Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
There are some things that can make you more likely to develop bladder cancer. These are called risk factors and they include:
- smoking chemicals in cigarettes can cause bladder cancer, so if you smoke, your risk is up to 3 times that of a non-smoker
- age most people with bladder cancer are over 60 years of age
- being male men are around 3 times more likely than women to develop bladder cancer
- chemicals being in contact with certain chemicals for a long period of time, like aromatic amines, benzene products and aniline dyes, which have been linked to bladder cancer
- chronic infections frequent infections of the bladder over a long period of time
- previous cancer treatments some types of radiation therapy around the pelvis, and the chemotherapy drug cyclophosphamide
- family history a first degree relative with bladder cancer increases risk up to nearly 2 times higher than the general population.
Having these risk factors doesnt mean you will develop bladder cancer. Often there is no clear reason for getting bladder cancer. If you are worried about your risk factors, ask your doctor for advice.
Cancer Survival Rates Dont Inform The Whole Story
Survival rates are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of individuals who had the disease, but they cannot anticipate exactly what will take place in any particular persons case. There are a variety of limitations to keep in mind:
- The numbers below are among the most existing readily available. However to obtain 5-year survival rates, doctors have to look at individuals who were alleviated at least 5 years ago. As treatments are enhancing in time, people who are now being detected with bladder cancer might have a much better outlook than these data reveal.
- These data are based on the stage of the cancer when it was first identified. They do not apply to cancers that later on returned or spread, for example.
- The outlook for people with bladder cancer varies by the stage of the cancer in general, the survival rates are greater for people with earlier phase cancers. But many other aspects can impact an individuals outlook, such as age and general health, and how well the cancer reacts to treatment. The outlook for each person is specific to their conditions.
Your physician can tell you how these numbers may use to you, as she or he recognizes with your certain scenario.
Occurrence In The United States
The American Cancer Society estimates that 81,180 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2022 and that 17,100 people will die of the disease. The incidence of bladder cancer increases with age, with the median age at diagnosis being 73 years bladder cancer is rarely diagnosed before age 40 years.
Bladder cancer is about 4 times more common in men than in women. The male predominance in bladder cancer in the United States reflects the prevalence of transitional cell carcinoma . With small cell carcinomain contrast to TCCthe male-to-female incidence ratio is 1:2.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men in the United States, after prostate, lung, and colorectal cancer, but it is not among the top 10 cancers in women. Accordingly, more men than women are expected to die of bladder cancer in 2022, with 12,120 deaths in men versus 4980 in women. Nevertheless, women generally have a worse prognosis than men.
The incidence of bladder cancer is twice as high in White men as in Black men in the United States. However, Blacks have a worse prognosis than Whites.
Limited data indicate that small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder probably has the same epidemiologic characteristics as urothelial carcinoma. Patients are more likely to be male and older than 50 years.
Also Check: What Can Cause Bladder Inflammation
How Is Bladder Cancer Treated
Treatment for bladder cancer depends on
- The stage of cancer.
- If cancer has spread beyond the lining of the bladder.
- The extent of cancer spread.
Treatment options based on tumor grade
- High-grade bladder cancer: High-grade cancers that are life-threatening and spread quickly need to be treated with chemotherapy, radiation or surgery.
- Low-grade cancers: Less aggressive cancers have a low chance of becoming high grade and do not require aggressive treatments, such as radiation or bladder removal.
Treatment options may vary depending on the tumor stage.
What Is The Five Year Survival Rate For Bladder Cancer
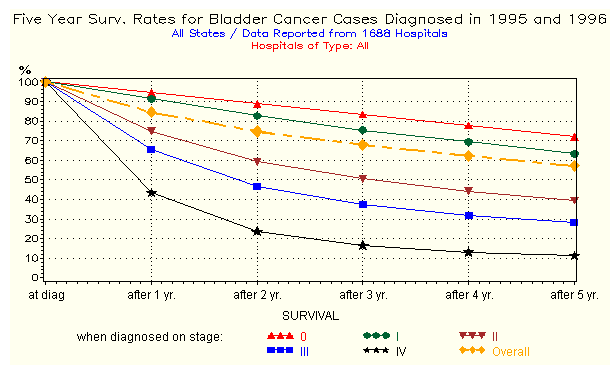
A five-year survival rate is the percentage of people in a study or treatment group who are alive five years after they were diagnosed with or started treatment for a disease such as bladder cancer. Their disease may or may not have recurred during that time.
