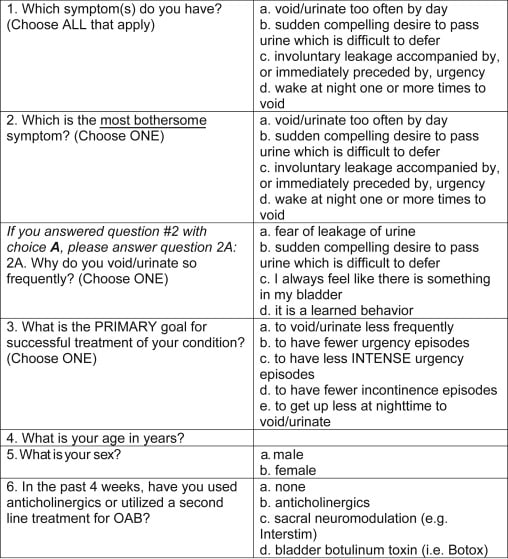
Diagnosis Of Overactive Bladder
Our urologists do a thorough physical examination and collect your medical history. We listen as you describe your symptoms and work with you to find the right diagnosis. You may have additional testing for OAB, such as:Cystoscopy. Test that passes a thin tube with a camera through the urethra to see the bladder. Cytometry. Test that measures the pressure in the bladderPost-void residual urine test. Measures the amount of urine left in the bladder after urinationUrinalysis. Tests urine after collecting it in a clean cup. Urinary stress test. Test involves adding fluid to the bladder with a catheter and having the patient cough to see if it leaks.Ultrasound. Uses a machine that makes sound waves to create images of the bladder.
Can Nerve Stimulation Help Overactive Bladder
Yes, nerve stimulation can help improve OAB. Your nerves help tell your brain that your bladder is full. By treating your nerves, you can improve your bladder control.
Nerve stimulation is a reversible treatment. Healthcare providers only recommend it if other treatments dont work.
There are several types of nerve stimulation treatments. These include:
Sacral nerve stimulation
Sacral nerve stimulation is a therapy that electrically stimulates the nerves that control your bladder.
A healthcare provider will implant a small device called a neurotransmitter under the skin near your upper buttock area. The neurotransmitter sends mild electrical impulses through a wire near your sacral nerve. Your sacral nerve is a nerve in your lower back. The impulses help you control your bladder.
Sacral nerve stimulation can reduce the number of times you have to use the bathroom or the number of times you accidentally leak pee. Its overall very effective. Its also an outpatient procedure, so you can go home afterward.
Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation
Percutaneous tibial stimulation sends small nerve impulses to a nerve branch near your ankle. It helps stimulate bladder control.
Percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation is an outpatient procedure. Many people need 12 weekly sessions and then monthly maintenance sessions afterward.
Botulinum toxin injections
Botox® is the most well-known botulinum toxin brand. A healthcare provider injects Botox into your bladder wall using a cystoscope.
You Think You Have A Kidney Stone
Kidney stones are most notably marked by severe pain on one side of your lower back, though other symptoms include nagging stomach pain, blood in the urine and urine that smells bad or looks cloudy. If you experience these symptoms, you should see your urologist as soon as possible for diagnosis and treatment.
Kidney stone pain can be very severe, and many patients report it as the worst they have ever experienced, says Mike Nguyen, MD, a urologist at Keck Medicine of USC and associate professor of clinical urology at the Keck School of Medicine of USC. How does this compare to the pain of childbirth? It turns out that the reported amount of pain in both situations is almost identical.
Recommended Reading: Loss Of Bladder Control During Pregnancy
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better
Pelvic floor exercises and changes to your lifestyle may take six to eight weeks before you start to see results.
Many medications start to relax your bladder muscles after a few hours. But they may take up to a month to work fully.
Botox should start to work after one to two weeks.
Most people start to see improvement after six nerve stimulation treatments. However, it may take up to 12 treatments to see results.
Who To Test And When
Supplemental testing should be considered for patients in whom the simple evaluation described above raises suspicion of a problem or condition that either needs evaluation or may predispose the patient to failure of therapy . In addition, further testing should be considered for patients who are refractory to treatment and those with significant neurological disease known to affect the lower urinary tract. The type of testing required will depend on the individual situation.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Control Medication Side Effects
Section : Patient Presentation
Symptoms. When symptoms of urinary frequency and urgency, with or without urgency incontinence, are self-reported as bothersome the patient may be diagnosed with overactive bladder .27 Additionally, a caregiver or partner may perceive these symptoms as bothersome and lead the patient to seek care. It is common for patients to have suffered with their symptoms for an extended time before seeking medical advice.
