Signs And Symptoms Of Cancer
Signs and symptoms are ways the body lets you know that you have an injury, illness, or disease.
- A sign, such as fever or bleeding, can be seen or measured by someone else.
- A symptom, such as pain or fatigue, is felt or noticed by the person who has it.
Signs and symptoms of cancer depend on where the cancer is, how big it is, and how much it affects nearby organs or tissues. If a cancer has spread , signs or symptoms may appear in different parts of the body.
Causes And Risk Factors
Researchers dont know exactly what causes bladder cancer, but they do know what increases the risk of getting it. These risk factors range from family history to certain types of medication.
Source: Valisure
Data published in 2021 on MedRxiv by researchers from the online pharmacy Valisure and Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center showed patients who took Zantac had elevated diagnosis rates of bladder, breast, prostate and thyroid cancer.
Patients should keep in mind that this data suggests a link between ranitidine and increased risk, but it doesnt prove that all people who take ranitidine will get bladder cancer.
How Long Can Someone Live With Untreated Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer or oral cancer occur in any part of the oral cavity, like the lips, two-thirds of the tongue, the inner lining of the cheeks, gums, hard palate, soft palate, pharynx, and sinuses. This type of cancer is grouped into head and neck type cancers. Oral can be perilous if it is not diagnosed and treated at the early stages. When cancer cells spread to the necks lymph nodes, oral cancer is discovered.
You May Like: How To Strengthen Your Bladder
Tests To Find Bladder Cancer
To find bladder cancer, doctors may run tests to see whether there are certain substancessuch as bloodin the urine. Tests may include:
For patients who have symptoms or have had bladder cancer in the past, newer tests that look for tumor markers in urine may include:
- NMP22 BladderChek®
Researchers dont know yet whether these tests are reliable enough to be used for screening, but they may help find some bladder cancers.
Most doctors recommend a cystoscopy to find bladder cancer, and its often performed without anesthesia. During this procedure, the doctor inserts a long, thin tube with a camera into the urethra to see the inside of the bladder for growths and collect a tissue sample . The tissue is studied in a lab to search for cancer and obtain more information. During a cystoscopy, doctors may also perform a fluorescence cystoscopy, or blue light cystoscopy, inserting a light-activated drug into the bladder and seeing whether any cancer cells glow when they shine a blue light through the tube.
Doctors may also order imaging tests to see whether the cancer has spread. The most common imaging tests include:
Magnetic resonance imaging uses magnets and radio waves to take pictures of the inside of the body. Before the test, a contrast medium is administered orally or by injection to help make the scan clearer.
Ultrasound uses sound waves to take pictures of the inside of the body.
Bladder cancer treatment: The care you need is one call away
Women And Bladder Cancer: Sharing Stories To Advance Research
BCAN was invited to share the experiences of women diagnosed with bladder cancer at the Bladder Cancer in Women: Identifying Research Needs to Improve Diagnosis and Treatment program sponsored by Johns Hopkins Greenberg Bladder Cancer Institute and the American Urological Association Translational Research Collaboration. Each of these womens stories are memorable and unique. Sadly, their stories are repeated around the country because women are not the typical bladder cancer patient. Read the the transcript of their presentation.
Recommended Reading: Symptoms Of Bladder Stones In Cats
What Kind Of Treatment Will I Need
There are many ways to treat bladder cancer. You might want to get a second opinion about the best treatment plan for you.
Bladder cancer is most often treated with:
Sometimes more than one type is used. The treatment plan thats best for you depends on:
- The stage and grade of the cancer
- Whether the cancer has spread into the bladder wall
- The chance that a type of treatment will cure the cancer or help in some way
- Other health problems you have
- Your feelings about the treatment and the side effects that come with it
What Is Renal Ultrasound
Renal ultrasound is the least invasive way to evaluate the kidneys. It does not require radiation and avoids contrast. It may be used in lower risk patients and those with contrast allergies or poor renal function. Unfortunately, it can miss small kidney stones and tumors. Also, it will not detect tumors in the ureter unless they are causing a blockage leading to hydronephrosis.
