What Happens During Bcg Cancer Treatment
Before beginning BCG treatment, local anesthesia is given to numb the area and keep you comfortable. Next, your healthcare provider will place a catheter into your urethra and inject the liquid BCG solution into your bladder.
The BCG solution needs to come in contact with cancer cells to kill them. So, once the medication is injected, your healthcare provider will remove the catheter and ask you to lie on your back, stomach and both sides for 15 minutes each.
When the process is complete, youre free to leave your appointment. However, you should avoid peeing for at least one more hour.
How long do you hold BCG in your bladder?
Once the BCG solution is injected into your bladder, youll hold it for a total of two hours. After this point, youll be able to pee.
What does BCG do to the bladder?
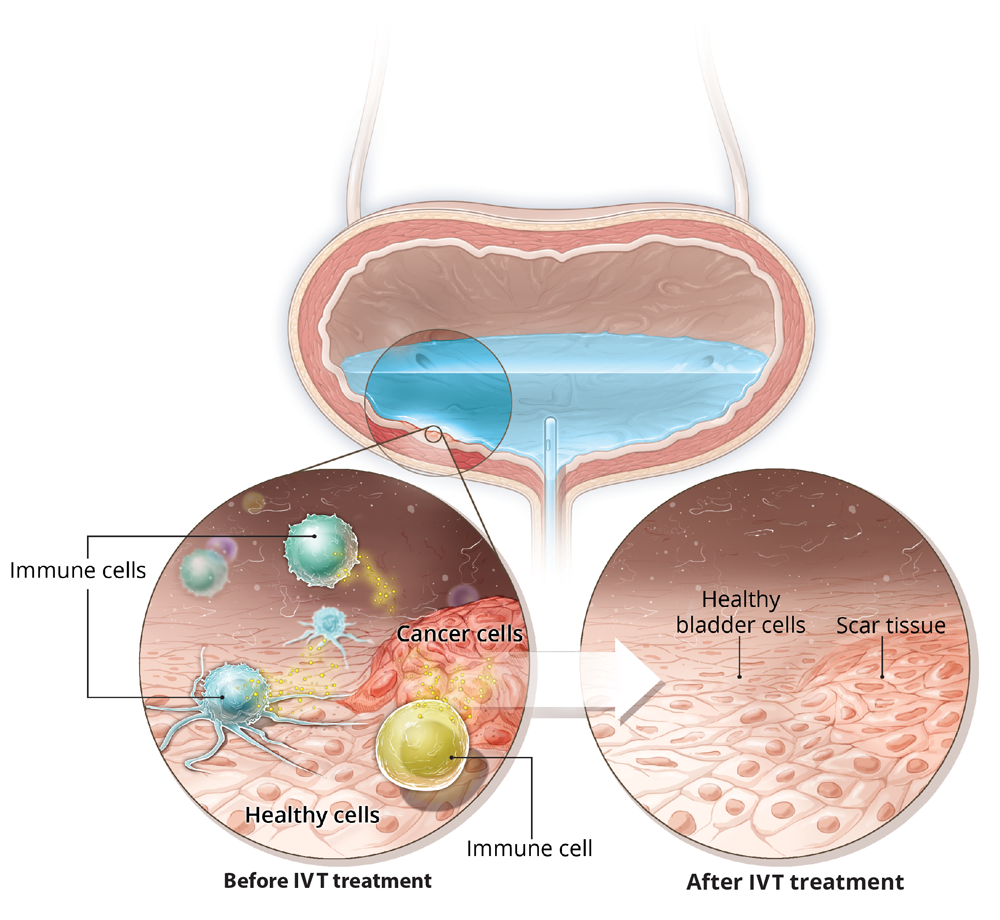
When the BCG solution enters your bladder, your immune system cells begin to attack the cancer cells in your bladder.
BCG treatment schedule
The initial BCG cancer treatment occurs weekly for six weeks. This is called induction therapy.
If the treatment is working, your doctor may prescribe BCG maintenance therapy. Maintenance therapy is given once a week for three weeks at the three-, six- and 12-month marks. For some people, this may be continued up to three years.
Bladder Cancer And Its Symptoms
Bladder cancer is an invasive type of cancer that develops within the bladder. It affects the cells in the bladder and progresses slowly. When the cancerous cells spread to other parts of the body, it is referred to as metastasized bladder cancer.
The symptoms of bladder cancer are often vague or non-existent and so it can be hard to detect or diagnose. The symptoms depend on where the cancer is in the bladder i.e., whether it is contained only in the bladder or it has spread to other parts of the body.
