Sexual Effects Of Radical Cystectomy In Men
After surgery, many men have nerve damage that affects their ability to have erections. In some men this may improve over time. For the most part, the younger a man is, the more likely he is to regain the ability to have full erections. If this issue is important to you, discuss it with your doctor before surgery. Newer surgical techniques may help lower the chance of erection problems.
For more on sexual issues and ways to cope with them, see Sex and the Man With Cancer.
What Is The Outlook For Someone Who Has Had Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection
Bladder tumor biopsy and resection is a successful treatment for early stage bladder cancer. It can prevent cancer from spreading into the bladder muscle wall. Invasive bladder cancers that spread require more extensive treatment.
However, bladder cancer often comes back . More TURBT procedures may be needed. Your doctor will do frequent follow-up checkups with you to look for signs that the cancer has returned. The risks of repeated TURBT procedures is small.
Some providers might choose to burn off smaller tumors rather than remove them.
If the TURBT shows that you have a more advanced bladder cancer, youll probably need further treatment. This could include:
- A more extensive TURBT.
- Surgery to remove the tumor.
- Surgery to remove the bladder.
- Bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy or BCG. This is a type of therapy that uses the bodys own immune system to fight the cancer.
Your urologist and pathologist will determine the best course of treatment based on the staging of the tumor and your personal medical history. TURBT can help in staging the cancer by determining if the cancer has invaded the bladder wall. Staging refers to determining how serious the cancer is.
What Are The Advantages Of Transurethral Resection Of The Prostate
Benefits of TURP include:
- Fast results: Most people notice an improvement in their urinary symptoms within a few days.
- Treats severe BPH symptoms: TURP may be helpful if you have moderate to severe urinary problems from BPH and medications havent worked. Your healthcare provider may also recommend TURP if you have kidney stones, bladder stones or kidney damage from BPH.
You May Like: Foods To Help Bladder Infection
Patient Recruitment Inclusion Criteria Exclusion Criteria And Study Design
Fig. 1
Design of the FLEBER study: inclusion criteria and endpoints. Patients should fulfill the indicated inclusion criteria to be eligible for this trial. *Hemoglobin, 9.0g/dL white blood cell count, 12,000/mm3 absolute neutrophil count, 2000 cells/mm3 platelet count, 100,000 cells/mm3 normal kidney and liver functions as determined by creatinine, total bilirubin, aspartate transaminase , and alanine transaminase 2× the upper limit of normal for the reference laboratory. Abbreviations: PDD, photodynamic diagnosis TURBT, transurethral resection of bladder tumor ECOG-PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group-Performance Status CIS, carcinoma in situ BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin
Patients with tumors less than 6mm in diameter will be excluded from this trial because small tumors can be resected with a single cut using a standard loop electrode. In addition, patients with tumors more than 30mm in diameter will be excluded because large tumors cannot be removed en bloc from the bladder using a 28-Fr TUR resectoscope sheath. Patients who are suspected of having carcinoma in situ will be excluded because these patients will have to be treated using intravesical Bacillus Calmette-Guérin postoperatively, and the carcinoma cannot be resected completely using EBTUR.
Monopolar Versus Bipolar Electrocautery

Both bipolar and monopolar electrocautery can be used for transurethral resection of bladder tumors. A recent study retroactively compared monopolar versus bipolar TURBT. The study examined perioperative complications in monopolar versus bipolar TURBT. They found that bipolar TURBT was associated with a lower incidence of bladder injury, with slightly shorter postoperative length of hospitalization and lower costs. In contrast, Venkatramani and colleagues found that bipolar transurethral resection was not superior to monopolar with regard to obturator reflex, bladder perforation, or hemostasis. However, other authors have reached the opposite conclusion.
Dont Miss: Do You Need Antibiotics For Bladder Infection
You May Like: Black And Yellow Antibiotic For Bladder Infection
Transurethral Resection Of The Bladder Tumor: Standard Technique And New Advancements
Urology Times Urologists in Cancer Care
Improvement in imaging modalities may help in performance of transurethral resection of the bladder tumor.
Since it was first described in 1910, transurethral resection of bladder tumor has evolved into the cornerstone of bladder cancer diagnosis and staging, and is one of the most common surgeries urologists perform. Following the introduction of video endoscopy in the late 1970s, TURBT has been characterized as a relatively simple procedure, often performed by junior residents in the academic setting. More recent data emphasize the importance of high-quality TURBT by experienced surgeons in order to improve patient outcomes.1 Significant variation in recurrence rates among urologists has been described, supporting the assumption that experienced technical skill matters. At our institution, junior residents slowly gain more responsibility as their technical skills develop under the close supervision of an experienced surgeon with a low threshold to take over the case when accurate staging may be difficult to obtain. Below, we discuss our standard technique for TURBT and describe new advancements that may help standardize outcomes in a procedure that has experienced little evolution during the past century.