Don’t Miss: Go Less Bladder Control Side Effects
Stages Of Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer treatment is essential at its early stages. The earlier the mouth cancer is diagnosed and treated, the higher the survival rates after the treatment. There are four stages of oral cancers, as explained below:
In Stage 1, the tumour has not spread to the lymph nodes, and the tumour size is less than or equal to two centimetres.
When the tumour grows between two and four centimetres but has spread to the lymph nodes, it is Stage 2 oral cancer.
In Stage 3, the tumour spreads to one of the lymph nodes, and the size of the tumour grows larger than four centimetres.
When the tumour develops of any larger size and gets spread to the lymph nodes and other surrounding organs, the cancer is of Stage 4.
What To Expect When Having A Ct Scan
A CT scan is a painless procedure that is typically performed on an outpatient basis, taking about 1030 minutes to complete.
The patient may be told not to eat or drink before the test, and a laxative or enema may be used to clear the bowels so the images are clearer. Some CT scans may be performed using special contrast dyes, which may be swallowed as a liquid, delivered intravenously, or administered with an enema. These contrast agents can help improve the quality of the CT image.
For the test, the individual lies on a flat table that slides through the middle of the scanner. Buzzing and clicking noises may be heard within the scanner. During the test, the patient may have to stay still for several minutes or to briefly hold his/her breath.
Read Also: What Can Cause Uncontrollable Bladder
How Is Bladder Cancer Treated
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on
- The stage of cancer.
- If cancer has spread beyond the lining of the bladder.
- The extent of cancer spread.
Treatment options based on tumor grade
- High-grade bladder cancer: High-grade cancers that are life-threatening and spread quickly need to be treated with chemotherapy, radiation or surgery.
- Low-grade cancers: Less aggressive cancers have a low chance of becoming high grade and do not require aggressive treatments, such as radiation or bladder removal.
Treatment options may vary depending on the tumor stage.
Next Steps After Urine Lab Tests
Depending on the results of the patients physical examination and urine laboratory tests, healthcare providers may need to carry out further testing to help make a diagnosis.1,2 The tests can also be used in patients who have already been diagnosed with bladder cancer to help gather more information about the cancer and develop the patients treatment plan.
Don’t Miss: What Does The Start Of A Bladder Infection Feel Like
Living With Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer usually means cancer that is unlikely to be cured. Some people can live for many months or years with advanced cancer. During this time palliative care services can help.
Most people continue to have treatment for advanced cancer as part of palliative care, as it helps manage the cancer and improve their day-to-day lives. Many people think that palliative care is for people who are dying but palliative care is for any stage of advanced cancer. There are doctors, nurses and other people who specialise in palliative care.
Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy or another type of treatment. It can help in these ways:
- slow down how fast the cancer is growing
- shrink the cancer
- help you to live more comfortably by managing symptoms, like pain.
