Radiotherapy With A Radiosensitiser
Radiotherapy is given by a machine that beams the radiation at the bladder . Sessions are usually given on a daily basis for 5 days a week over the course of 4 to 7 weeks. Each session lasts for about 10 to 15 minutes.
A medicine called a radiosensitiser should also be given alongside radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer. This medicine affects the cells of a tumour, to enhance the effect of radiotherapy. It has a much smaller effect on normal tissue.
As well as destroying cancerous cells, radiotherapy can also damage healthy cells, which means it can cause a number of side effects. These include:
- erectile dysfunction
- difficulty passing urine
Most of these side effects should pass a few weeks after your treatment finishes, although there’s a small chance they’ll be permanent.
Having radiotherapy directed at your pelvis usually means you’ll be infertile .
After having radiotherapy for bladder cancer, you should be offered follow-up appointments every 3 months for the first 2 years, then every 6 months for the next 2 years, and every year after that. At these appointments, your bladder will be checked using a cystoscopy.
You may also be offered CT scans of your chest, abdomen and pelvis after 6 months, 1 year and 2 years. A CT scan of your urinary tract may be offered every year for 5 years.
Tumours On The Lateral And Anterior Walls
Resection of lateral wall tumours may result in stimulation of ONR resulting in increased risk of perforation . Strategies that have been shown to reduce the likelihood of ONR would include avoidance of bladder overfilling, reduced cutting current, use of short intermittent burst current , use of bipolar electrocautery, and use of neuromuscular blockade .
Tumours on the anterior wall could be challenging to resect and may require suprapubic depression by an assistant as well as proper resectoscope angles. More effective resection might be achieved by using open-angled loops.
En Bloc Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumors
En bloc transurethral resection of bladder tumors is newer technique in which the tumor and the surrounding normal urothelium are removed as a single unit. A meta-analysis of seven trials found that ETURBT was associated with shorter hospital stays and catheterization time,fewer complications, and a lower recurrence-free rate than conventional TURBT. In a separate systematic review of 17 studies, the results were comparable to conventional TURBT. Both papers cited the ability to provide high-qualityspecimens for histological assessment as a significant advantage of ETURBT over TURBT.
A prospective, non-randomized interventional study was performed to compare ETURBT to TURBT in the setting of NMBIC, in terms of progression and recurrence. Cohort groups were comparable with 21 patients undergoing ETURBT vs 24 TURBT, with results being notable for significantly decreased recurrence rate and recurrence-free survival while progression rate and progression-free survival rate were not significantly different.
Interesting, Uphadhyay et al. found that with non-pedunculated bladder tumors 2-4 cm in size that were resected via ETURBT vs TURBT, a greater yield of detrusor muscle was found in histopathological examination of specimens obtained with ETURBT .
While these results are attractive, there are several limitations of ETURBT to consider :
You May Like: Why Is My Bladder So Weak All Of A Sudden
Palliative Or Supportive Care
