Embedded Or Biofilm Infection
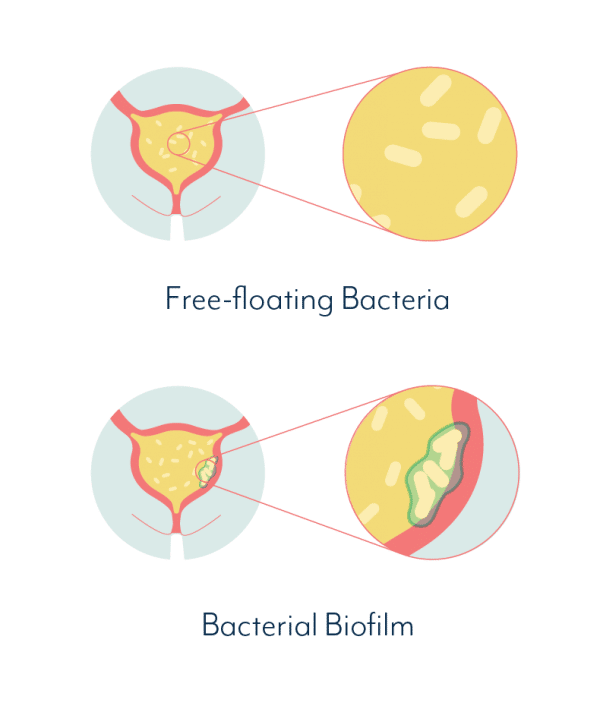
When bacteria first enter the urinary tract, they are free-floating . However, under the right circumstances, these bacteria can stick to the bladder lining, and form a networked community, shielded by a protective slimy material. This slimy material protects the bacteria from antibiotics, as well as shielding it from the bodys natural defences. This is known as biofilm and can allow bacteria to survive for long periods. Once such a biofilm develops, whenever you get a UTI, instead of recovering completely, your body can be left with an embedded infection adherent to bladder wall, that is difficult to treat.
In addition to biofilms attached to the bladder wall, bacteria can also invade bladder cells and then rapidly replicate within the cells to form intracellular bacterial communities with enhanced resistance to antibiotics. However, within hours of IBC development, the progeny of successfully invasive bacteria emerge from the bladder cells, again in a free-floating state, ready to invade neighbouring cells to start the cycle anew. This form of invasion and intracellular replication affords a survival advantage for the bacteria to persist within the bladder as it sheds it lining.
Only in the last 10-15 years have biofilms and intracellular bacterial communities been recognised as a contributor to chronic bladder infection. Fortunately, research is now throwing further light on these mechanism and potential treatments to combat them.
How To Avoid The Recurrence Of Utis
Drinking lots of water, urinating before and after sexual intercourse, and not waiting to urinate can all help reduce your incidence of urinary tract infections. Other remedies include wiping from front to back after urinating, wearing cotton underwear, and seeking treatment at the first sign of a UTI.
Contact Cleveland Urology Associates at if you are experiencing early signs of a urinary tract infection.
Dont Miss: Antibiotics For Uti Or Bladder Infection
How To Feel Better
If your healthcare professional prescribes you antibiotics:
- Take antibiotics exactly as your healthcare professional tells you.
- Do not share your antibiotics with others.
- Do not save antibiotics for later. Talk to your healthcare professional about safely discarding leftover antibiotics.
Drink plenty of water or other fluids. Your healthcare professional might also recommend medicine to help lessen the pain or discomfort. Talk with your healthcare professional if you have any questions about your antibiotics.
You May Like: Drugs Used To Treat Overactive Bladder
Similar Articles Being Viewed By Others
Carousel with three slides shown at a time. Use the Previous and Next buttons to navigate three slides at a time, or the slide dot buttons at the end to jump three slides at a time.
07 December 2020
Catherine S. Forster, Michael H. Hsieh & Michael D. Cabana
26 January 2022
Abdikhaliq Hussein Ali, Dawit Yihdego Reda & Moges Desta Ormago
07 July 2020
Rokaia B. Elamary, Fawziah M. Albarakaty & Wesam M. Salem
03 December 2020
Bin Cheng, Xinyi Zeng, Yan Wang
volume 15, pages 750776
Recurrent Cystitis In Women
Some women have recurring bouts of cystitis, sometimes defined as two proven infections within six months, or three infections in a year.