The American Cancer Society periodically reports on the five-year survival rate for bladder cancer. The most recently period studied was from 2010 to 2016 and that rate was 77%. This means that from the time of diagnosis, 77 out of 100 people diagnosed with bladder cancer were alive in five years. From 1987 1989 , the five-year survival rate was 79% and from 1975 1977, it was 72%. The survival rates are not the same for everyone, however.
Don’t Miss: Interstim Implant For Bladder Control
Chemotherapy In Palliative Care
Many patients with bladder cancer present with distant metastases at diagnosis or develop metastatic disease during the course of their illness. The survival time for patients with untreated metastatic bladder cancer is usually less than 6 months, and a variety of disabling symptoms can develop during this interval that disrupt quality of life.180,181 Chemotherapy may be effective in ameliorating these symptoms.
Other regimens comprising active agents with nonoverlapping toxic effects are being investigated with the aim of enhancing the therapeutic ratio. They include combinations of cisplatin with gemcitabine or paclitaxel.181 An update of a large international randomized study that compared M-VAC with gemcitabine plus cisplatin for patients with metastatic bladder cancer186,187 revealed no differences in response rate, survival rate, or quality of life between the treatment groups. However, gemcitabine plus cisplatin was significantly less toxic more patients completed the full course of treatment, fewer had significant neutropenia or sepsis, and the rate of death from side effects was lower. These findings have led to gemcitabine plus cisplatin becoming the standard of care for patients with metastatic bladder cancer.181
Bin S. Teh MD, … Arnold C. Paulino MD, in, 2008
How Does Recurrence Of Bladder Cancer Affect Survival Rate
Recurrent bladder cancer is cancer that has returned after initial treatment. Recurrence rates for bladder cancer depend on the stage of the original tumor, with 5-year recurrence rates of approximately 65% in patients with non-invasive or in situ tumors and 73% in patients with slightly more advanced disease at first diagnosis.16
Many patients with non-invasive bladder cancer have recurrences that are typically not life threatening however, the prognosis is generally worse if the disease has spread into deeper layers of the bladder wall or beyond to the lymph nodes or other organs.
You May Like: Blood In Urine Female Bladder Infection
Case : Metastatic Bladder Cancer To Adrenal Gland/liver/lung
A 56-year-old man with bladder cancer was initially treated with radical cystectomy followed by chemotherapy. Follow-up scan including a PET-CT showed an isolated area with high uptake in his left adrenal gland consistent with recurrent metastatic bladder cancer. He was also having side effects from systemic chemotherapy and needed a break. He was referred for consideration of SBRT to his isolated recurrence after surgery and chemotherapy. He was simulated in the supine position in an immobilization device. PET-CT images were co-registered with simulation CT images. Target delineation was performed by the radiation oncologist and the nuclear medicine radiologist. Tumor motion data from 4D-CT dataset were used to plan PTV. SBRT with daily image-guidance approach was taken whereby the metastatic tumor was prescribed 30 Gy in 5 fractions . Rapid fall off was achieved with the treatment plan to for conformal avoidance of small bowels and kidney . Follow-up imaging showed decrease in the adrenal mass.
Ho Kyung Seo, ⦠Sung Han Kim, in, 2018
Bladder Instillation Of Chemotherapy
Instillation of chemotherapy drugs into the bladder can reduce the incidence of superficial cancer recurrences, but no single drug has been confirmed to reduce progression of superficial cancer to invasive bladder cancer. This means that multiple small new cancers can be prevented, but progression to a more invasive bladder cancer may occur despite treatment.
The optimal time to administer chemotherapy is immediately after TUR, as the drugs might prevent reseeding of cancer cells that were disrupted with surgery. Mitomycin is probably the preferred drug because it produces few side effects and is not well absorbed into the system, which allows more of the drug to remain in the bladder to treat the cancer. Thiotepa is rapidly absorbed and produces low blood counts. Doxorubicin produces the most local side effects.