If your cancer is at an advanced stage and can’t be cured, your medical team should discuss how the cancer will progress and which treatments are available to ease the symptoms.
You can be referred to a palliative care team, who can provide support and practical help, including pain relief.
Page last reviewed: 01 July 2021 Next review due: 01 July 2024
Tumours At The Ureteral Orifices
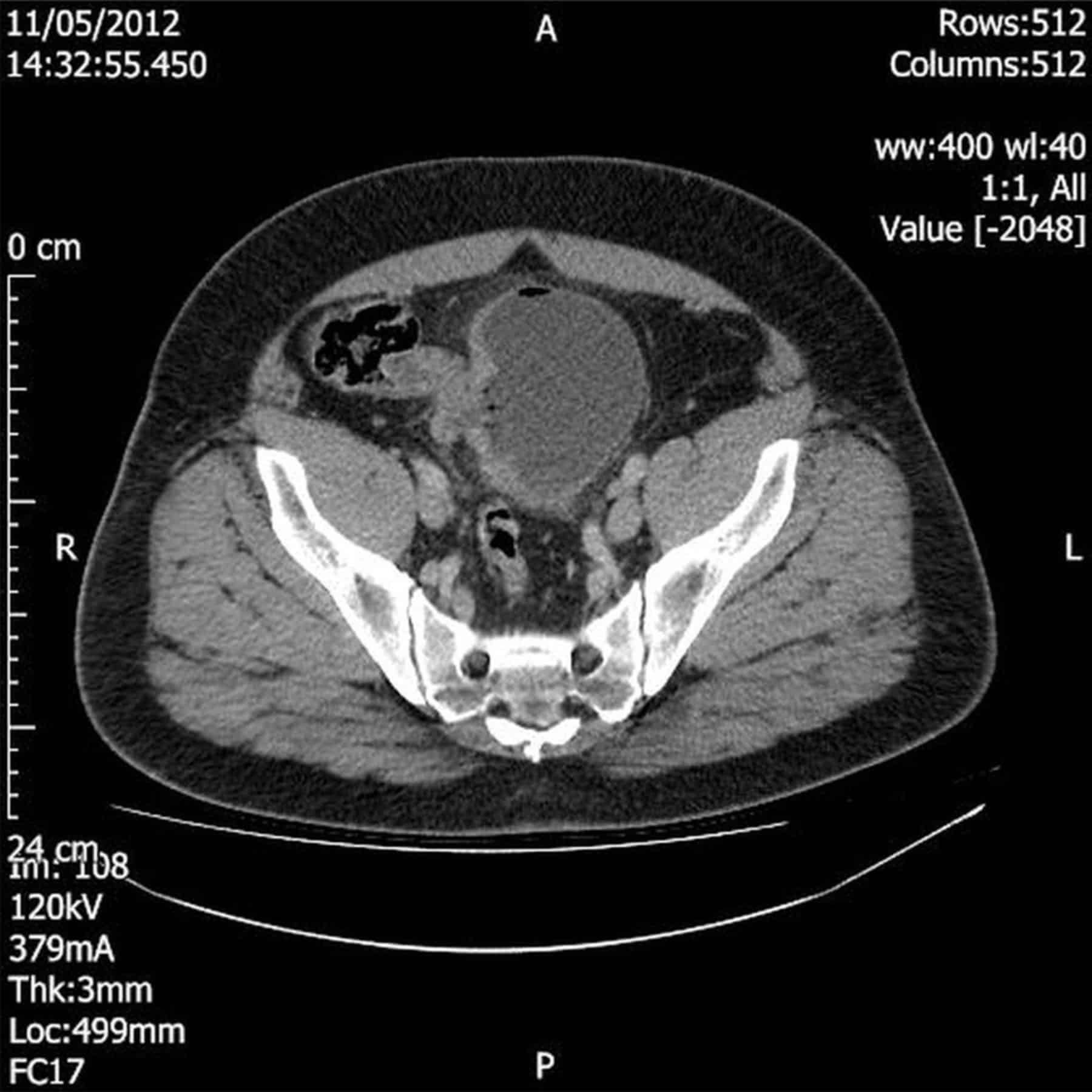
Coagulation close to the ureteral orifices should be avoided as it may cause scarring and lead to ureteric obstruction . However, tumours that involve the ureteral orifices can be resected judiciously under pure cutting settings. This would be particularly beneficial as satisfactory renal function can be facilitated if cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy is considered for MIBC. Although it may result in vesicoureteric reflux and would be uncommon to cause stricture, a temporary ureteric stent placement between 2 and 6 weeks can further reduce the risk. A form of imaging such as renal ultrasound, CT urogram or Diethylenetriamine Pentaacetic Acid renal scan after resection is recommended.
Read Also: Holistic Treatment For Overactive Bladder
What Is Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor
This surgical procedure is used in both the diagnosis and treatment of bladder cancer. Transurethral resection of bladder tumor allows your surgeon to biopsy your tumor, or remove an entire small tumor from the inside of your bladder, while leaving the bladder intact. TURBT is essential to obtain a biopsy to confirm the cancer diagnosis and determine the stage and grade of your cancer.
Sexual Effects Of Urostomy
Its normal people to be concerned about having a sex life with a urostomy. Having your ostomy pouch fit correctly and emptying it before sex reduces the chances of a major leak. A pouch cover or small ostomy pouch can be worn with a sash to keep the pouch out of the way. Wearing a snug fitting shirt may be more comfortable. Choose sexual positions that keep your partners weight from rubbing against the pouch. For more tips, see Urostomy Guide.
Also Check: High Risk Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Factors That Would Affect Recurrence And Progression
Bladder cancer is associated with a high rate of recurrence among patients with NMIBC. A number of studies assessed the factors that might be associated with recurrence and progression of bladder cancer following TURBT. The majority of the studies were rated as low quality and no strong recommendations were made in the guidelines due to study heterogeneity and hence low grade evidence. Nevertheless, there were a number of factors that have been shown to significantly influence the outcomes.
The largest randomised controlled trial included 2,596 patients in seven European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer trials. It demonstrated recurrence rates ranging from 15% to 61% and progression rates of less than 1% to 17% at one year. At five years, the probabilities of recurrence and progression ranged from 31% to 78% and from less than 1% to 45%, respectively. The risk of recurrence was linked to a number of clinicopathologic factors including size, multifocality, prior recurrence, stage, CIS and grade . Based on these key factors the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer scoring system and risk tables for recurrence and progression in patients with NMIBC have been developed as shown in Tables 1-3 .