TURBT technique
Although postoperative continuous irrigation has been associated with lower recurrence rates, we typically avoid this in our patients because of concern for inducing or worsening bladder perforation.8
References
Guidelines For Use Of Turbt
The guidelines are in agreement that the final diagnosis of bladder cancer is based on cystoscopic examination and bladder tumor histology. The guidelines further agree that all visible lesions should be resected during TURBT with bimanual examination under anesthesia and that adequate sampling is required for proper tumor identification and staging. Lastly, imaging of the upper urinary tracts should be evaluated to assess for concomitant disease involvement.
The AUA/SUO recommendations for repeat TURBT are as follow :
- In patients with incomplete initial resection, repeat TURBT if technically feasible.
- For high-risk, high-grade Ta tumors, consider performing repeat TURBT of the primary tumor site within 6 weeks of initial TURBT.
- In T1 disease, repeat TURBT of the primary tumor site, including muscularis propria, within 6 weeks of initial TURBT.
EUA guidelines recommend performing a second TURBT 2-6 weeks after the initial resection in any of the following situations :
- After incomplete initial TURBT
- If there is no muscle in the specimen after initial resection, with exception of Ta low-grade tumors and, possibly, completely resected primary CIS
- In all T1 tumors
- In all high-grade tumors, except primary CIS however, it may be beneficial to attempt to resect all CIS lesions at repeat TURBT
The NCCN recommends TURBT as standard treatment for low-grade Ta NMIBC.
For treatment of T1 tumors NCCN recommends repeat TURBT.
- Smaller solitary tumors
Recommended Reading: Can You Live Without A Bladder
What Is Transurethral Resection Of The Prostate
Transurethral resection of the prostate, also called TURP, is surgery to remove part of your prostate gland. Your prostate gland is only found in men and people assigned male at birth , and wraps around your urethra . If your prostate gets too large, it can interfere with urination.
During TURP, your healthcare provider inserts a thin tool into your urethra. This tool has an electric current or laser that allows them to remove part of your prostate. Because the tool goes in through your urethra, you dont have any incisions.
Preoperative Details Of Turbt
Patients will undergo pre-anesthesia testing in order to evaluate physical condition and medical conditions. As antithrombotic therapy has become more prevalent, the decision whether to hold anticoagulants or antiplatelet agents is a commonly discussed topic. While there are no guidelines to follow regarding the perioperative management of these medications, it is an often-debated balance between adverse cardiovascular events and persistent perioperative hematuria. While low-dose aspirin can be continued in most cases, all other antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are almost always held perioperatively, with the duration and plan for resumption made on a case-by-case basis.
Patients scheduled for anesthetic cystoscopy with TURBT must have sterile urine documented prior to instrumentation. Sterility is usually presumed on the basis of a microscopic urinalysis showing no bacteria or white blood cells . Patients with a positive urine culture are conventionally treated with a course of culture-specific antibiotics to achieve this desired sterility.
Also Check: Is Bladder Cancer Fast Growing
How Is Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection Performed
You may have general anesthesia for this procedure, which means youll be asleep for it. Some providers might use regional anesthesia, which means youll be awake. However, you wont feel any pain.
Bladder tumor biopsy and resection is performed when a doctor inserts a rigid instrument called a resectoscope into the bladder through the urethra. Inserting the resectoscope in this way means that no incisions are necessary.
Your provider will use the resectoscope to remove the tumor, which will be sent to a pathology lab for testing. Once the tumor is removed, your doctor will attempt to destroy any remaining cancer cells by burning the area using electric current by a process called fulguration or cauterization.
Your provider may decide to insert some type of chemotherapy medicine into the bladder using the scope. This is called intravesical chemotherapy. Your provider might suggest that you have maintenance intravesical chemotherapy for a period of time, meaning that you’ll have regular treatments.
Transurethral Resection Of Bladder Tumor
A transurethral resection of bladder tumor or a transurethral resection is often used to find out if someone has bladder cancer and, if so, whether the cancer has spread into the muscle layer of the bladder wall.
TURBT is also the most common treatment for early-stage or superficial bladder cancers. Most patients have superficial cancer when they’re first diagnosed, so this is usually their first treatment. Sometimes, a second, more extensive TURBT is done to better ensure that all the cancer has been removed. The goal is to take out the cancer cells and nearby tissues down to the muscle layer of the bladder wall.
