Surgery For Women With Cystocele Or Rectocele
Women may need surgery to lift a fallen bladder or rectum. The most common procedure for cystocele and rectocele repair is for the surgeon to make an incision in the wall of the vagina to find the defect or hole in the membrane-a wall of tissue called fascia-that normally separates the vagina from the other pelvic organs. The surgeon places sutures in the fascia to close up the defect, then closes the incision in the vaginal wall with more stitches, removing any excess tissue. These suturing steps tighten the layers of tissue that separate the organs, creating more support for the pelvic organs.
How Oab Can Affect Your Life Your Browser Does Not Support Html5 Audio Playback You May Download The Audio File Directly Here
Without treatment, OAB symptoms are uncomfortable. It can be hard to get through the day without many visits to the bathroom. OAB can impact relationships. You may not want to do things you enjoy because you worry about finding a bathroom in time. It can disrupt your sleep and sex life. It can leave you tired and short-tempered, or leaks can lead to a rash or infections. The whole experience can make anyone feel hopeless and very unhappy.
The good news is that OAB can be controlled. There are treatments available to help.
I stopped running, I stopped taking walks. Basically, I stopped doing things that didn’t allow me immediate access to a bathroom. I was so embarrassed that I didn’t talk to anyone about it for a long time. That was a mistake.
Your browser does not support HTML5 audio playback. You may download the audio file directly here Who gets OAB?
- Both men and women can get OAB.
- Older women who have gone through menopause and men who have had prostate problems are more likely to get OAB.
- Growing older is a factor, but not all people get OAB as they age. It’s not a normal part of aging.
- People with diseases that affect the brain or spinal cord such as stroke and multiple sclerosis are more likely to get OAB.
Once your doctor understands the problem, he or she can tell you about treatment options. There’s no single treatment that’s right for everyone.You may try one treatment, or a few at the same time.
What Are The Complications Of Urinary Retention And Its Treatments
Some complications of urinary retention and its treatments may include:
- Urinary Tract Infections Because urine is normally sterile and the normal flow of urine usually prevents bacteria from infecting the urinary tract, developing urinary retention means an abnormal urine flow gives bacteria at the opening of the urethra a chance to infect the urinary tract.
- Bladder damage If your bladder is stretched too far or for extended periods, the muscles may become permanently damaged and lose their ability to properly contract.
- Kidney damage Sometime urinary retention can cause urine to flow back into the kidneys. This is called reflux and can damage or scar the kidneys.
- Urinary incontinence Transurethral surgery to treat an enlarged prostate can result in urinary incontinence in some men. Its often temporary with most men gaining bladder control in a few weeks or months after surgery. The removal of tumours or cancerous tissue in the bladder, prostate, or urethra may also result in urinary incontinence.
You May Like: Does Overactive Bladder Go Away
Blockage Or Narrowing In The Urethra Or Bladder Neck
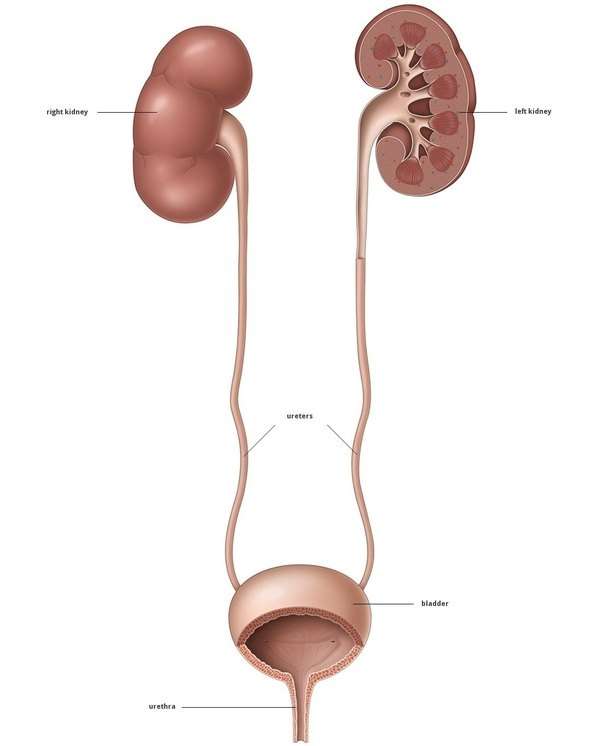
For you to be able to urinate normally, all parts of your urinary tract need to work together in the correct order. Urine normally flows from your kidneys, through the ureters to your bladder, and out the urethra. If a blockage or narrowing occurs somewhere along the urinary tract, you may have difficulty urinating, and if the blockage is severe, you may not be able to urinate at all.
Medical problems that may narrow the urethra and block urine flow include
Empty Your Bladder Before And After Sexual Intercourse
There is nothing worse than frequent urination to put a damper on your sex life.