The signs you should look out for include frequent urination, blood in the urine, pressure in your bladder and pain when urinating.
When cancer spreads out of the bladder, it is called metastasis. The most common place for metastasis of bladder cancer is in the bones, lymph nodes, liver and lungs. The symptoms of bladder cancer from its initial stage to the advanced stage include dizziness, difficulty in breathing, rashes, joint pain and in rare cases fever.
Q: Why Is There A Shortage Of Bcg
A. Merck & Co., Inc. is the sole maker and supplier of BCG to the United States. They are also the only source of BCG to many other countries around the world.
Although Merck has boosted its production of BCG by more than 100 percent and is producing the drug to the fullest extent of their manufacturing capacity, they are not able to sustain the increasing global demand of this product. This has led to supply constraints and a BCG shortage.
Recommended Reading: Is High Grade Bladder Cancer Curable
How Should I Prepare For Bcg Treatment For Bladder Cancer
Prior to BCG treatment, your healthcare provider will give you a list of specific guidelines to help you prepare. In general, you should avoid caffeinated beverages and diuretics for four hours before your appointment. When you arrive for your procedure, you should pee to ensure that your bladder is empty.
What Are The Side Effects
Some patients have difficulty completing long-term BCG therapy because of irritation in the bladder.2 To help with this irritation, the treatment frequency may be adjusted to give you a longer break between treatments. You may not notice any reaction after the first few BCG treatments. After the third treatment, patients usually start to experience bladder irritation pain or burning during urination, joint pain, fatigue, and flu-like symptoms that can last a few days. Most symptoms and side effects can be treated with over-the-counter pain medicines.
While BCG is a fairly common treatment for bladder cancer, every person has different experiences. Its important to talk to your doctor about any questions or concerns you may have at any point during your treatment. Being mentally prepared for what to expect can help to reduce stress or uncertainty about treatment or help you think of additional questions for your healthcare team.
Also Check: Best Remedy For Bladder Infection
You May Like: How To Relieve Bladder Infection Pain Fast
Intravesical Therapy For Bladder Cancer
With intravesical therapy, the doctor puts a liquid drug right into your bladder rather than giving it by mouth or injecting it into your blood. The drug is put in through a soft catheter that’s put into your bladder through your urethra. The drug stays in your bladder for up to 2 hours. This way, the drug can affect the cells lining the inside of your bladder without having major effects on other parts of your body.
When You Have It
You usually have BCG into the bladder once a week for 6 weeks. This is called the induction course.
You may then have BCG into the bladder every few weeks or months for the next 1 to 3 years. This will depend on your risk of developing invasive bladder cancer. This is called maintenance BCG therapy.
You usually have treatment at the cancer day clinic.
You May Like: Will Z Pack Cure Bladder Infection
Is Bcg Treatment Contagious To Others
Yes. The drugs used for BCG treatment contain live bacteria, which can be passed to other people. To reduce the risk of contamination, follow these instructions for six hours after every BCG treatment:
- Dont use public toilets.
- Drink lots of fluids to dilute your pee.
- Sit down on the toilet to avoid splashing.
- After you pee, add 2 cups of undiluted bleach to the toilet, close the lid, wait 15 to 20 minutes and then flush.
- If you have urinary incontinence , immediately wash your clothes in a washing machine. Dont wash them with other clothes.
- If you wear an incontinence pad, pour bleach on the pad, allow it to soak in, then place it in a plastic bag and discard it in the trash.
Typically, youll need to refrain from having sex for a few days after each BCG treatment session. In addition, use a condom any time you have sex throughout the entire course of treatment. Ask your healthcare provider about specific guidelines regarding sex.
Prediction Of Bcg Failure
What is the best method for predicting BCG failure? With complex interactions between mycobacteria, a host and a tumour, it is unlikely that one single parameter could be predictive for all patients, regardless of their immunological and tumour background.29 Although host, tumour and immunologic parameters can be useful, no single prognostic factor is capable of predicting a positive response. An excellent review by F. Saint30 adequately summarizes the knowledge on prognostic parameters of remission versus relapse following BCG therapy.
Substaging in T1 NMIBC may also be predictive of BCG failure.33 Van Rhijn, Van der Kwast and colleagues combined patients from Toronto and Rotterdam with primary high-grade NMIBC patients treated with BCG and found that substaging was a very significant predictor of BCG recurrence and progression when separating minimal and extensive pT1 high-grade NMIBC .
You May Like: Feels Like I Have To Pee But Bladder Is Empty
Trending Now: Surgeons Often Take A Fifth Of The Lungs To Remove A Small Tumor There May Be A Better Way
If theres a silver lining to the BCG situation, Fox said, its that theres growing evidence that smaller doses show efficacy in battling bladder cancers.
