Bladder Cancer In The Elderly Patient: Challenges And Solutions
Accepted for publication 27 March 2015
10 June 2015Volume 2015:10 Pages 939949
Introduction
Bladder cancer is an age-associated malignancy, with a median age at diagnosis of 73 years, and individuals aged 7584 years accounting for the largest percentage at 30% of new cases.1 Curative therapy with either radical cystectomy , with or without perioperative chemotherapy, or combined-modality therapy with a goal of bladder preservation through a combination of maximal transurethral resection of bladder tumor, radiation therapy , and concurrent chemotherapy, offers varying rates of long-term survival dependent upon the stage at diagnosis. The risk of recurrence estimated by a post-RC nomogram ranges from 20% for patients with organ-confined disease to 70% for those with limited lymph node involvement.2 In contrast, metastatic disease remains incurable with currently available therapies. The average life expectancy for metastatic BC is 14 months in patients who receive systemic treatment and 8 months without treatment, making it the eighth leading cause of cancer-related death in 2013.3,4
Management of muscle invasive bladder cancer in the elderly
Radical cystectomy
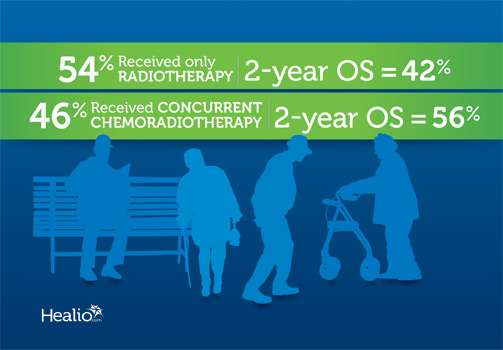
Definitive chemoradiation
Chemotherapy: neoadjuvant and adjuvant
Management of metastatic bladder cancer in the elderly
|
Table 2 Risk factors for chemotherapy toxicity in the elderlyNote: Data from Montgomery et al.35 |
Health-related quality of life for patients with bladder cancer
Disclosure
Treatment Of Bladder Cancer By Stage
Most of the time, treatment of bladder cancer is based on the tumors clinical stage when its first diagnosed. This includes how deep its thought to have grown into the bladder wall and whether it has spread beyond the bladder. Other factors, such as the size of the tumor, how fast the cancer cells are growing , and a persons overall health and preferences, also affect treatment options.
Involving Patients In Care Discussions
Among the themes that emerged from interviewing the study participants was a consistent desire for early, honest, and transparent communication from caregivers. They expressed a desire for information about what to expect with changes to their physical abilities, mobility, and independence.
We learned that they really do want to be involved in discussions of their care and to have clear expectations for their treatment, Kessler says. They want to be engaged early in the process and not feel like theyre waiting or wishing for information.
Also, while there was some variation among study participants about how they wanted their care partners, who often were spouses or family members, involved in discussions of their care, they expressed a desire for a clear understanding of what the care partners role would be.
Researchers further found that study participants didnt feel that discussions of their prognosis and treatment had to happen only with medical doctors, but could happen with nurses, physician assistants, or other informed members of their care team.
What weve found is that patients really do want to talk about their prognosis and treatment right from the beginning, Kessler says. Instead of focusing on alignment at end-of-life, now were looking at ways to come up with a treatment plan that better aligns care for people right from the start.
Read Also: Why Do I Get Recurring Bladder Infections
Recommended Reading: Can A Bladder Infection Make You Feel Tired
Low Grade And High Grade Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer starts in the lining of the bladder in about 90 percent of people diagnosed with this cancer. Bladder cancer is called low grade or high grade.
- Low-grade bladder cancer means the cancer has not invaded the muscles around the bladder . People rarely die from this type of bladder cancer, it often recurs after treatment.
- High-grade bladder cancer also often recurs and has a higher chance of spreading to other parts of the body. Almost all deaths from bladder cancer result this type so it is treated more aggressively.
Bladder Cancer In Women
In 2016, about 18,000 women will be told they have bladder cancer. Your bladder is an organ in your pelvic area that holds urine. Most bladder cancers start in the cells that line the inside of the bladder.
One of the first signs of bladder cancer is blood in the urine . Blood can either be seen with the naked eye or seen only under a microscope . Many women ignore blood in their urine because they think its normal in females. Other signs of bladder cancer are frequent or painful passing of urine, back pain, stomach pain and the feeling as if you need to go to the bathroom right away . Be sure to see a health care provider if you have any of these signs.
If youve been told you have bladder cancer, your health care team will talk with you about your treatment choices. Based on the stage of the cancer and other factors, your treatment could include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation or other therapies.