Differentiation. OAB symptoms may occur only at night, causing a single symptom of nocturia. The differential of nocturia includes nocturnal polyuria ,28 low nocturnal bladder capacity or both. In nocturnal polyuria, nocturnal voids are frequently normal or large volume as opposed to the small volume voids commonly observed in nocturia associated with OAB. Sleep disturbances, vascular and/or cardiac disease and other medical conditions are often associated with nocturnal polyuria. As such, it is often age-dependent, increasing in prevalence with aging and with poorer general health.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose Overactive Bladder
A healthcare provider may order tests to help diagnose overactive bladder. These tests may include:
- Urinalysis. A urinalysis examines the visual, chemical and microscopic aspects of your pee. A provider will look for red blood cells, white blood cells and bacteria. If you have any of them in your pee sample, you may have an infection that causes OAB.
- Urodynamic testing. Urodynamic tests measure how much pee remains in your bladder after you go to the bathroom, how much you pee, how fast you pee and how much pressure is on your bladder as it fills with pee.
- Ultrasound. An ultrasound is a noninvasive imaging test that allows a healthcare provider to take a detailed look at your bladder.
- Computed tomography scan. A CT scan is a noninvasive imaging test that produces 3D images of your bladder.
- Cystoscopy. A healthcare provider will use a special instrument to look inside your bladder from your urethra. The provider typically uses a numbing gel so you dont feel pain in your urethra. In rare cases, they may use general anesthesia, so you arent awake, wont move and wont feel any pain.
Recommended Reading: Small Cell Bladder Cancer Treatment
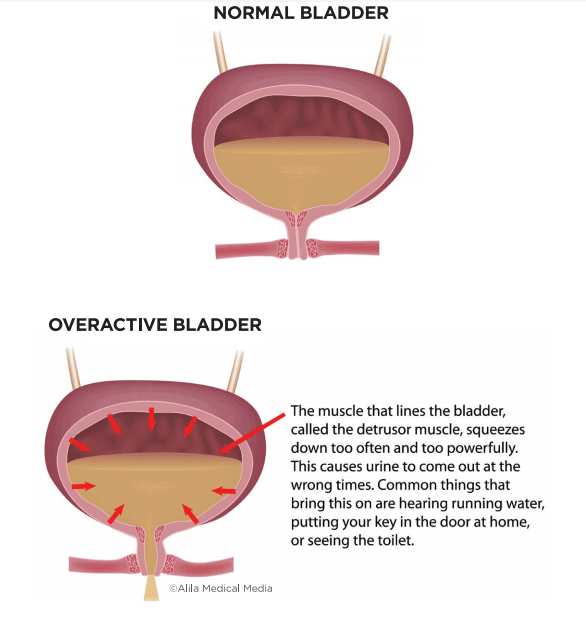
What Are The Symptoms Associated With Overactive Bladder
Symptoms of overactive bladder include:
- A frequent and sudden urge to urinate
- Involuntary loss of urine
- Increased urinary frequency during the daytime
- Increased urinary frequency at night
Although many patients may ignore symptoms associated with overactive bladder because they believe they are a normal part of aging, the condition typically has an underlying medical cause.
Pelvic Floor Exercises Can Help Immensely
Although your pelvic floor muscles are not visible, they nonetheless lose strength if they are not used, much like other muscles in your body. Exercises for the pelvic floor, often known as Kegel exercises, assist the pelvic floor in becoming stronger when performed faithfully at least twice each day.
Recommended Reading: Can A Bladder Infection Go Away
Keeping A Bladder Diary
Your doctor will ask you questions about your symptoms as part of the diagnostic process. A bladder diary can provide useful information. This is something you can bring to your appointment. It will give your doctor details on your condition. To create a bladder diary, record the following information over the course of several days:
- Record everything you drink, how much, and when.
Your doctor will perform a physical exam after discussing your symptoms. The exam might include one or more of the following tests:
What Happens During A Bladder Ultrasound
In some facilities, you may need to see a special technician for an ultrasound. But some medical offices can do this test in the examination room during a routine appointment.