In this article
Cystitis means inflammation of the bladder. It is usually caused by a urine infection. Some women have repeated bouts of cystitis. Doctors define a recurrent infection as either three proven separate infections in a year or as two in six months. In many cases there is no apparent reason for a woman to get frequent attacks of cystitis. There are a number of treatment options to consider. This might be treating each episode promptly with a short course of antibiotics, a regular low dose of antibiotics taken long-term, or taking a single dose of antibiotic after having sex . You can read more about cystitis in the separate leaflet called Cystitis in Women.
You May Like: How Do I Stop Bladder Leakage
Causes Of Recurrent Urinary Tract Infections
The most common recurrent urinary tract infection causes in women are
- The female urethra is shorter than a mans, which means that bacteria has a shorter distance it needs to travel in order to get to the bladder, multiply, and cause infection.
- The proximity of the female urethra and rectum can result in a bacteria exchange from the rectum to the urethra, particularly if the patient wipes back to front instead of front to back after defecating.
They can be prevented by:
- Staying hydrated aka drinking plenty of water, ideally a gallon per day, to flush out bacteria.
- Being cautious when using a diaphragm during sex. Diaphragms can push up against the urethra, which makes it harder to fully empty the bladder during urination. The urine that doesnt empty is more likely to grow bacteria.
Why Do Utis Return Despite Treatment
There are about a half-dozen oral antibiotics that treat UTIs. Sometimes a doctor will prescribe one drug, then switch to another after a urine culture identifies which bacteria is at work. Adjusting the medication can take time, and recurrent infections may occur in the meantime.
Sometimes a person starts to feel better and decides to stops taking the antibiotic contrary to the doctors instructions and another infection soon follows. Its never a good idea to stop taking antibiotics before your dosage is complete.
But even people who take medication as the doctor prescribes may get recurrent infections, Dr. Vasavada says.
If youre a younger woman who is sexually active, your doctor may prescribe an antibiotic to take before and after sexual activity. For post-menopausal women, a vaginal estrogen cream may help reduce infections.
If infections persist, your doctor may test for other health problems in the kidney, bladder or other parts of the urinary system.
Also Check: Ou Pelvic And Bladder Health Clinic
Symptoms Of Recurrent Utis
UTIs cause a range of symptoms, which can vary depending on which part of the urinary tract is affected.
Common symptoms include:
- A feeling of pain or burning during urination
- Pain or pressure in the pelvic area
- A strong urge to urinate
- Frequent urination in small amounts
- Urine that is cloudy
- Urine that is colored slightly red, pink, or brown
- Urine with a strong, unpleasant odor
A UTI that has spread to the kidneys is a potentially serious infection that requires immediate medical attention. Contact your physician right away if you have a UTI along with nausea, vomiting, fever, chills, and/or back pain below your ribs on one side.
What Are Chronic Urinary Tract Infections
A chronic urinary tract infection is a repeated or prolonged bacterial infection of the bladder or urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
While urinary tract infections are common, some women suffer from repeated or recurrent infections .
Women suffering from chronic urinary tract infections may have:
- Two or more infections in a 6-month period and/or three or more infections in a 12-month period
- Symptoms that don’t disappear within 24 to 48 hours after treatment begins
- A urinary tract infection that lasts longer than two weeks
Chronic urinary tract infections can be a painful and frustrating disorder, but effective treatment is available.
You May Like: Do I Have A Bladder Problem
If You Are Concerned About Bladder Cancer Speak To Your Doctor About Cxbladder
Early detection saves lives and is a crucial factor when it comes to the treatment of bladder cancer. Cxbladder is a clinically proven cutting-edge genomic urine test that quickly and accurately detects or rules out bladder cancer in patients presenting with blood in the urine and those being monitored for recurrence. The test works at a molecular level, measuring five biomarker genes to detect the presence or absence of bladder cancer.
Cxbladder is discreet, quick and non-invasive. It comes as a suite of test options, each optimized for a different point in the patient journey.
- Triage: Incorporates known bladder cancer risk factors to help rapidly rule out the disease.
- Detect: Designed to work alongside other tests to improve overall detection accuracy.