Indeed, to help prolong the supply of BCG, most urologists wind up dividing the dosage into thirds. There are studies, actually, that suggest that these lower doses are similarly effective in treating bladder cancer.
The Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network, a Maryland-based patient advocacy group, along with the American Urological Association and several other physician groups, have come up with treatment guidelines to help navigate the shortage. The suggestions include dividing up doses, and stopping maintenance therapy entirely, as was the case with Fields.
Dr. Karim Chamie, an associate professor of urology at University of California, Los Angeles, said the BCG shortage hasnt affected his practice just yet. But although the stockpile of BCG at UCLA is still in good shape, Chamie projects that will soon change.
Urologists in the community have already hit a shortage, and theyre referring their patients to me, Chamie said. So my clinics clogging up with patients who need BCG and they may be using some of the BCG I might have given someone else.
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
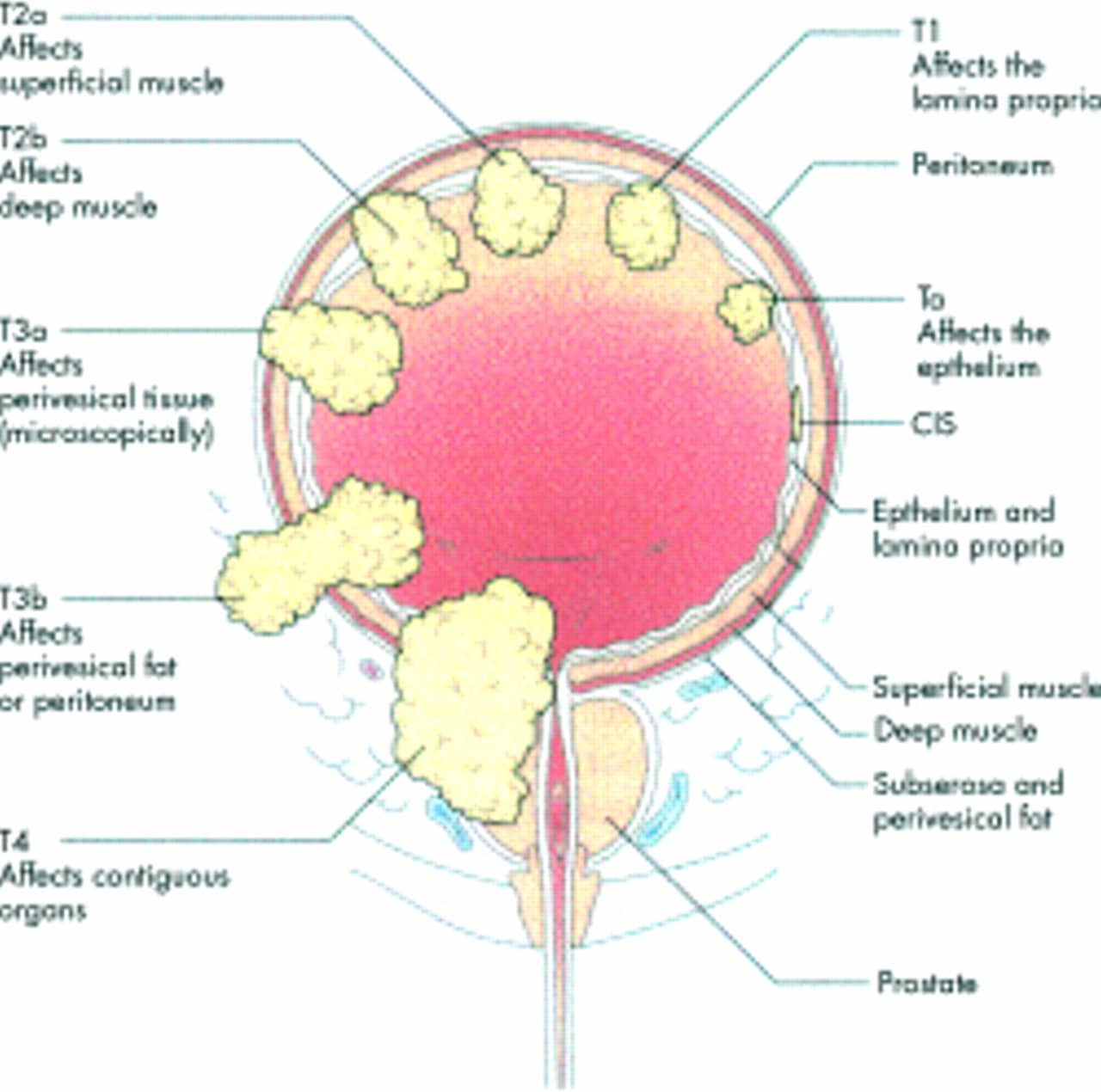
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
Also Check: Overactive Bladder After Prostate Surgery
Adverse Effects Of Bcg
Common adverse effects include cystitis, dysuria, malaise, fatigue, and a low fever . These can be managed by NSAIDS, phenazopyridine, and anticholinergics. If symptoms become intense or last longer than 24 hours, consider either delaying additional instillations until symptoms improve or reducing the dose.