Whether you have the test done in an examination room or an imaging center, the process will be similar:
Don’t Miss: What Causes An Overactive Bladder In Males
Lab Tests And Other Screening
To help rule out other conditions other than overactive bladder, and to help evaluate your bladder function, your doctor may recommend the following tests:
Urinalysis This involves taking a urine sample and culturing it, then looking at it under a microscope to check for bacteria or blood.
It can point to a possible urinary tract infection , kidney problems, or diabetes.
Bladder Scan This is a type of ultrasound scan that can show how much urine is left in your bladder after you urinate.
Cystoscopy This test involves inserting a narrow tube containing a tiny camera into your bladder to look for potential problems.
Bladder Function Tests Also known as urodynamic tests, these are designed to evaluate how well your bladder stores and releases urine.
Specifically, these tests may measure:
- How much urine is left in your bladder after you urinate
- Your urine flow rate
- Your bladder pressure under test conditions
While the remaining urine in your bladder can be estimated using an ultrasound scan, it can be measured more accurately by passing a thin tube into your urethra to drain it.
Your urine flow rate the speed and volume of your urination is measured using a device called a uroflowmeter, into which you urinate. The data can then be used to create a graph of how your flow rate changes.
In this procedure, your doctor uses a catheter to slowly fill your bladder with warm water while using a pressure sensor inserted into your rectum or to measure your bladder pressure.
What Happens After An Urodynamic Test
You might have mild discomfort or soreness when you urinate. This should only last a few hours. You might even see a small amount of blood due to the catheter. These symptoms might ease up if you drink eight to 16 ounces of water every hour for two hours.
Your healthcare provider might also suggest taking a warm bath or holding a warm, damp washcloth over the urethral opening. You might also be told to take over-the-counter pain medication if you need it.
In some cases, your provider might give you a prescription for an antibiotic to prevent infection, but this is not always necessary. However, if you have any symptoms of infection, such as a fever, chills or a lot of pain, you should call your healthcare provider immediately.
Don’t Miss: Does Ibuprofen Irritate The Bladder
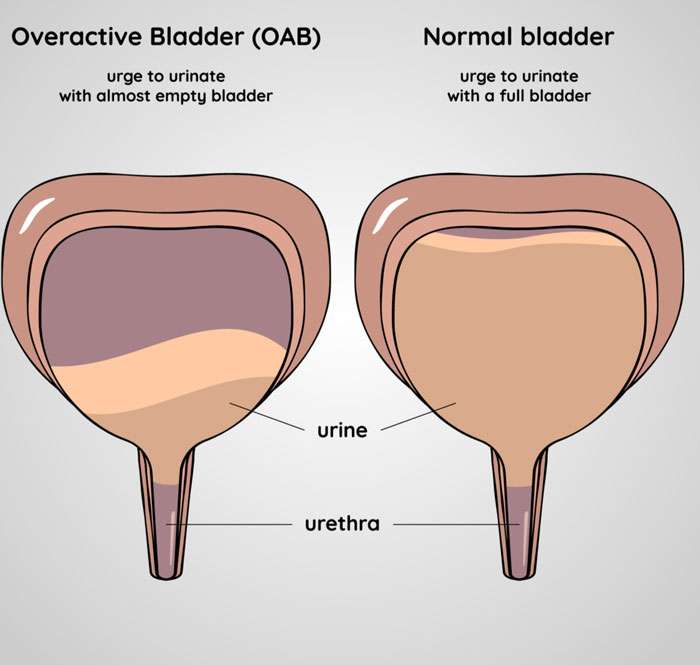
What Are The Symptoms Of Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder represents a collection of symptoms. These symptoms include:
- Urinary urgency. Urinary urgency is a sudden, uncontrollable need to pee. Once you feel the need to pee, you have a short amount of time to get to a bathroom.
- Frequent peeing. A frequent need to pee means you have to go to the bathroom more often than usual.
- Urge incontinence. Urge incontinence is a sudden, uncontrollable need to pee, and you may leak pee.
- Nocturia. Nocturia is the need to get up to pee at least two times each night.
Symptoms Of Overactive Bladder And Diagnosis
The most common symptoms of overactive bladder are urinary frequency and the sudden urge to urinate. If a woman is urinating more than eight times a day, this might be a symptom of OAB. Waking up in the middle of the night to urinate often indicates OAB, as well.
A urologist or urogynecologist may perform a number of tests to diagnosis OAB. These may include:
- Physical exam, medical history review and symptom questionnaire.