- Monitor: Optimized for bladder cancer surveillance, reducing the need for further invasive tests
Cxbladder gives you peace of mind and will help your doctor make informed treatment decisions. Speak to your general practitioner or urologist to learn more about Cxbladder and which test might be right for you. You can also contact our Customer Service Team directly.Learn more about Cxbladder Contact Us for more information
Can You Test For Biofilms In The Bladder
The presence of biofilms in the bladder is not far-fetched science.
The National Institutes of Health estimates around 80% of all bacterial infections in humans involve biofilms.
Although the existence of biofilms in human infection has been accepted in medicine for decades, it is much more recently that attention has turned to their involvement in chronic UTI.
Traditionally, testing labs have focused on culturing and testing free-floating pathogens. If free-floating pathogens are identified, their susceptibility to antibiotics is also tested while they are in a free-floating state.
Once the susceptibility has been tested, it is possible to prescribe the right treatment.
The problem with these types of tests is that they do not specifically detect biofilm formations in the bladder. And therefore, they are not helpful in deciphering which treatments may be effective against microbes within a biofilm.
You May Like: How To Deal With A Weak Bladder
What Can You Do To Prevent Recurrent Utis
If you are suffering from recurrent UTIs, you must get in touch with your primary care physician or a urologist. After carefully evaluating your condition, he/she will design an appropriate course of treatment.
Also, there are a lot of ways through which you can minimize your chances of getting UTIs. For this,
- Drink plenty of water It will help you get flush out all the bacteria through urine.
- Do not hold your pee If you feel the urge to urinate, find a bathroom and go.
- Maintain good sexual hygiene Do not indulge in unhealthy sexual activities. Also, urinate shortly after sex.
- Always use clean washrooms Make sure the washroom that you are using is clean and fresh.
- Use dermatologically tested products Always use sprays, deodorants and powders that are medically approved. And avoid using sprays close to your genitals.
- Keep your genitals clean Always wipe yourself from front to back after urinating.
- Wear cotton underwear Always prefer cotton panties to help keep your urethra dry.
Also Check: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
What Causes Recurrent Utis
Bacteria can enter the urinary tract from the outside to cause a UTI to come back, or a recurrent infection can be caused by bacteria that remain in the urinary tract after a previous infection. Symptoms of recurrent UTI in men and women include the frequent urge to urinate, burning pain or pressure, cloudy or discolored urine, bloody urine, and chills and fever. Children with UTIs are more likely to have fever without the other symptoms. Common conditions that can lead to recurrent UTIs include:
- Being in a nursing home or hospital
- Having an infected or enlarged prostate
- Being born with an abnormality of the urinary tract
You May Like: Intravesical Chemotherapy In Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer
Why Does My Child Keep Getting A Uti
Common causes of UTIs are constipation, wiping from back to front, holding in pee, taking bubble baths or staying in a wet bathing suit for extended periods.
However, recurrent UTIs could be a sign of a malformation or malfunction of the urinary tract, such as vesicoureteral reflux . VUR occurs when the flow of urine goes the wrong direction from the bladder to the kidneys and is common among infants and children.
Your childs doctor can help rule out other conditions related to UTIs and discuss treatment options.
Treatment For Recurrent Utis
You can typically get rid of a simple UTI with antibiotics, the Mayo Clinic explains. But, when you have chronic UTIs, your doctor may recommend the following, per the Mayo Clinic:
Low-dose antibiotics, for six months but maybe longer
Self-diagnosis and treatment, if you stay in touch with your doctor
A single dose of an antibiotic after sex, if your recurrent UTIs are related to sex
Vaginal estrogen therapy, if youre postmenopausal
Recommended Reading: Hill’s Science Diet Bladder Stones
What Conditions Are Related To Recurrent Utis
Recurrent UTIs sometimes happen along with other conditions, such as:
- vesicoureteral reflux , which is found in 30%50% of kids diagnosed with a UTI. In this congenital condition, pee flows backward from the bladder to the ureters. Ureters are thin, tube-like structures that carry pee from the kidney to the bladder. Sometimes the pee backs up to the kidneys. If its infected with bacteria, it can lead to pyelonephritis.
- hydronephrosis, which is an enlargement of one or both kidneys due to backup or blockage of urine flow. Its usually caused by severe VUR or a blocked ureter. Some kids with hydronephrosis might need to take daily low doses of antibiotics to prevent UTIs until the condition producing hydronephrosis gets better or is fixed through surgery.