Table 1Table 4
What Is A Turbt Procedure
Transurethral is the medical term for a very small device thats inserted into the urethra .
To diagnose and stage the disease, the doctor removes tissue from inside the bladder during a TURBT procedure and has it examined under a microscope for cancer cells.
When used to treat non-muscle invasive bladder cancer, the TURBT procedure is performed to remove as many cancer cells as possible. The patient may require repeated TURBT procedures to remove other cancer cells that have been detected or to treat a cancer recurrence. These successive procedures may be more extensive than the first, and repeated TURBT procedures may scar the bladder, causing incontinence or frequent urination.
To treat muscle-invasive bladder cancer, patients may require additional treatment, which may include surgery, radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
You May Like: How Aggressive Is Bladder Cancer In Dogs
Treatment For Hg T1 Bladder Cancer With Pt0 Histology At Second Tur
TURBT followed by intravesical BCG therapy provides lower incidences of recurrence and progression than those obtained by TURBT alone . Sylvester et al. performed a meta-analysis on the efficacy of intravesical BCG therapy. They evaluated 24 trials involving a total of 4863 patients and concluded that intravesical BCG significantly reduces the risk of progression after TURBT in NMIBC patients who receive maintenance treatment. Since T1 bladder cancer is considered to be high-risk cancer regardless of the pathological findings for the second TUR specimen , various guidelines recommend full-dose intravesical BCG for 13 years except in the case of immediate cystectomy. Alternatively, mitomycin C is also recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network guidelines . This is based on a meta-analysis that showed no statistically significant difference between BCG and MMC for progression and survival .
Protocol and study design of the JCOG1019 trial .
Bcg Or Intravesical Chemotherapy
BCG produces generally better results but has more serious treatment effects. Intravesical chemotherapy has fewerserious treatment effects but may not be as effective as BCG. If you have a high-risk tumour you would usually receive BCG, if anintermediate risk tumour you would often receive intravesical chemotherapy.
When you are given a single dose of intravesical chemotherapy during youroperation, it is because when a tumour is removed from the bladder there is aworry that some of the cancer cells can break off and stick to the bladder wallwhere they can grow and form new tumours. It is now the recommended standard practice to put a singledose of intravesical chemotherapy into the bladder at the end of the surgerywhich destroys any cancer cells floating about and can reduce the chances of gettingfurther recurrences. BCG is not given at this time because of the risk ofabsorption of the BCG through the operation site.
Cystectomy isrecommended for non-invasive tumours or carcinoma-in-situ that are resistant orrefractory to intravesical treatment. While offering long-term control,removing the bladder has major implications and potential complications, andwould not be undertaken unless the risks of progression are high.
Radiotherapy and systemic chemotherapy arenot effective treatments for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Recommended Reading: Over The Counter Bladder Infection Medicine Walgreens
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when it’s first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.
What Happens After Turbt Surgery
You will either go home the same day or stay in the hospital overnight. You will probably wear a small drainage tube called a catheter, to help drain your urine for a few days. You may also have to urinate more often. These side effects should go away with in two weeks of the operation. Be sure to tell your physician or nurse if you have any bleeding or pain. Your provider will need to know how much bleeding you have and will be able to give you medication to relax your bladder and avoid spasms.
Some patients will have intravesical chemotherapy in which the chemotherapy drug is delivered directly into the bladder through the catheter. The chemotherapy fills the bladder and destroys any microscopic tumor cells not removed by the surgery.
Read Also: Risk Of Bladder Cancer After Bcg Treatment
The Value Of Repeat Turbt In High Grade T1 Bladder Cancer
- Massari M1*, OMalley P1, Bozorgmehri S2, Dennis M1 and Crispen PL1
- 1 Department Of Urology, University Of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, United States
- 2 Department Of Epidemiology, University Of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, United States
*Corresponding Author:
Tel:Received DateAccepted DateDOI:
How Turbt Is Done
This surgery is done using an instrument put in through your urethra, so there’s no cutting into the abdomen . You’ll get either general anesthesia or regional anesthesia .
A type of thin, rigid cystoscope called a resectoscopeis put into your bladder through your urethra. The resectoscope has a wire loop at the end that’s used to remove any abnormal tissues or tumors. The removed tissue is sent to a lab for testing.
After the tumor is removed, more steps may be taken to try to ensure that the cancer has been completely destroyed. For instance, the tissue in the area where the tumor was may be burned while looking at it with the resectoscope. This is called fulguration. Cancer cells can also be destroyed using a high-energy laser through the resectoscope.
Also Check: What To Take For Overactive Bladder
Sexual Effects Of Radical Cystectomy In Men
After surgery, many men have nerve damage that affects their ability to have erections. In some men this may improve over time. For the most part, the younger a man is, the more likely he is to regain the ability to have full erections. If this issue is important to you, discuss it with your doctor before surgery. Newer surgical techniques may help lower the chance of erection problems.
