.
-
Metastatic bladder cancer: Bladder cancer that has spread to nearby organs and lymph nodes.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Implant For Overactive Bladder
Moffitt Cancer Centers Approach To Squamous Cell Carcinoma
At Moffitt Cancer Center, our multispecialty team of cancer experts takes a highly individualized approach to squamous cell carcinoma treatment. We offer the latest diagnostic and treatment options, and we work closely with each patient to offer customized guidance and help ensure the best possible outcome. For instance, there are many steps a patient can take to improve his or her own squamous cell carcinoma prognosisregardless of the general survival ratesuch as:
- Performing self-examinations from head to toe, including parts of the body that are not regularly exposed to UV rays, at least monthly, and promptly reporting any suspicious or unusual changes in skin texture or appearance to a physician
- Seeing a physician for a professional skin cancer examination yearly
- Avoiding exposure to the suns ultraviolet rays while outdoors, preventive measures include seeking shade, wearing sunglasses and a brimmed hat, covering up with clothing and using a broad-spectrum sunscreen with both UVA and UVB protection
- Never using indoor tanning beds
Treating Stage Iii Bladder Cancer
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs and/or lymph nodes . They have not spread to distant parts of the body.
Transurethral resection is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy is then the standard treatment.Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers.
Chemotherapy before surgery can shrink the tumor, which may make surgery easier. Chemo can also kill any cancer cells that could already have spread to other areas of the body and help people live longer. It can be especially useful for T4 tumors, which have spread outside the bladder. When chemo is given first, surgery to remove the bladder is delayed. The delay is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the cancer, but it can be harmful if it continues to grow during chemo. Sometimes the chemo shrinks the tumor enough that intravesical therapy or chemo with radiation is possible instead of surgery.
Some patients get chemo after surgery to kill any cancer cells left after surgery that are too small to see. Chemo given after cystectomy may help patients stay cancer-free longer, but so far its not clear if it helps them live longer. If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasnt given before surgery.
Read Also: What Color Ribbon Is For Bladder Cancer
Understanding The Statistics: Cancer Survival
It is important to remember that all cancer survival numbers are based on averages across huge numbers of people. These numbers cannot predict what will happen in your individual case.
Survival rates will not tell you how long you will live after you have been diagnosed with bladder cancer. But, these numbers can give you an idea of how likely your treatment will be successful. Also, survival rates take into account your age at diagnosis but not whether you have other health conditions too.
Dont Miss: How Do You Fix Overactive Bladder
Prognosis And Survival For Bladder Cancer
If you have bladder cancer, you may have questions about your prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors best estimate of how cancer will affect someone and how it will respond to treatment. Prognosis and survival depend on many factors. Only a doctor familiar with your medical history, the type and stage and other features of the cancer, the treatments chosen and the response to treatment can put all of this information together with survival statistics to arrive at a prognosis.
A prognostic factor is an aspect of the cancer or a characteristic of the person that the doctor will consider when making a prognosis. A predictive factor influences how a cancer will respond to a certain treatment. Prognostic and predictive factors are often discussed together. They both play a part in deciding on a treatment plan and a prognosis.
The following are prognostic and predictive factors for bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: Can Overactive Bladder Start Suddenly
You May Like: Overactive Bladder At Night Time Only
Is Combination Chemotherapy And Radiation Used For Bladder Cancer Treatment
In recent years, chemotherapy and radiation have been combined to provide a bladder preservation therapy for higher risk cases. In the past radiation therapy alone was used because it effectively shrunk tumors. Bladder cancer tumor cells are chemosensitive, susceptible to the cell-killing effects of anticancer drugs. Adding combined chemotherapy to radiation has improved results. To ensure the success of bladder preservation therapy, there are at least three requirements which should be met: 1) complete resection of the tumor by TURBT 2) no obstruction of 1 or both kidneys as a result of the bladder tumor and 3) no T4 bladder tumors.
If the tumors do not respond to an initial course of chemotherapy and radiation, it may be reasonable to perform, if medically possible, a cystectomy.
Information and services provided by the Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network are for informational purposes only. The information and services are not intended to be substitutes for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. If you are ill or suspect that you are ill, seek professional medical attention immediately! BCAN does not recommend or endorse any specific physicians, treatments, procedures, or products even though they may be mentioned on this site.