In a review including 2602 patients treated with intravesical BCG instillation , the most common side effects were fever > 103ºF, hematuria, granulomatous prostatitis, pneumonitis and/or hepatitis, arthralgia, epididymitis, sepsis, rash, ureteral obstruction, bladder contracture, renal abscess, and cytopenia.
Early-onset BCG infection often presents as systemic manifestations. In contrast, delayed-onset infection presents as localized disease. Manifestations are as follows:
- Systemic manifestations occur when BCG disseminates outside of the genitourinary tract. They include sepsis syndrome, pulmonary issues from dyspnea, granulomatous hepatitis, osteomyelitis, reactive arthritis, monoarthritis, psoas abscess, and vascular complications due to mycotic aneurysms.
- Localized manifestations include cystitis, bladder contracture, granulomatous prostatitis, prostate abscess, epididymo-orchitis, testicular abscess, pyelonephritis, renal abscess, urethral stricture, and balanitis.
The AUA has noted the following with regard to BCG2:
Contributor Information and Disclosures
Fellow in Urologic Oncology and Minimally Invasive Surgery, University of Chicago Medical Center
What Happens During Treatment
A urinary catheter is inserted through your urethra and into your bladder. Then the BCG solution is injected into the catheter. The catheter is clamped off so the solution stays in your bladder. Some doctors may remove the catheter at this time.
You have to hold the medicine in your bladder. Youll be instructed to lie on your back and to roll from side to side to make sure the solution reaches your entire bladder.
After about two hours, the catheter is unclamped so the fluid can be drained. If the catheter was already removed, youll be asked to empty your bladder at this time.
Also Check: Wellmate Pressure Tank Bladder Replacement
When To See A Doctor
There are a few side effects that can be especially dangerous, so make sure to talk to your doctor if you notice that you:
- Have a severe skin rash
- Are wheezing or having difficulty breathing
- Are finding swallowing to be difficult
- Have a high fever that isnt lowered with Tylenol or other over-the-counter fever reducers
Q: How Is Merck Determining How Much Bcg Each Physician Office In The United States Will Receive During This Shortage
A. As the sole supplier of BCG to the United States, Merck is allocating the quantity of available supply across states based on historical demand.
To minimize disruption to patient care, in January, Merck announced an immediate change to their BCG distribution model, and began allocating BCG exclusively to wholesalers and distributors based on product supply and historical purchasing patterns of physicians and hospitals. Wholesalers and distributors in turn, began utilizing the same allocation model to fulfill physician and hospital orders directly.
Read Also: Reasons For Lack Of Bladder Control
Practical Issues Of Bcg Administration
Some practical points need to be considered when using BCG for bladder cancer treatment. BCG manufacturers recommend evaluating the tuberculosis status of the patient with a PPD tuberculosis skin test before initiation of therapy, with some practitioners obtaining chest radiographs in all patients. This procedure has never proven necessary, probably owing to the exceedingly low incidence of tuberculosis in developed nations, where most bladder cancer patients do not meet the criteria for disease screening as recommended by the Centers of Disease Control and Prevention. In fact, patients with a positive PPD test without active disease should not be excluded from BCG therapy, as the presence of a systemic immune response might help augment the antitumour response as noted above. In addition, patients with a positive PPD result were shown to display adverse effect profiles during BCG treatment that are similar to patients with a negative test.
Is Bcg Treatment Contagious
Because BCG contains live bacteria, precautions are necessary to prevent it from being passed to others.
Patients should go to the bathroom sitting down to reduce splashing and wash their hands thoroughly after urinating. Pouring bleach into the toilet after use may also prevent contamination.
Once home, a patient should drink plenty of liquids and avoid sexual contact with others for 24 hours.
Research has shown that BCG may also reduce the risk of contracting a respiratory tract infection, giving your immune system a boost. However, precautions are still necessary to stay healthy.
The care team will talk to the patient about what to expect and provide instructions to follow at home.
