Bladder Cancer Survival Rates
The survival rates for a certain period of time depend on the number of people who are diagnosed and treated during the same period of time. The following are some of the data on the survival rates of people who have been treated and lived for a different number of years:
- For patients treated five years ago, the survival rate is estimated to be at 77%.
- For those who underwent treatment ten years ago, it may be estimated to be at 70%.
- For people who had been treated fifteen years ago, the survival rate will be placed at an estimate of 65%.
Since bladder cancer occurs in stages, other statistics will also place their survival rates on patients based on the stages of their cancer. Here, we will look at patients who had been treated five years ago.
- For those whose cancer was at stage 0, their survival rate will be estimated to be at 98%.
- For patients who had stage I, their survival rate is placed at 88%.
- For stage II, the estimate is at 63%.
- For patients with stage III cancer, the estimate of their survival is at 46%.
- Finally, for those whose cancer was at stage IV, their survival rate is estimated to be 15%.
However, the higher the stage of cancer, the more adverse effects will be experienced by the affected individual. It is better that you visit a doctor in case you experience any unusual symptoms that seem connected with bladder cancer.
Risk Factors For Late Recurrence
While there dont seem to be many risk factors for early bladder cancer recurrence, there are a few risk factors for late recurrence of bladder cancer that have been noted in multiple studies. Multiple studies have shown that having a radical cystectomy at a younger age can be a risk factor for recurrence. Patients who have bladder cancer that is not confined to the bladder, or that has involvement in the surrounding muscle tissue may also be at risk for late recurrence, but there is a need for more studies to show a better correlation. Finally, bladder cancer that involves the prostate may also be at risk for a late recurrence.
Patients Refusal Of Surgery Strongly Impairs Breast Cancer Survival
This was a Swiss study by Verkooijen et al, published in 2005 in the Annals of Surgery that looked at 5339 patients under the age of 80 with non-metastatic breast cancer. It didnt examine CAM, just the decision to refuse breast cancer surgery. It compared patients who refused breast cancer with those that those that accepted surgery. Only 1.3% of women refused surgery. Of that group, 37 had no treatment, 25 had hormone-therapy only, and 8 had other types of treatments. So only a small percentage refused all treatment. In this study, the five-year survival of women that refused surgery was 72% versus 87% of women who had surgery. Adjusting for prognostic factors, the authors estimated that women that refused surgery had a 2.1-fold increased risk of death from breast cancer compared to conventional treatment. The survival curves make this clear:
The bottom line in this paper was that a decision to forgo surgery for breast cancer is associated with dramatically worse outcomes and survival.
You May Like: What Antibiotics Treat Bladder And Kidney Infections
What Is A 5
A relative survival rate compares people with the same type and stage of bladder cancer to people in the overall population. For example, if the 5-year relative survival rate for a specific stage of bladder cancer is 90%, it means that people who have that cancer are, on average, about 90% as likely as people who dont have that cancer to live for at least 5 years after being diagnosed.
How Is Bladder Cancer Treated
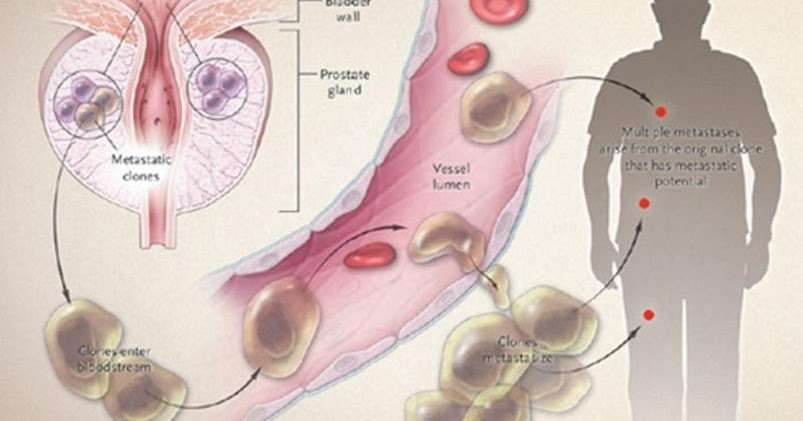
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on
- The stage of cancer.