But not all cases of recurrent UTIs can be traced back to these body structure-related problems. For example, dysfunctional voiding when a child doesnt relax the muscles properly while peeing is a common cause of UTIs. Not peeing often enough also can also increase a childs risk for recurrent infections. Both dysfunctional voiding and infrequent urination can be associated with constipation.
Rarely, unrelated conditions that harm the bodys natural defenses, such as diseases of the immune system, also can lead to recurrent UTIs. Use of a nonsterile urinary catheter can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract and also cause an infection.
The Absence Of Recurrent Uti Guidelines
Because there are no guidelines on managing complex or recurrent UTI, primary care doctors are generally not in a position to help.
| Most UTI guidelines are aimed at management of simple uncomplicated UTI. It can be very difficult to successfully manage complex or recurrent UTI in primary care. If symptoms persist, or where there is diagnostic uncertainty GPs will need to make a referral for specialist assessment.” |
For females that progress from a single UTI, to recurrent UTI or chronic urinary tract infection, or to a diagnosis of Interstitial Cystitis, there has historically been very little hope of effective treatment. We hope to help change this.
Don’t Miss: Va Bladder Cancer Decision Granted
Are Utis The Same In Older Women As Younger Women
Although women can get UTIs at any age, they can affect older women differently. UTI symptoms can be different or more severe in older women. Sometimes older women can have a UTI and be asymptomatic.
In addition to the general symptoms listed above, older women should be aware of these additional symptoms:
- Delirium or hallucination
- Agitation and restlessness
- Social withdrawal
Older women are also more likely to have an underlying medical condition thats triggering their recurrent UTIs or causing UTI-like symptoms. For example, pelvic organ prolapse can cause symptoms that are very similar to UTIs, such as a frequent urge to urinate or pain and pressure in the lower abdomen.
Since these conditions cant be treated with the antibiotics often prescribed for UTIs, its important to have a comprehensive medical exam. At Alpenglow Gynecology, we rule out underlying causes or conditions that may be causing your UTI symptoms.
Urinary Tract Infections Refer To Any Type Of Irritation That Affects The Urinary System
While UTIs often occur in or around the bladder, the kidneys and connecting tubes called ureters are sometimes affected. Some UTIs are a one-time occurrence with mild symptoms.
- However, there are times when urinary tract infections keep returning.
- Its severe and recurring infections that often require attention from a doctor specializing in urological conditions.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Cancer Is It Curable
How Is A Recurrent Uti Treated
A UTI is diagnosed with a urine test. The test is sent to a lab to determine which bacteria are causing the infection.
UTIs are treated with antibiotics. If you have an active UTI, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotics to take over several days.
If UTIs are recurrent, your doctor might prescribe lower dose antibiotics to take for several months. This keeps bacteria from invading the bladder, and allows the bladder to heal from the chronic inflammation of repeated infections.
Long-term use of antibiotics may cause some side effects, such as yeast infections or diarrhea.
How Are Chronic Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed

Prompt diagnosis is key to treating chronic urinary tract infections. Testing may be performed to help rule out other conditions. Diagnostic testing may include:
- Urinalysis. To look for the presence of bacteria and red or white blood cells
- Urine culture. To determine which bacteria are present and possibly test different antibiotics
- Imaging. To view the health of the urinary tract , including CT scan, ultrasound, and x-ray: a special dye is used in some cases to aid in imaging
- Cystoscopy. Use of a scope to view inside the bladder and urethra and check for abnormalities
Don’t Miss: Estrogen Cream For Prolapsed Bladder
How Do Utis Affect Pregnancy
Changes in hormone levels during pregnancy raise your risk for UTIs. UTIs during pregnancy are more likely to spread to the kidneys.
If you’re pregnant and have symptoms of a UTI, see your doctor or nurse right away. Your doctor will give you an antibiotic that is safe to take during pregnancy.
If left untreated, UTIs could lead to kidney infections and problems during pregnancy, including:
- Premature birth
- Low birth weight
Causes Of Chronic Utis
Urinary tract infections arecommon, affecting more than half of all women at some point in their lives. Furthermore, these infections account for almost 25% of bacterial infections in women. But the fact that you have plenty of company wont make the pain or burning any easier to deal with.
If you have a UTI or think your condition is chronic, the urogynecologists atSoutheast Urogyn can help. Their doctors areUTI specialists, and they can give you a thorough exam and get to the root cause of your UTIs.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Best Underwear For Bladder Leakage