- Bladder stress test, performed by filling up the bladder and having the patient cough to ascertain how much urine leaks.
- Postvoid residual volume test checks if the bladder is actually fully emptying by inserting a catheter through the urethra and into the bladder after urination. The catheter measures any remaining urine.
- Urodynamic testing is a series of tests typically reserved for unusual cases and primarily measures urine flow to test for obstruction as well as evaluating urge sensation.
- Urinalysis screens for the presence of bacteria and may rule out other similar conditions such as a UTI.
- Cystoscopy examines the inside of the bladder by placing a long thin tube with a magnifying glass up the urethra.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Cancer Metastasis To Lung Symptoms
How Much Does A Bladder Ultrasound Cost
If you have medical insurance, your copayment for a bladder ultrasound can vary or may even be free. Without insurance, the average cost of an ultrasound in the United States is between about $250 and $400.
If you have Medicare, an ultrasound may be covered under your Part A coverage if you have the procedure during an inpatient hospital stay.
At an outpatient facility, an ultrasound is covered by Medicare Part B. Your share of the cost can be between about $17 and $30 depending on where the test is done.
Keeping A Bladder Diary May Help Identify Triggers
Although it may seem time-consuming, keeping a journal will allow you and your doctor to pinpoint any triggers for your overactive bladder and track how frequently you use the restroom each day.
How should someone with an overactive bladder keep a journal?
- Specify the types and amounts of fluids you consume.
- Record the kind and amount of food you consume.
- Keep track of your bathroom visits and indicate whether they were effective .
- Describe what you were doing when the need to urinate or a leakage happened
Recommended Reading: Can Diabetes Cause Bladder Problems
Who Does Overactive Bladder Affect
Overactive bladder is most common in people 65 and older. Women may have OAB at a younger age, usually around 45.
How common is overactive bladder?
Overactive bladder is common. It affects up to 33 million adults in the U.S., including as many as 30% of men and 40% of women. However, that number may be higher because many people may feel embarrassed and wont get help.
How does overactive bladder affect my body?
Overactive bladder symptoms can cause stress and affect your quality of life.
Things You Can Do To Help Make A Diagnosis
To help diagnose your condition, your doctor may ask you to keep a bladder diary.
To do this, youll most likely fill out a chart that your doctor gives you. This chart typically has lines for different times of the day, and asks you to record:
- How often you urinate
- The amount of urine you pass
- What liquids you drink, and how much
- Any episodes of urgency to urinate
- Any accidental urine leakage
- What you were doing at the time in question
Your doctor will probably ask you to keep this diary for at least three days. These days may not need to be consecutive, and should ideally be days that are fairly typical in terms of your activities.
On days when youre keeping a diary, its advised that you measure each serving of beverages that you consume.
You should also measure how much you urinate. To do this, your doctor may give you a special urine collection device that sits under your toilet seat.
You should rinse this device with water after each use, and keep it next to your toilet or carry it with you, if youll be outside of your home.
If youre keeping a bladder diary before seeing your doctor, you can collect your urine in a paper cup and estimate the amount based on the size of the cup.
Read Also: Can A Bladder Infection Cause Dizziness
Behavioral And Lifestyle Changes
Performing pelvic floor exercises, known as Kegels, strengthens the pelvic floor muscles and the sphincter, a urinary muscle. Scheduling toilet trips for every couple of hours, as well as managing and reducing fluid intake, will help women normalize their urine schedule. Bladder training involves delaying urination after the initial sensation hits and building up the intervals between urinating over time.
Why Is A Bladder Ultrasound Done
About a quarter of all people in the United States experience some level of incontinence, or the inability to hold urine in the bladder until you purposely release it.
There are many causes of incontinence, and it can be difficult for a doctor to pinpoint a reason for the problem just by asking you questions or examining the outside of your body.
The following symptoms may lead a doctor to order a bladder ultrasound:
- difficulty urinating
Don’t Miss: Antibiotic For Bladder Infection In Elderly
What Is The Bladder
The bladder is a muscular, elastic organ located in the lower abdomen that collects urine secreted by the kidneys. At the bottom of the bladder is the urethra, which is controlled by a sphincter muscle, through which urine leaves the body. When urine is released, the sphincter muscle relaxes while a bladder muscle contracts, allowing urine to pass out of the body. A typical bladder can hold slightly over two cups of fluid, although the urge to urinate can start with as little as five ounces of urine in the bladder.