- If cancer has spread beyond the lining of the bladder.
- The extent of cancer spread.
Treatment options based on tumor grade
- High-grade bladder cancer: High-grade cancers that are life-threatening and spread quickly need to be treated with chemotherapy, radiation or surgery.
- Low-grade cancers: Less aggressive cancers have a low chance of becoming high grade and do not require aggressive treatments, such as radiation or bladder removal.
Treatment options may vary depending on the tumor stage.
Don’t Miss: Can Anxiety Cause Overactive Bladder
Outlook For Men With Localised Prostate Cancer
Most localised prostate cancer is slow-growing and may not need treatment or shorten a mans life. For many men who have treatment for localised prostate cancer, the treatment will get rid of the cancer. For others, treatment may be less successful and the cancer may come back. If this happens, you might need further treatment.
How Long Will You Live If You Have Bladder Cancer
The survival rate depends on the stage of cancer at diagnosis and other health issues.
Overall, 70 to 90 percent of people with localized bladder cancer will live for at least five years or more. The physician calculates this with the help of survival rates. Survival rates indicate the percentage of people who live with a certain type of cancer for a specific time. The physician often uses an overall five-year survival rate. Factors that may affect survival rate include
Table. Five-year survival rates of different stages of bladder cancer
| Bladder cancer SEER stages | |
|---|---|
| All SEER stages combined | 77 |
The surveillance, epidemiology, and end results stages are taken from the SEER database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute. SEER database groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages.
- Localized: There is no indication that cancer has spread outside the bladder.
- Regional: Cancer has invaded the nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, or bones.
Thus, bladder cancer, if detected in the early stage is treatable and has higher survival rates. However, if the cancer is detected in the advanced stages, treatment becomes difficult and the survival rate is low.
Dont Miss: Causes Of Repeated Bladder Infections
Read Also: Bladder Infection Every Time I Have Intercourse
Questions To Ask Your Doctor
To help understand the progression of prostate cancer, discuss these questions with your doctors:
- What is my Gleason score?
- Has the cancer spread outside my prostate?
- Whats my prostate cancer stage?
- Are other tests needed to determine my cancer stage?
- What are the treatment options for my stage of cancer?
- Can I avoid treatment right now and go on active surveillance?
Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
There are some things that can make you more likely to develop bladder cancer. These are called risk factors and they include:
- smoking chemicals in cigarettes can cause bladder cancer, so if you smoke, your risk is up to three times that of a non-smoker
- age most people with bladder cancer are over 60 years of age
- family history a first degree relative with bladder cancer increases risk up to nearly 2 times higher than the general population
- chemicals being in contact with certain chemicals for a long period of time, like aromatic amines, benzene products and aniline dyes, which have been linked to bladder cancer
- frequent infections of the bladder over a long period of time
- some types of radiation therapy around the pelvis, and the chemotherapy drug cyclophosphamide.
Having these risk factors doesnt mean you will develop bladder cancer. Often there is no clear reason for getting bladder cancer. If you are worried about your risk factors, ask your doctor for advice.
You May Like: Does Uti Cause Bladder Leakage
Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on how quickly the cancer is growing. Treatment is different for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and muscle-invasive bladder cancer. You might feel confused or unsure about your treatment options and decisions. Its okay to ask your treatment team to explain the information to you more than once. Its often okay to take some time to think about your decisions.
Stages Of Prostate Cancer
In order to determine the stage of a patients prostate cancer, most doctors start by using the TNM staging system, which helps describe different aspects of the cancers growth.