Don’t Miss: Does Prostate Cancer Spread To Bladder
Survival Rates For Bladder Cancer
Survival rates can give you an idea of what percentage of people with the same type and stage of cancer are still alive a certain amount of time after they were diagnosed. They cant tell you how long you will live, but they may help give you a better understanding of how likely it is that your treatment will be successful.
Keep in mind that survival rates are estimates and are often based on previous outcomes of large numbers of people who had a specific cancer, but they cant predict what will happen in any particular persons case. These statistics can be confusing and may lead you to have more questions. Your doctor is familiar with your situation ask how these numbers may apply to you.
Signs And Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
Sometimes bladder cancer doesnt have many symptoms. Signs or symptoms can include:
- blood in your urine
- pain or burning when passing urine
- not being able to pass urine when you need to.
Not everyone with these symptoms has bladder cancer. If you have any of these symptoms or are worried, always see your doctor.
Read Also: How To Cope With Overactive Bladder
Other Terms Often Used To Describe Bladder Cancer
Although bladder cancer types are assigned based on the cells that the cancer originates from, several other terms may be used to describe the disease.
- Advanced bladder cancer is another term that may be used to describe metastatic bladder cancer. It means that the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs, bones, liver, or lymph nodes outside the pelvis.
- Locally advanced bladder cancer refers to cancer that has grown through the bladder wall, and possibly into nearby lymph nodes or organs, but has not spread to distant sites in the body.
- Bladder cancer stage describes where the cancer is located within the bladder and any sites of spread. As described above, the TNM staging system assigns a patients bladder cancer to a tumor , lymph node and metastasis category. These categories may also be combined to give an overall stage number: an overall stage of 0 or 1 describes early disease, while stage 4 is the most advanced. For further information regarding staging, see Bladder Cancer Stages.
- Bladder cancer grade is based on the microscopic appearance of cancer cells and suggests how fast a cancer might grow. Low-grade cancer cells appear similar to normal cells and usually grow slowly, whereas high-grade cancer cells have a very abnormal appearance and tend to grow quickly. High-grade cancers are more likely than low-grade cancers to spread.
Substantial Improvement In Survival
Dr. Powles and his colleagues enrolled 700 people with locally advanced or metastatic bladder cancer in the international JAVELIN Bladder 100 study, which was funded by Pfizer, the drugs manufacturer.
All trial participants had already received chemotherapywith either cisplatin and gemcitabine or carboplatin and gemcitabine, if their health did not allow them to receive cisplatinand their disease had not worsened during chemotherapy.
Participants were then randomly assigned to receive either maintenance treatment with avelumab plus supportive care or supportive care alone. People in the maintenance group received infusions of avelumab every 2 weeks until their cancer started growing again or they left the study for other reasons. Supportive care for both groups included pain management, nutritional support, and treatment of infections.
People in the supportive care group whose cancer got worse did not receive avelumab as part of the trial. However, they could receive it or any other immunotherapy drug after leaving the study.
Maintenance treatment with avelumab after chemotherapy turned out to have substantial benefits. The median overall survival for people who received maintenance avelumab was more than 21 months, compared with about 14 months for people who received only supportive care until their cancer got worse.
Read Also: Ways To Help Bladder Infection
Environmental And Occupational Exposure
The second greatest preventable risk factor for bladder cancer is occupational exposure to carcinogens, including aromatic amines, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and chlorinated hydrocarbons . These compounds are commonly found in the industrial production of dyes, paint, metal, rubber or petroleum products . Among those in the rubber industry, an increased mortality risk of 253× was reported for those in storage and shipment and an increased risk of 159× was reported for those with general work in the industry . Other industries implicated in a greater risk of bladder cancer include firefighters, hairdressers, and farmers who use fungicides. Overall, occupational exposures are estimated to be responsible for 18% of bladder cancer cases. While 2 years exposure seems to be sufficient to increase ones risk, the disease often does not develop until decades after exposure, much like with tobacco smoke .
A large prospective observational study from Chile suggested that exposure to arsenic, a naturally occurring metalloid in air, soil, and water, also increased the risk of bladder cancer . Another study from Finland found that exposure to low concentration Arsenic and tobacco smoke had a synergistic effect in increasing the risk of bladder cancer . Other carcinogens in the water supply, such as disinfection byproducts or nitrates, along with metals in the diet such as selenium and zinc, could also modify the risk of developing bladder cancer .