For more on sexual issues and ways to cope with them, see Sex and the Man With Cancer.
Treatment For Hg Pt1 Bladder Cancer With Pt2 Or More Histology At Second Tur
There is no doubt about the need to perform radical cystectomy for patients with muscle-invasive disease at the second TUR. Most of these tumors are understaged at the initial TURBT due to technical problems, and may not be large or bulky like muscle-invasive tumors that are diagnosed at the initial TURBT and/or with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. The discussion on the treatment strategies for these tumors does not include whether cystectomy should be performed but whether neoadjuvant chemotherapy and/or extended lymph node dissection should be performed.
Several randomized Phase III trials and meta-analyses demonstrated the survival benefit of cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients with MIBC. However, whether neoadjuvant chemotherapy prolongs the survival of patients with T1 cancer at the initial TURBT and with muscle-invasive disease detected by a second TUR is unclear. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy offers potential advantages in tumor downstaging and eradication of micrometastases, so this therapy should be indicated for patients who have risk factors for locally advanced disease or nodal metastasis.
Recommended Reading: Natural Supplements For Overactive Bladder
Sexual Effects Of Radical Cystectomy In Women
If the surgeon takes out the end of the urethra where it opens outside the body, the clitoris can lose some of its blood supply, which might affect sexual arousal. Talk with your surgeon about whether the end of the urethra can be spared.
For more on ways to cope with these and other sexual issues, see Sex and the Woman With Cancer.
What Happens During The Surgery
At the start of the procedure, you will be given a numbing drug . Generally, two options are available: general anesthesia where you take a nap for the entire procedure, or local anesthesia, where you remain awake, but are given a drug through a needle in your back to numb the lower half of your body.
During a TURBT procedure, the surgeon inserts a tool called a resectoscope through the urethra to reach the inside of your bladder. This tool has a surgical loop on it that resects or cuts off a sample of tumor tissue to be analyzed by a pathologist, or resects the entire tumor from your bladder . TURBT is used as a treatment for patients with early-stage bladder cancer, and is typically followed by intravesical therapy.
Don’t Miss: Does Bladder Cancer Cause Back Pain
How Do You Prepare For A Turbt
Normally, you have to stop eating and drinking the night before any procedure that requires anesthesia. Make sure your provider knows about all of the medications that you take, including over-the-counter medicines and supplements.
Your healthcare provider will tell you if you need to avoid taking any of your medication for instance, blood thinners and when you should stop. Dont just stop taking medication without discussing it with your provider.
If youre allowed to take medications in the morning before the TURBT, make sure you only take a sip or two of water.
Take a bath or shower before you go in for the procedure. Dont use any kind of lotions or perfumes or deodorants after your shower.
Dress comfortably the day of the procedure. Bring identification, but leave your money, credit cards and jewelry at home.
Bring someone who can drive you home. Between anesthesia and pain medication, it wont be safe for you to drive yourself.
Current And Future Perspectives
ERBT seems to be a safe and effective resection technique. A new envisaged goal is also to decrease the number of second TURBTs. It can be facilitated by achieving higher rate of detrusor in the initial specimen and minimal tumour fragmentation using the correct ERBT technique. Large randomised prospective multicentre comparative trials are needed to clarify outcomes and to further assist in identifying suitable patients for this technique. This will enable us to offer more personalized approach to management of patients with bladder cancer. Moreover, it would be important to acquire appropriate instruments and dedicated surgical team as well as genitourinary pathologist who are familiar with the procedure.
Read Also: Side Effects Of Immunotherapy For Bladder Cancer
What Is The Outlook For Someone Who Has Had Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection
Bladder tumor biopsy and resection is a successful treatment for early stage bladder cancer. It can prevent cancer from spreading into the bladder muscle wall. Invasive bladder cancers that spread require more extensive treatment.
However, bladder cancer often comes back . More TURBT procedures may be needed. Your doctor will do frequent follow-up checkups with you to look for signs that the cancer has returned. The risks of repeated TURBT procedures is small.
Some providers might choose to burn off smaller tumors rather than remove them.
If the TURBT shows that you have a more advanced bladder cancer, youll probably need further treatment. This could include:
- A more extensive TURBT.
- Surgery to remove the tumor.
- Surgery to remove the bladder.
- Bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy or BCG. This is a type of therapy that uses the bodys own immune system to fight the cancer.
Your urologist and pathologist will determine the best course of treatment based on the staging of the tumor and your personal medical history. TURBT can help in staging the cancer by determining if the cancer has invaded the bladder wall. Staging refers to determining how serious the cancer is.