- T the T category measures the size and extent of the Tumor
- N the N category measures whether and how far the cancer has spread to the Lymph Nodes
- M the M category whether the cancer has spread to other organs in the body (a process called Metastasis
The score for each of these categories is determined based on a pre-determined set of criteria. Your doctor cannot feel or see the tumor with a score of T1. A score of T3 means that the tumor has begun to grow outside of the prostate.
After calculating the TNM categories, doctors will combine the TNM score with the patients Gleason score and PSA levels assigning of a specific stage to the patients cancer.
Prostate cancer prognosis and survival rates can help give patients an idea of their chances of surviving the disease based on the stage and time of diagnosis. While some patients may find this information helpful, others may not want to know.
Donât Miss: Does Prostatitis Go Away Without Treatment
Don’t Miss: Immediate Relief For Bladder Infection
Strategies To Improve Treatment
Most new treatments are developed in clinical trials. Clinical trials are studies that evaluate the effectiveness of new treatment strategies. The development of more effective cancer treatment for bladder cancer requires that new and innovative therapies be evaluated in patients. Participation in a clinical trial may offer access to better treatments and advance the existing knowledge about treatment of bladder cancer. Patients who are interested in participating in a clinical trial should discuss the risks and benefits with their physician.
Rejecting Cancer Treatment: What Are The Consequences

There have been several studies of people who have refused scientific treatments for cancer. The results have not been good.
These do not cure cancer
One of the points Ive tried to emphasize through my contributions to Science-Based Medicine is that every treatment decision requires an evaluation of risks and benefits. No treatment is without some sort of risk. And a decision to decline treatment has its own risks. One of the challenges that I confront regularly as a pharmacist is helping patients understand a medications expected long-term benefits against the risks and side effects of treatment. This dialogue is most challenging with symptomless conditions like high blood pressure, where patients face the prospect of immediate side effects against the potential for long-term benefit. Ones willingness to accept side effects is influenced, in part, by and understanding of, and belief in, the overall goals of therapy. Side effects from blood-pressure medications can be unpleasant. But weighed against the reduced risk of catastrophic events like strokes, drug therapy may be more acceptable. Willingness to accept these tradeoffs varies dramatically by disease, and are strongly influenced by patient-specific factors. In general, the more serious the illness, the greater the willingness to accept the risks of treatment.
Also Check: Can You Get A Uti From Holding Your Bladder
Signs Of Approaching Death
Death from cancer usually occurs after a person has become weaker and more tired over several weeks or months. It is not always possible to predict how long someone will live. But some common signs and symptoms show that a person is entering the final weeks and days of life. Knowing what to expect helps relieve anxiety and allows better planning.
The following are signs and symptoms that suggest a person with cancer may be entering the final weeks of life:
-
Worsening weakness and exhaustion.
-
A need to sleep much of the time, often spending most of the day in bed or resting.
-
Weight loss and muscle thinning or loss.
-
Minimal or no appetite and difficulty eating or swallowing fluids.
-
Little interest in doing things that were previously important.
-
Loss of interest in the outside world, news, politics, entertainment, and local events.
-
Wanting to have only a few people nearby and limiting time spent with visitors.
As the last days of life approach, you may see the following signs and symptoms:
Of course, every person is different. The signs and symptoms that people experience vary. And the order in which signs and symptoms occur may differ.
Most Patients Did Not Progress
With active surveillance, the patients had physical exams and PSA tests every six months, with biopsies recommended every one to two years.
Over an average of two and a half years of follow-up, 43 of the study participants showed evidence of cancer progression and received treatment.
In two patients, cancer spread beyond their prostate.
The study is published in the April issue of the Journal of Urology.
The findings support the idea that some men with prostate cancer may not need treatment, American Cancer Society Deputy Chief Medical Officer Len Lichtenfeld, MD, tells WebMD.
He says the addition of a second biopsy should help refine the search for men who are appropriate candidates for active surveillance, but he also agrees that the strategy of watchful waiting is not without its risks.
âThe real advance will be when we have tests that will tell us with a high degree of accuracy when treatment is needed and when it is not,â he says.