Even worse is if you get a UTI shortly after having sexyou might blame it on your partner and think you “picked up” something from them.
That might not be so. It might just be a case of poor planning. Use the method in this article before having sex and you will be much more comfortable both right after sex and the morning after.
- Always empty your bladder before sex and, just as importantly, again after sex. Make this a habit! Once you do the method a few times, you will be able to do it in about two minutes total. The first few times, it will take you about 6 to 8 minutes until you get the hang of it.
- Urinating before and after sex helps to eliminate the re-occurrence of that “Oh, I think I’m getting a UTI” feeling the morning after sex. Everyone has experienced this at least once.
- There is no sense in treating what you think is a UTI when, in fact, it is just an irritated bladder from sexual intercourse.
- Follow this method, as noted above, drink more water throughout the day after sex, and you should be fine.
Don’t Miss: Urine Test For Bladder Infection
How Is It Diagnosed
To diagnose urinary retention, a doctor will first ask about the history of your symptoms and perform a physical exam. The physical will include an examination of your genitals and rectum to look for any symptoms affecting those areas that may also affect the urinary tract.
Some other tests that may be used to confirm a diagnosis
likely be inserted to help quickly drain the urine. Local anesthesia will be used to make sure you dont feel pain or discomfort from the catheter.
If a catheter doesnt work or cant be used because of an injury or other condition, a doctor may insert a suprapubic catheter into the skin above your bladder to drain the urine.
Does Bladder Empty Completely After Urination
The bladder never empties completely so some residue is normal. You may find it difficult to start to pass water and that even when you have started the flow is weak and slow. You might find that you dribble after you have finished passing water. Perhaps you dribble urine all the time, even without noticing.
Read Also: How To Pass Bladder Stones
How Is Chronic Urinary Retention Diagnosed
History and physical exam: During the diagnosis process, your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and how long you have had them. He or she will also ask about your medical history and your drug use. A physical exam of the lower abdomen may show the cause or give your provider additional clues. After this, certain tests may be needed. Men may have a rectal exam to check the size of their prostate.
Your urine may be saved and checked to look for infection.
Ultrasound of the bladder: The amount of urine that stays in your bladder after urinating may be measured by doing an ultrasound test of the bladder. This test is called a postvoid residual or bladder scan.
Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is a test in which a thin tube with a tiny camera on one end is put into your urethra. This lets the doctor look at pictures of the lining of your urethra and bladder. This test may show a stricture of the urethra, blockage caused by a stone, an enlarged prostate or a tumor. It can also be used to remove stones, if found. A computed tomography scan may also help find stones or anything else blocking the flow of urine.
Urodynamic testing: Tests that use a catheter to record pressure within the bladder may be done to tell how well the bladder empties. The rate at which urine flows can also be measured by such tests. This is called urodynamic testing.
What Causes Chronic Urinary Retention
Urinary retention can happen for several different reasons. These causes can include:
- A blockage to the way urine leaves your body.
- Medications youre taking for other conditions.
- Nerve issues that interrupt the way your brain and urinary system communicate.
- Infections and swelling that prevent urine from leaving your body.
- Complications and side effects of medications given to you for a surgical procedure.
Blockage
When something blocks the free flow of urine through the bladder and urethra, you might experience urinary retention. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body. In men, a blockage can be caused when the prostate gland gets so big that it presses on the urethra. This is the most common cause of chronic urinary retention in men. One cause in women is a bladder that sags. This is called cystocele. It can also be caused when the rectum sags into the back wall of the vagina a condition called rectocele. Some causes can happen to both men and women. The urethra can get narrow due to scar tissue. This is called a stricture. Urinary stones can also block the flow of urine out of your body.
Medications
Nerve issues
- Trauma to the spine or pelvis.
- Pressure on the spinal cord from tumors and a herniated disk.
- Vaginal childbirth.
Urinary retention from nerve disease occurs at the same rate in men and women.
Infections and swelling
Surgery
Also Check: Does Bladder Cancer Feel Like A Uti
Techniques For Complete Bladder Emptying
Bowel Cancer: Dr Chris Reveals Symptoms And How To Test
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
Bowel cancer can progress by infecting and destroying nearby tissues. The cancer can even travel to other parts of the body . Eventually, the cancer can lead to death. To improve chances of survival rates, early diagnosis is paramount.
The next time you come back from the toilet, does it feel as though your bladder has been completely emptied?
If not, this is cause for alarm. The sensation that your bladder is still partially full after releasing yourself is one symptom of bowel cancer.
Bowel cancer can either begin in the large bowel or the back passage (in other words, the rectum, a chamber that begins at the end of the large intestine and ends at the anus.
Read Also: 3 Types Of Bladder Cancer
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
The lower urinary tract includes the bladder and the tube that urine passes through as it leaves the body .