What You Need to Know:
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If You Have Bladder Problems
Treatment Of Invasive Bladder Cancer In The Elderly And Frail Patient
I think this is a very contemporary topic because we are living in an aging society. If you look here, and you know if you really want to look at the life expectancy you should look at charts of the insurance company and governmental agencies rather than medical reports. And this is the life expectancy nowadays where in North America. So, you can see that if you are at the octogenarians, octogenarians for the sake of this talk is 80 years old, 80 to 90, and nonagenarians are 90 and plus. And you see so when you hit 80 you still have at least seven years as a male, and nine years or more as a female. So, we are actually talking about increased population that, and Ill show you data, has more bladder cancer, and theyre actually destined to live quite long if they are in the average risk. So, if you live for example to 90 years old youre expected to live about four years if youre a male and four and a half or five years if youre a female. So, we have to bear these figures in mind.
But once its diagnosed we have a very poor, we poorly address that. This is a paper by Gore et al, and it shows that only 21% of muscle invasive bladder cancer patients over the age of 65 here actually received radical cystectomy. He shows also that there was a better overall survival, but obviously this is biased by selection.
Partial cystectomy there is very few data, none in octogenarian. This is just a series from Wes Kassouf, so I will omit that because we really dont have enough data.
Where Do These Numbers Come From
The American Cancer Society relies on information from the SEER* database, maintained by the National Cancer Institute , to provide survival statistics for different types of cancer.
The SEER database tracks 5-year relative survival rates for bladder cancer in the United States, based on how far the cancer has spread. The SEER database, however, does not group cancers by AJCC TNM stages . Instead, it groups cancers into localized, regional, and distant stages:
- Localized: There is no sign that the cancer has spread outside of the bladder.
- Regional: The cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby structures or lymph nodes.
- Distant: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, liver or bones.
Recommended Reading: Loss Of Bladder Control While Coughing
Read Also: Is Caffeine A Bladder Irritant
Surgical Treatment Of Bladder Cancer Benefits Patients Older Patients
Researchers from the University of Michigan have reported that aggressive surgical management of bladder cancer in patients over the age of 80 may improve survival.
Bladder cancer occurs predominantly in elderly men and less frequently in women and younger men. Most bladder cancers are not diagnosed until they have become very large. As a result, bladder cancers are typically treated with surgery and in many cases, the surgery is very aggressive, or extensive, in order to remove all of the cancer. In patients 80 years old or older, the management of bladder cancer typically includes watchful waiting , radiotherapy alone , full or partial cystectomy , and transurethral resection .
Data for this study was derived from the National Cancer Institutes Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results cancer registry. The researchers evaluated treatment and survival information from 13,796 patients who were diagnosed with bladder cancer. In this group, 24% were older than 80 years of age.
Patients 80 years or older were less likely to be treated with curative surgery. However, results indicate that the elderly patients who were treated with aggressive surgery consisting of a radical or partial bladder removal experienced the greatest reduction in risk of death.
Changes In Bladder Habits Or Symptoms Of Irritation
Bladder cancer can sometimes cause changes in urination, such as:
- Having to urinate more often than usual
- Pain or burning during urination
- Feeling as if you need to go right away, even when your bladder isn’t full
- Having trouble urinating or having a weak urine stream
- Having to get up to urinate many times during the night
These symptoms are more likely to be caused by a urinary tract infection , bladder stones, an overactive bladder, or an enlarged prostate . Still, its important to have them checked by a doctor so that the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
Don’t Miss: Types Of Pessaries For Bladder Prolapse
Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Caregivers should look for these symptoms of bladder cancer in their elderly mothers and fathers. Common symptoms of bladder cancer include:
- Blood in the urine
- Pain during urination
- Frequent urination, or feeling the need to urinate without results. These symptoms are not sure signs of bladder cancer. It could be some form of incontinence.
Infections, benign tumors, bladder stones, or other problems also can cause these symptoms. Anyone with these symptoms should see a doctor so that the doctor can diagnose and treat any problem as early as possible. People with symptoms like these may see their family doctor or a urologist, a doctor who specializes in diseases of the urinary system.
How Common Is Bladder Cancer
The American Cancer Societys estimates for bladder cancer in the United States for 2022 are:
- About 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer
- About 17,100 deaths from bladder cancer
The rates of new bladder cancers and deaths linked to bladder cancer and have been dropping slightly in women in recent years. In men, incidence rates have been decreasing, but death rates have been stable.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men, but it’s less common in women.
Recommended Reading: Mesh Bladder Sling Failure Symptoms
Future Directions And Research Priorities
Elderly adults with bladder cancer are faced with difficult choices with regard to the optimum management of their condition. Health-care providers need to consider the unique needs of older patients with bladder cancer. When facing any potentially catastrophic illness, issues related to functional independence and quality of life must be considered, as these factors may assume an importance equal to or even greater than that of survival. Many studies fail to include clinical outcome measures that are truly meaningful for older adults therefore, these studies are not able to appreciate the tremendous variability between individuals as they age. As the earlier discussion indicates, aging represents a very large risk factor for the development of bladder cancer, and may also increase the likelihood of muscle-invasive disease. Nevertheless, based on the available evidence, comorbidity, functional status and frailty may represent far better predictors of undesirable outcomes than chronological age alone. With these considerations in mind, future studies of elderly patients will need to incorporate these other dimensions of health status, as is normally done in the context of a geriatric assessment.37 Clinical domains that should be assessed include function, objective measures of physical performance, comorbidity, nutrition, social support, cognition and depression.