Recommended Reading: Bladder Infection After C Section
What Is A Turbt
Generally, after the diagnosis of a bladder tumor, the urologist will suggest that the patient have an outpatient surgical procedure in the hospital. The doctor may refer to this procedure as a TURBT . The TURBT will allow the doctor to examine the bladder more completely under anesthesia . To see inside the bladder, they use a resectoscope. Like the cystoscope, the resectoscope is introduced through the urethra into the bladder.
This tool has a small electrified loop of wire at the end that can resect a tumor. The loop also cauterizes the blood vessels to help stop any bleeding. This is sometimes called electrocauterization or fulguration. One of the advantages of this procedure is that it can be performed repeatedly with minimal risk to the patient and with excellent results. There is less than a 10% risk of infection or injury to the bladder, and both are easily correctable.
Who Performs This Procedure And Where Is It Performed

Transurethral bladder resections are usually performed in a hospital by a urologist, a medical doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the urinary systems in men and women and also treats structural problems and tumors or stones in the urinary system. Urologists can prescribe medications and perform surgery. If a transurethral bladder resection is required by a female patient, and there are complicating factors, an urogynecologist may perform the surgery. Uro-gynecologists treat urinary problems involving the female reproductive system.
predict exactly what will happen in every case these numbers provide an overall picture.
Mortality rates are two to three times higher for men than women. Although the incidence of bladder cancer in the white population exceeds those of the black population, black women die from the disease at a greater rate. This is due to a larger proportion of these cancers being diagnosed and treated at an earlier stage in the white population. The mortality rates for Hispanic and Asian men and women are only about one-half those for whites and blacks. Over the past 30 years, the age-adjusted mortality rate has decreased in both races and genders. This may be due to earlier diagnosis, better therapy, or both.
You May Like: Muscle Spasm In Bladder Area
Trans Urethral Removal Of Bladder Tumour
A trans urethral resection of bladder tumour is usually the first treatment you have for non muscle invasive bladder cancer.
Your surgeon removes the tumour in your bladder through the urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of your body.
The surgeon puts a thin rigid tube called a cystoscope into your urethra. The cystoscope has optic fibres inside it, a light, camera and eyepiece at one end. The surgeon can look through the eyepiece or see images on a TV screen.
The surgeon passes small instruments down the cystoscope to cut any tumours out of your bladder lining.
Taking A Biopsy During A Turbt Procedure
When it is used to help diagnose bladder cancer, the TURBT procedure may involve taking small tissue samples from the area with abnormal cells or removing all of the tissue that contains abnormal cells. The urologist may also take samples from other parts of the bladder lining to check for cancer cells.
The biopsied tissue is then sent to the lab where it is analyzed to see if it contains cancer cells. Small samples of muscle from the walls of the bladder near the area of abnormal cells may also be taken for analysis, to see if it contains cancer cells that have grown into the muscle.
Recommended Reading: How To Improve Bladder Capacity
Recommended Reading: Bladder Outlet Obstruction In Females
Tumours On The Lateral And Anterior Walls
Resection of lateral wall tumours may result in stimulation of ONR resulting in increased risk of perforation . Strategies that have been shown to reduce the likelihood of ONR would include avoidance of bladder overfilling, reduced cutting current, use of short intermittent burst current , use of bipolar electrocautery, and use of neuromuscular blockade .
Tumours on the anterior wall could be challenging to resect and may require suprapubic depression by an assistant as well as proper resectoscope angles. More effective resection might be achieved by using open-angled loops.
You May Like: Can A Bladder Infection Heal Itself
What Happens After Transurethral Resection Of The Prostate
After your procedure is done, you go to a recovery area. Some people stay in the hospital for one to two days after TURP, others might be discharged the same day.
During your hospital stay, you have a catheter in your urethra. The catheter helps ensure that urine flows freely after your surgery. Usually, your healthcare provider removes the catheter before you go home.
Recommended Reading: Can Hernia Mesh Cause Bladder Problems
A Single Immediate Postoperative Intravesical Instillation Of Chemotherapy
All participants will undergo IPIC unless bladder perforation occurs or is suspected during TUR. Within 24h postoperatively, one intravesical instillation of 60mg of epirubicin in 30ml of saline will be administered. The catheter will be clamped and left for 1h, and subsequently unclamped. The patients who do not undergo IPIC will be excluded from the analysis of primary endpoint, but included in the analysis of secondary endpoints.
How Well It Works
This surgery may be done to find out if a bladder tumour is cancer. If the tumour is cancer, removing it is the most common and effective treatment for early-stage bladder cancer. It may also be effective for more advanced cancer if all the cancer is removed and biopsies show that no cancer remains.
You May Like: Painful Bladder Syndrome Bladder Training
Intraoperative Details Of Turbt
In most cases, general or regional anesthesia must be used to establish nerve paralysis, to minimize risk of obturator nerve reflex and subsequently, bladder perforation.