Lower urinary tract symptoms are common as people get older.
They can include:
- problems with storing urine, such as an urgent or frequent need to pass urine or feeling like you need to go again straight after you’ve just been
- problems with passing urine, such as a slow stream of urine, straining to pass urine, or stopping and starting as you pass urine
- problems after you’ve passed urine, such as feeling that you’ve not completely emptied your bladder or passing a few drops of urine after you think you’ve finished
Experiencing LUTS can make urinary incontinence more likely.
Page last reviewed: 07 November 2019 Next review due: 07 November 2022
What Are The Complications Of Urinary Retention

Urinary Tract Infection
Urine is normally sterile, and the normal flow of urine usually prevents bacteria from growing in the urinary tract. When urine stays in the bladder, however, bacteria have a chance to grow and infect the urinary tract.
Bladder Damage
If the bladder becomes stretched too far or for long periods, the muscle may be permanently damaged and lose its ability to contract.
Chronic Kidney Disease
If urine backs up into the kidneys, permanent kidney damage can lead to reduced kidney function and chronic kidney disease. If you lose too much of your kidney function, you will need dialysis or a kidney transplant to stay alive.
You May Like: Bladder Problems After Gastric Bypass
History Of Complaints And Physical Examination
A physician will suspect urinary retention by your symptoms and will attempt to confirm the diagnosis with a physical examination of the lower abdomen. The physician may be able to feel the distended bladder by lightly tapping on your lower belly. Tapping or striking for diagnostic purposes is called percussing.
When Should I See A Health Care Professional
See a health care professional right away if you are unable to urinate or have severe pain in your abdomen. Acute urinary retention can be life threatening.
If you have any of the other symptoms of urinary retention, such as trouble urinating, frequent urination, or leaking urine, talk with your health care professional about your symptoms and possible treatments. Chronic urinary retention can cause serious health problems.
Don’t Miss: What Can You Do For A Bladder Infection
What Is Neurogenic Bladder
Your bladder relies on muscles to contract and release when youre ready to urinate. Your brain typically regulates this process, but sometimes the message that you need to urinate isnt sent from your brain to your bladder. This is a condition known as neurogenic bladder. Treatment for this condition can help you regain control.
Neurogenic bladder causes you to lose control over your ability to urinate. This can cause you to urinate too much or not enough, both of which can have harmful consequences.
Neurogenic bladder symptoms include:
- a dribbling stream when urinating
- an inability to fully empty your bladder
- straining during urination
- difficulty determining when your bladder is full
See your doctor if you have these symptoms or others that are related to urinating.
Neurogenic bladder is a condition caused by the nerves along the pathway between the bladder and the brain not working properly. This can be due to a brain disorder or bladder nerve damage.
Examples of brain disorders that can cause neurogenic bladder include:
- injury to the spinal cord
- spinal cord birth defects, such as spina bifida
Conditions that affect the bladder muscles include:
- diabetes, which can cause nerve damage
- long-term alcohol abuse
What Are The Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
The signs can vary. Some people with the chronic form have a hard time starting the flow of urine. Some have a weak flow once they start. Others may feel the need to go but cant start. Others have to go a lot, while others still feel the need to go right after going. You may leak urine when you arent going because the bladder is full.
With the acute form, youre all of a sudden not able to go at all, or only able to go very small amounts. This occurs even though you have a full bladder. See a healthcare provider right away if this happens to you.
Also Check: Where Do You Feel Bladder Spasms
Managing Bladder Or Urinary Incontinence
Sometimes urinary incontinence can last a short time, depending on what’s causing it. But sometimes incontinence can be long-term and uncomfortable, making some everyday activities difficult to manage.
Your health care team will ask you questions to determine the type of bladder incontinence you might have. Then, you might need tests to verify the type and learn the cause of it which will help them know the best way to manage it.
- Pelvic floor muscle strengthening may be recommended. A physical therapist that specializes in pelvic floor muscle exercises can help. This might help muscle strength and bladder control get better by doing exercises that tighten and relax muscles that control the flow of urine.
- Bladder training canhelp manage how often you need to urinate throughout the day, by assigning certain time intervals to empty your bladder.
What Can Cause Frequent Urination
Recurrent UTI’s are very annoying.
Frequently getting up during the night to urinate is annoying, too. Although this is usually caused by some type of infection, the good news is that your symptoms won’t always be due to a urinary tract infection .
Sometimes it’s just because of the bad habits we developholding urine in, not wanting to use a public bathroom , body positioning, frequently using over-the-counter sanitary wipes to cleanse, or maybe some unusual health habits .
Assuming your doctor has ruled out other causes for your frequent urination, such as kidney disease, dropped bladder, UTI, cystitis, kidney diseases, etc., I may have some useful suggestions for you.
Out of Desperation Came Relief
Also Check: Tb Virus Treatment For Bladder Cancer