A great deal of research is being done to identify genetic tests or tumor markers that can do this, but Lichtenfeld says it will be years before these tests are validated.
Read Also: What Can You Take For Bladder Pain
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you.
Bladder cancer is most often treated with:
- Surgery
- Chemo
- Immunotherapy
Sometimes more than one type is used. The treatment plan thats best for you depends on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- Whether the cancer has spread into the bladder wall
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
Study Of People Who Underwent A Radical Cystectomy
In 2017, a group of researchers looked at the long-term outcomes of 1652 patients who underwent a radical cystectomy and removal of lymph nodes to treat their bladder cancer. These patients were treated at 3 different centers and had their surgeries between 1988 and 2012. None of these patients had post-surgery chemotherapy or biologic agents, also known as neoadjuvant therapy, which could change the results of the data.
Read Also: Natural Remedies For Bladder Spasms
Is Bladder Cancer Treatable
Many types of therapy are used to treat bladder cancer. In general, the treatment pathway chosen depends on the type and stage of bladder cancer present and a patients overall health and individual preferences. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: to remove tumor cells and surrounding tissue. The type of surgery used depends on factors such as the size and progression of the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: which refers to the use of drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be local or systemic .
- Immunotherapy: which uses naturally occurring or man-made substances to improve or bolster the bodys immune system function. Like with chemotherapy, immunotherapy may be delivered locally or systemically.
- Radiation therapy: which uses x-rays or other high-energy waves or particles to kill cancer cells.
Read Also: Catheterizing The Female Urinary Bladder
How Is Bladder Cancer Diagnosed
Several different diagnostic tests and procedures may be used to detect bladder cancer, often in combination. They are selected based on a patients symptoms and risk factors and may include:
- Urinalysis: a quick test used to detect blood and other substances in urine.
- Urine cytology: urine is examined microscopically to see if cancer cells are present.
- Genomic urine tests: non-invasive molecular tests, such as Cxbladder, which measure gene expression to detect or rule out bladder cancer.
- Cystoscopy: a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera is inserted into the bladder through the urethra. If an abnormal area is seen, a small sample of tissue is usually collected for laboratory examination.
- Imaging: several types of imaging test can be used to visualize the inside of the body, such as ultrasound, CT scan, MRI scan, and x-ray.
Don’t Miss: How To Clear A Bladder Infection
Expectancy And Survival Rates
An expectancy rate can be termed as the same as survival rate. However, a survival rate can be given in terms of a certain duration of time, whereas an expectancy rate is mostly in terms of a person’s whole life. Bladder cancer is a disease that affects many people differently. Hence, determining its expectancy rate can be difficult. Nevertheless, looking at the disease’s survival rate can give the right answers.
Survival rates are figures that give you how many people have survived with a certain similar disease after diagnosis and for how long. Through this, one can be able to estimate the expectancy rate of a person living with the disease.
In the case of bladder cancer, it happens in stages, which means that every stage has a different effect on the patient.
When Do Signs And Symptoms First Appear
Typically, cancer signs and symptoms first appear when the cancerous tumor or mass has grown large enough that it begins to push against nearby organs and tissue, blood vessels, and nerves.
This can lead to pain, a change in how the nearby organs function, or both. A brain tumor pressing against the optic nerve will affect vision, for example.
Some cancers are fast moving, such as liver and pancreatic cancers. Prostate cancer, however, is usually slow moving. This is why many older men with prostate cancer forego treatment theyre more likely to die with prostate cancer than because of it.
Screenings for certain cancers should be part of your normal preventive healthcare. These include cancers of the:
- prostate
- cervix
- skin
Your age, sex, family history, and your own medical history will dictate when routine screenings should begin and how often they should be done.
If youre concerned about symptoms associated with various cancers, then you shouldnt hesitate to see your doctor. You can connect to a physician in your area using the Healthline FindCare tool.
Also Check: Surgery For Prolapsed Uterus And Bladder