What Affects Survival
Your outlook depends on the stage of the cancer when it is diagnosed. This means whether the cancer is just in the bladder lining or whether it has spread into the muscle wall of the bladder or beyond.
The type of bladder cancer can affect your likely survival. And the grade of the cancer may also be important. Grade means how abnormal the cells look under the microscope.
Most bladder cancers are diagnosed when they are still only in the bladder lining. These are called early bladder cancers. The outlook for early bladder cancers depend on several factors, including:
- exactly how far the cancer cells have gone into the bladder lining
- the number of tumours
- how wide the tumours are
- how abnormal the cancer cells look under the microscope
- whether CIS is present
- whether this a recurrence and how often a tumour has recurred
Your doctor looks at all these factors. They use them to decide whether there is a low, medium or high risk of the cancer coming back or spreading into the muscle of the bladder. Your doctor will be able to tell you about your risk group and how this affects your outcome.
Don’t Miss: Erectile Dysfunction After Bladder Removal
What Is A Bladder
The bladder can be described as a hollow organ, which is located next to the kidneys. The bladder functions by collecting all the urine coming from the kidneys through the ureter. It then stores the urine until it is removed from the body.
Having a bladder cancer causes an uncontrolled growth and development of cells in the bladder. The increasing production of cells is abnormal. Once the cells have grown, they can cause some complications in the personâs body including pain.
Have a question about
You May Like: Side Effects Of Immunotherapy For Bladder Cancer
What Are The Layers Of The Bladder
The bladder consists of three layers of tissue. The innermost layer of the bladder, which comes in contact with the urine stored inside the bladder, is called the mucosa and consists of several layers of specialized cells called transitional cells, which are almost exclusively found in the urinary system of the body. These same cells also form the inner lining of the ureters, kidneys, and a part of the urethra. These cells form a waterproof lining within these organs to prevent the urine from going into the deeper tissue layers. These cells are also termed urothelial cells, and the mucosa is termed the urothelium.
The middle layer is a thin lining known as the lamina propria and forms the boundary between the inner mucosa and the outer muscular layer. This layer has a network of blood vessels and nerves and is an important landmark in terms of the staging of bladder cancer .
The outer layer of the bladder comprises of the detrusor muscle. This is the thickest layer of the bladder wall. Its main function is to relax slowly as the bladder fills up to provide low-pressure urine storage and then to contract to compress the bladder and expel the urine out during the act of passing urine. Outside these three layers is a variable amount of fat that lines and protects the bladder like a soft cushion and separates it from the surrounding organs such as the rectum and the muscles and bones of the pelvis.
Recommended Reading: Holding Your Bladder Can Cause
Bladder Cancer Survival Trends Over Time
Bladder cancer survival trends are difficult to interpret because of changes to classification and coding practices affecting the definition of invasive carcinoma of the bladder.The decrease in bladder cancer survival since the 1990s is likely to be due to an increasing proportion of bladder tumours now being coded as in situ or uncertain.
One-year age-standardised net survival for bladder cancer in men has increased from 63% during 1971-1972 to 80% during 1990-1991 and then decreased to 77% during 2010-2011 in England and Wales. In women, one-year survival has increased from 53% to 70% and then decreased to 62% over the same time periods.
Bladder Cancer , Age-Standardised One-Year Net Survival, Adults , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Five-year age-standardised net survival for bladder cancer in men has increased from 41% during 1971-1972 to 63% during 1990-1991 and then decreased to a predicted survival of 57% during 2010-2011 in England and Wales. In women, five-year survival has increased from 35% to 55% and then decreased to 46% over the same time periods.
Bladder Cancer , Age-Standardised Five-Year Net Survival, Adults , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Five-year survival for 2010-2011 is predicted using an excess hazard statistical model
Bladder Cancer , Age-Standardised Ten-Year Net Survival, Adults , England and Wales, 1971-2011
Ten-year survival for 2005-2006 and 2010-2011 is predicted using an excess hazard statistical model