Treatment depends on:
Recommended Reading: Cramping In Bladder Or Uterus
Where Does Bladder Cancer Most Often Spread
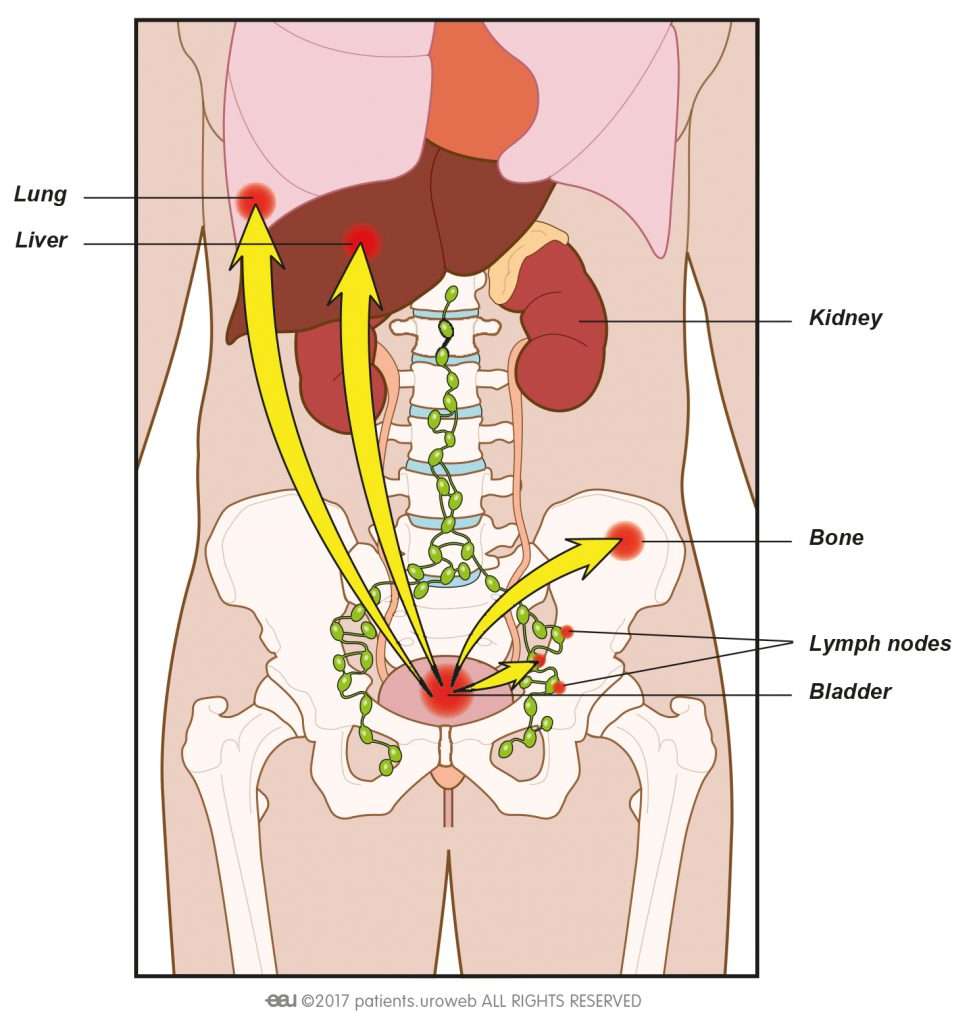
Lymph nodes, bones, lung, liver, and peritoneum are the most common sites of metastasis from bladder cancer. Tumors in a more advanced T category and those with atypical histologic features metastasize earlier. Tumors with atypical histologic features also have a higher frequency of peritoneal metastasis.
Also Check: Bladder Infection Or Kidney Stone
Is Bladder Cancer A Fatal Illness
Left untreated, bladder cancer may spread to other parts of your body. Cancer thats metastasized, or spread, may affect how long youll live with bladder cancer. Like many types of cancer, early detection and treatment increase the chance of living longer with bladder cancer. According to the National Cancer Institute, 96% of people who received treatment for early-stage cancer were alive five years after diagnosis. Overall, 77% of people with bladder cancer were alive five years after diagnosis.