Complete eradication of tumor is the first step in TURBT. Most tumors are papillary and are easily removed by endoscopically transecting their narrow stalk or base. Following this, biopsy of the base or deeper resection is performed to ensure complete removal and the absence of invasion. The goal is that muscle tissue must is present in the base biopsy specimen to ensure accurate staging.
Medium and large tumors are resected in a controlled serial fashion prior to transection of the stalk. This ensures that large segments do not remain that might be too large to evacuate through the resectoscope.
Smaller and more friable tumors may be removed at least partially by knocking off fragments with the cutting loop of the resectoscope without the electricity turned on. This sometimes allows partial removal with less risk of bladder perforation.
Pulling the cutting loop away from the tumor is generally much safer than pushing it toward the tumor. Lifting the tumor away from the surrounding normal bladder tissue using the cutting loop is also advisable.
Transurethral resection syndrome, which results from absorption of electrolyte-free irrigating fluid, has become uncommon since the advent of bipolar resectoscopes, which utilize normal saline irrigation.
How Turbt Is Done
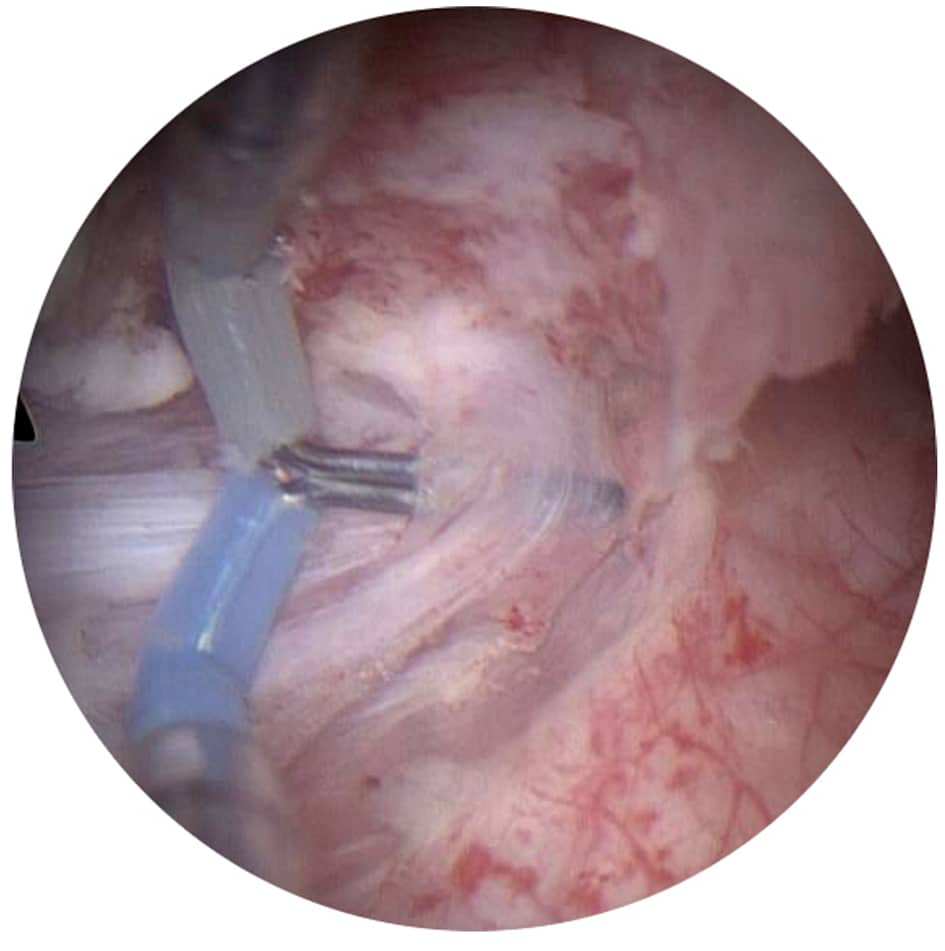
This surgery is done using an instrument put in through your urethra, so theres no cutting into the abdomen . Youll get either general anesthesia or regional anesthesia .
A type of thin, rigid cystoscope called a resectoscopeis put into your bladder through your urethra. The resectoscope has a wire loop at the end thats used to remove any abnormal tissues or tumors. The removed tissue is sent to a lab for testing.
After the tumor is removed, more steps may be taken to try to ensure that the cancer has been completely destroyed. For instance, the tissue in the area where the tumor was may be burned while looking at it with the resectoscope. This is called fulguration. Cancer cells can also be destroyed using a high-energy laser through the resectoscope.
Read Also: Medications That Cause Overactive Bladder
You May Like: Can Being Constipated Affect Your Bladder