Don’t Miss: How To Get Rid Of A Bladder Infection Quickly
Mechanism Of Action Of Bcg
The mechanism of action of bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy is incompletely understood. Some early studies purported that an immune response against BCG surface antigens cross-reacted with putative bladder tumor antigens, and this was proposed as the mechanism for the therapeutic effect of BCG however, multiple subsequent studies refute this claim.
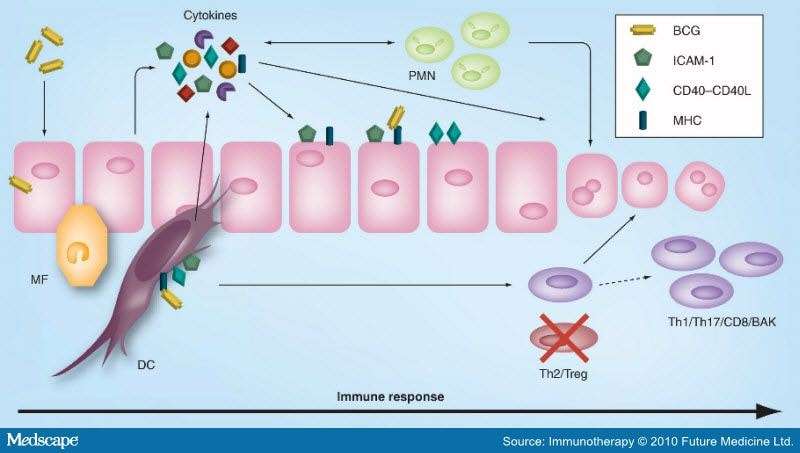
The most likely mechanism of action of BCG immunotherapy involves a combination of its direct effect on tumor cells along with the patients immune response to the therapy. These effects are summarized by Kawai et al into three categories: infection of cancer cells, induction of immune response, and antitumor effects.
The infection of cancer cells is mediated by the glycoprotein fibronectin, which allows the internalization of BCG, breakdown of proteins, and cellular changes that trigger the immune system. This is similar to the immunologic reaction that occurs in patients with tuberculosis. This immune response comprises specific cellular changes including surface receptor changes and release of various cytokines. Interferon is considered to be an important part of this process and has been used in the past to determine appropriate response to treatment. The immune response crescendos to antitumor activity in which cells recognize the cancer cells, target them for destruction, and subsequently decrease cancer burden.
The overall response to BCG is limited if the patient is immunosuppressed.
Physical Emotional And Social Effects Of Cancer
Cancer and its treatment cause physical symptoms and side effects, as well as emotional, social, and financial effects. Managing all of these effects is called palliative care or supportive care. It is an important part of your care that is included along with treatments intended to slow, stop, or eliminate the cancer.
Palliative care focuses on improving how you feel during treatment by managing symptoms and supporting patients and their families with other, non-medical needs. Any person, regardless of age or type and stage of cancer, may receive this type of care. And it often works best when it is started right after an advanced cancer diagnosis. People who receive palliative care along with treatment for the cancer often have less severe symptoms, better quality of life, and report that they are more satisfied with treatment.
Palliative treatments vary widely and often include medication, nutritional changes, relaxation techniques, emotional and spiritual support, and other therapies. You may also receive palliative treatments similar to those meant to get rid of the cancer, such as chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Learn more about the importance of tracking side effects in another part of this guide. Learn more about palliative care in a separate section of this website.
Read Also: Gemcitabine Bladder Instillation Side Effects
How You Have It
BCG is a liquid. Your doctor or nurse puts the liquid into your bladder through a tube in the urethra . Usually, they then remove the catheter.
You must not pass urine for 2 hours. This gives the BCG time to be in contact with the lining of the bladder. Some hospitals may ask you to change position every now and again to make sure the drug reaches all parts of your bladder lining.
When you do pass urine, you need to be careful for 6 hours after the treatment because the vaccine contains bacteria. Men should sit down to pass urine to reduce the chance of splashing.
After you’ve been to the toilet, pour about half a pint of neat bleach into the toilet bowl and leave it for 15 minutes before flushing.
Wash your hands and genitals immediately with warm soapy water after you pass urine.
Catheterizable Continent Diversion Pouch
This is a reservoir of bowel with a stoma that is catheterizable for emptying the bladder. The urine is siphoned out of the urinary reservoir with a small catheter every four to six hours. The catheterizable pouch may require surgical repair at some point after surgery due to the wear and tear of frequent catheterization. This type of reconstruction is not performed on patients with a history of bowel disease.
Recommended Reading: Erectile Dysfunction After Bladder Removal
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when it’s first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.