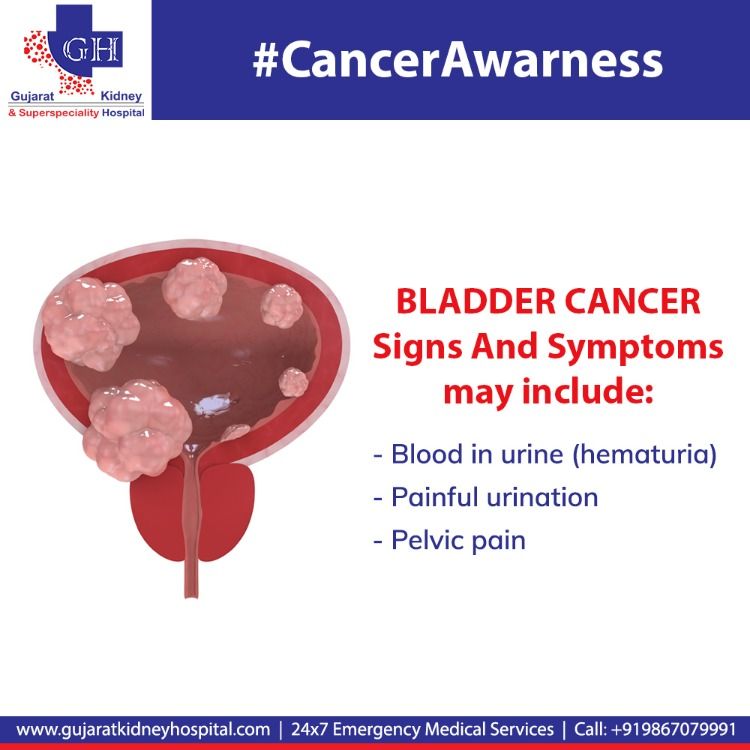
What Are The Signs Of Bladder Cancer
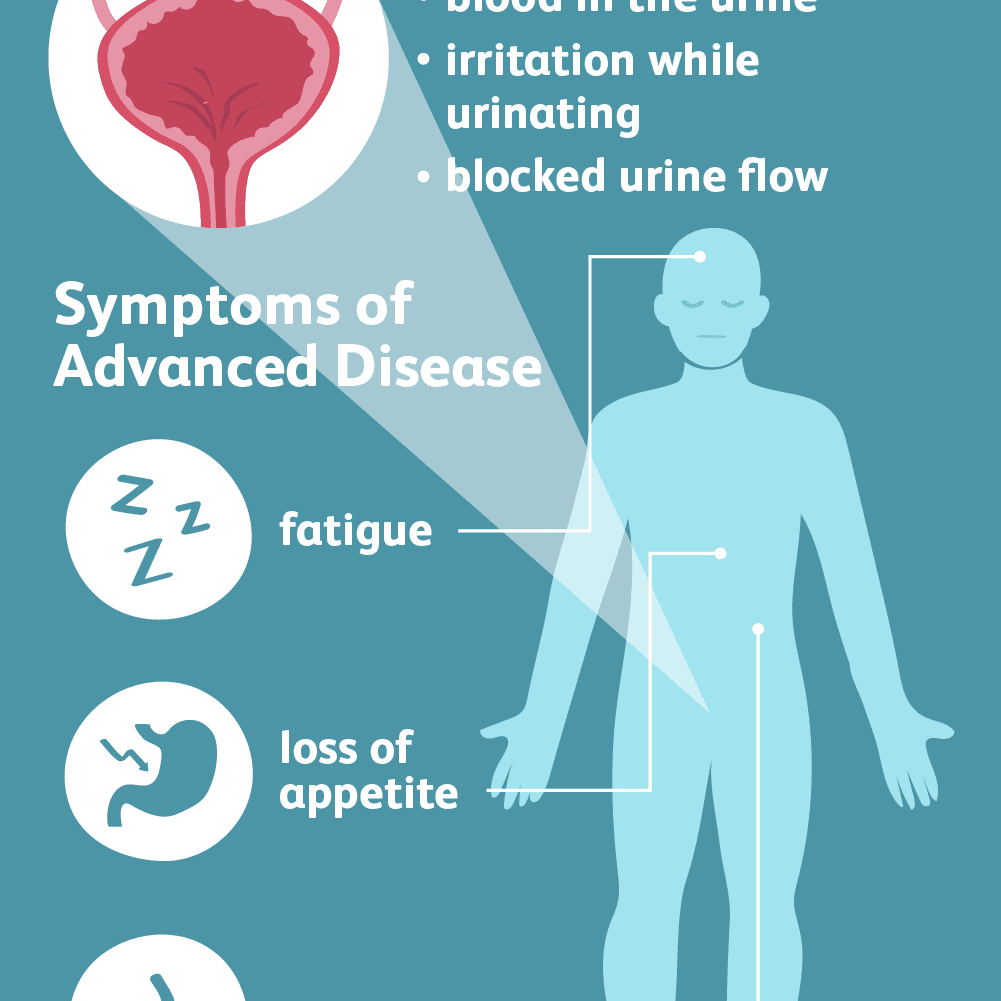
The most common sign of bladder cancer is blood in the urine, called hematuria. Gross hematuria is blood that can be seen in the urine. Your urine can be pink, red, or dark red. In some cases, urine can only be seen with a microscope, called microscopic hematuria. Other signs of bladder cancer include increased frequency of urination, a feeling of urgency to urinate, nocturia , pain with urination, and feeling like your bladder is not empty. These can all be caused by irritation of the bladder wall by the tumor, but can also be signs of infection or other bladder problems.