In A Recent Study Elizabeth Kessler Md Found That Older Patients Want Honest Communication And Family Involvement In Care Planning

minute read
The median age for receiving a bladder cancer diagnosis is 73, and a significant number of those living with the disease are in their 70s and 80s.
A longstanding stereotype in cancer care is that older patients favor a more paternalistic style of care, one in which they defer to the authority of a care provider and may not ask many questions or seek more in-depth information.
However, recently published research examining the care planning priorities of older adults with advanced bladder cancer found that patients want more transparent communication with their care providers, including what to expect from treatment, how their quality of life might change, and how their families can be involved in care planning.
What we learned is we need to work to find ways to engage patients very early on in the treatment process, says study author Elizabeth Kessler, MD, a University of Colorado Cancer Center member and associate professor of medical oncology in the CU School of Medicine. We need to continue to work on ways to allow for these discussions.
Read Also: What Causes Chronic Bladder Infections
Diet Related Tips For Bladder Problems In Older Women
Drink lots of water
Hydration! Hydration! Hydration! Remain hydrated by drinking at least 6 -8 eight ounce glasses of water a day. If you are like me, with a preference for drinking other fluids, it is recommended that you try to make half of your fluid intake water because water is the best fluid for bladder health.
Limit your consumption of alcohol and caffeinated drinks or beverages. The key word is limit and not necessarily cut out.
Maintain a healthy high fiber diet fruits, vegetables and whole grains to prevent constipation. Straining for bowel movement can weaken your sphincter muscles and could also result in incontinence.
Avoid bladder irritants. Avoid or eliminate any foods that irritate your bladder. Some of these may include spicy and acidic foods, caffeine, alcohol and carbonated beverages
Bladder Cancer In The Elderly: Balancing Disease And Surgical Risk
Release Date: November 2013
Estimated time to complete the educational activity: 1 hour
This activity is jointly sponsored by Medical Education Resources and Haymarket Medical Education.
Statement of Need: Given the decision-making intricacies associated with radical surgeryfor invasive bladder cancer, there is a real need for improved risk assessment tools to objectifypatients perioperative risk for adverse outcomes post-surgery versus their disease risk andlikelihood of cure with invasive/maximal therapy.
Target Audience: This activity has been designed to meet the needs of urologists,and supporting clinicians who treat patients with bladder cancer.
Educational Objectives: After completing the activity, the participant should be better able to:
- Evaluate preoperative mechanisms for assessing surgical risk in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
- Examine existing objective criteria for making treatment decisions in this patient population.
- Relate the question of surgical frailty to stratify risk in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Accreditation Statement: This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and Policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint sponsorship of Medical Education Resources and Haymarket Medical Education. MER is accredited by the ACCME to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Also Check: Can You Feel A Bladder Sling
Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Your doctor is familiar with your situation ask how these numbers may apply to you.
Eau : Treatment Options For Elderly Patients With Muscle
Figure 1Figure 2
- Monitoring patients and treating them according to their symptoms without applying oncological or invasive treatments during their follow-up
- These patients can be managed with analgesics, continuous saline bladder irrigation, or blood transfusion, but without oncological surgery, bladder instillations, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy
Figure 3
You May Like: How Long To Get Rid Of Bladder Infection
Prognosis And Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
When someone is diagnosed with bladder cancer, their doctor will give them a prognosis. A prognosis is the doctors opinion of how likely the cancer will spread and the chances of getting better. A prognosis depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the persons age and general health.
Bladder cancer can usually be effectively treated if it is found before it spreads outside the bladder.
If you have bladder cancer, your doctor will talk to you about your individual situation when working out your prognosis. Every persons experience is different, and there is support available to you.
Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
MIBC is an aggressive tumor with a poor prognosis the 5- and 10-year overall survival rates are around 65% and 45% respectively, closely related to the disease stage . MIBC may arise de novo or as the result of a progression of NMIBC. If untreated it will lead to local invasion of adjacent structures, hydronephrosis, incoercible hematuria, lymph node and distant metastases . Nowadays the only treatment with a curative intent is RC, eventually preceded by neoadjuvant CHT when possible. Despite these evidences, many older patients do not receive curative treatments. Analyzing the report of the SEER, Gore et al. found that only 21% of MIBC patients older than 65 years received a RC . The predictors for this were urologist choice, longer travel distances and residence in rural areas. These observations have been confirmed analyzing data from the USA National Cancer Database. Cystectomy rate was 55% in patients younger than 70 years, 45% in those 70 to 79 years, and it decreased to 21% in those older than 79 years. Half of patients older than 85 years received no treatment . Reasons for denying old patients major surgery are multi-factorial, but they are mainly based on the perception that many patients will not tolerate RC and urinary diversion because of age and comorbidities. For this reason, an integrate and multidisciplinary approach to this category of patients is mandatory. The evaluation has to be run by the urologist, oncologist, radiotherapist and geriatricians.
You May Like: Reasons For Frequent Bladder Infections