In advanced cases of bladder cancer, the tumor can stop urine from entering the bladder, or from exiting the bladder. This may cause severe flank pain, infection, and damage to the kidneys. Other signs of advanced bladder cancer are loss of appetite, weight loss, feeling tired, bone pain, and swelling in the feet.
Don’t Miss: Extra Long Bladder Control Pads
Why Is There A Disparity Between Men And Women With Bladder Cancer
In many cases, there are significant delays in diagnosing bladder cancer in women. Many women ignore the most basic symptomblood in the urine. They may associate it with menstruation or menopause and delay reporting this symptom to their doctors. Even after reporting the problem to their doctors, blood in the urine may be initially misdiagnosed. It may be seen as a symptom of post-menopausal bleeding, simple cystitis or a urinary tract infection. As a result, a bladder cancer diagnosis can be overlooked for a year or more.
If A Loved One Declines Treatment
If a loved one decides to forego lung cancer treatment, it can be a difficult, heart-wrenching thing to hear. You may not be able to fully comprehend it at first. In such instances, let your loved one know that you hear them and love them, but that you need a day or two to process the news.
If you do decide you need more information, ask compassionately. Avoid judgmental questions starting with why, and give your loved one time to express themselves fully without interruption or displays of panic or disapproval.
In the end, there will come a time when you need to respect your loved ones decision, however hard that may be. Acceptance will ultimately make you a better caregiver and prepare you emotionally for when your loved one is no longer with you.
Dont Miss: Uti Bladder Infection Kidney Infection
Recommended Reading: Can You Train Your Bladder
Surgery For Bladder Cancer
Surgery is done for most bladder cancers. The type you have depends on the stage of the cancer.
Removing the tumor from the inside bladder is the most common surgery for early bladder cancer. This can be done during a cystoscopy. A a cystoscope with a looped wire on the end is used to remove the tumor.
When the cancer is more invasive, the cancer is removed along with part of the bladder or the entire bladder.
If only part of the bladder is removed, you’ll still be able to hold and release urine as normal, though in smaller amounts. If the entire bladder is removed, you’ll need another way to store and pass urine. Your doctor can explain the options for this.
Side effects of surgery
Any type of surgery can have some risks and side effects. For instance, removing the bladder not only changes how your body passes urine, but it can also cause sexual side effects. If you have these or any other problems, let your doctors know. There are ways to help deal with many side effects.
If Youve Been Diagnosed With Bladder Cancer Seek Out A Team Of Experts
Most people require a combination of therapies to treat bladder cancer successfully. The best plan is different for each person, says Dr. Donat. This customized treatment approach requires the expertise of multiple specialists.
At MSK, most people with bladder cancer meet with a urologic surgeon and medical oncologist as well as a radiation oncologist when needed. This close collaboration helps ensure that MSK patients receive the best care possible. The benefit of MSK is that we bring world-class expertise in each type of treatment to bear for every individual we care for, and we are on the forefront of developing new treatments, says Dr. Donat.
Its also important to know that expert bladder cancer care means not only lifesaving treatments but preserving your quality of life and, if possible, your bladder. We want all of our patients female and male to feel their best after bladder cancer surgery, says Dr. Donat. As surgeons, we do that through a variety of techniques, including minimally invasive approaches and other specialized techniques to preserve or reconstruct the bladder and to maintain sexual function.
Read Also: How To Get Better Bladder Control
How Bladder Cancer Is Diagnosed
There are many tests used for diagnosing bladder cancer. Not all tests described here will be used for every person. Your doctor may consider these factors when choosing a diagnostic test:
-
The type of cancer suspected
-
Your signs and symptoms
-
Your age and general health
-
The results of earlier medical tests
The earlier bladder cancer is found, the better the chance for successful treatment and cure. However, there is not yet a test accurate enough to screen the general population for bladder cancer, so most people are diagnosed with bladder cancer once they have symptoms. As a result, some people have more advanced disease when the cancer is found. Still, most people are usually diagnosed with noninvasive bladder cancer .
The following tests may be used to diagnose and learn more about bladder cancer:
The following imaging tests may be used to find out if the bladder cancer has spread and to help with staging. Imaging tests show pictures of the inside of the body.
After diagnostic tests are done, your doctor will review the results with you. If the diagnosis is cancer, these results also help the doctor describe the cancer. This is called staging and grading.
The next section in this guide is Stages and Grades. It explains the systems doctors use to describe the extent of the disease and the way cancer cells look under a microscope. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
How To Make The Right Treatment Decision
Current expert guidelines for treatment of localized prostate carcinoma recommend potentially curative therapy for patients whose life expectancy is at least 10 years., Patients with limited life expectancy are more likely to die from health conditions other than prostate cancer. Men with a life expectancy of more than 10 years are more likely to die from progressive prostate cancer. This 10-year rule enjoys broad acceptance among urologists and radiation oncologists.,
Conservative management proved to be an acceptable treatment option for men with low-grade Gleason scores, clinically localized disease, and life expectancies of less than 10 years. Increasing age was described as a risk factor for receiving inadequate treatment for prostate cancer. Thus, older men have been shown to receive potentially curative therapy less often than younger men., Radical prostatectomy is preferred treatment in men younger than 70 years, whereas radiation therapy is applied predominantly in patients older than 70 years. Conservative therapy such as watchful waiting or androgen deprivation by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone analogs is preferentially applied in men older than 80 years. Watchful waiting or hormonal therapy is used to treat 82% of men older than 80 years.
Read Also: Does Cialis Shrink The Prostate
Recommended Reading: Foods Good For Bladder Cancer
Radiological Test: What Is A Ct Urogram
The CT urogram is a radiological test to explore possible reasons for blood in the urine or other symptoms. This specialized scan uses intravenous contrast . A CT urogram examines the upper urinary tract in detail.
This test is good at finding tumors of the kidney, renal pelvis, and ureter, as well as other urologic abnormalities. It may identify kidney stones and hydronephrosis . In addition, the entire abdomen and pelvis is also imaged. This allows a radiologist to identify other abnormalities in these parts of the body. In patients with cancer, it will help identify signs of spread to lymph nodes or other organs like the liver.
Your healthcare provider will request blood work to see if you have normal kidney function before you can receive the contrast required for a CT urogram. If the contrast cannot be given, your doctor may decide to perform a CT scan without contrast or other imaging study. A procedure called cystoscopy with retrograde pyelograms may be suggested. The urologist performs x-rays while injecting dye into the ureters. Like a CT urogram, it can help to identify abnormalities of the ureter and renal pelvis.
While some bladder tumors may be found on a CT urogram or other imaging test, others will not. A urologist will often recommend a cystoscopy to evaluate the lower urinary tract for a source of blood in the urine or to workup other urologic symptoms.