Interstitial Cystitis Diet: What To Eat & What To Avoid
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic bladder condition characterized by pelvic pain, bladder pain, urinary frequency and urgency , and bladder pressure. Its also known as painful bladder syndrome.
What are the different types of IC? The different types of IC are ulcerative IC and non-ulcerative IC. Ulcerative IC patients develop painful Hunners ulcers on the inner surface of the bladder. Non-ulcerative IC patients form tiny hemorrhages on the bladder wall.
According to the Interstitial Cystitis Association, about 9 out of 10 cases of IC are non-ulcerative. Regardless of the type of IC, your diet can make a profound impact on your symptoms.
What Foods Cause Flare Ups Of Interstitial Cystitis
Most patients with Interstitial Cystitis will notice a significant decrease in pain severity and episodes after following an elimination diet utilizing the Bladder Friendly Foods in “The IC Foods List” PDF provided. If this occurs, then you have confirmation of the diet link to your pain. Once you have established that there is a dietary component to your pain, the next step is to figure out which foods are the culprits. To do this, you will want to add in a small amount of one food item per day to determine which foods are safe for you or cause pain and should be avoided. For additional information and guidance with this diet, and to assure you are still meeting your nutrient needs, call us and make an appointment with our Registered Dietitian, Kaylie Brand, RD, LD.
Effect Of Diet On Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis is a chronic health condition that causes pain and pressure in the bladder and pelvic area. Because of this, it is sometimes called painful bladder syndrome. IC can cause an urgent need to urinate, a frequent need to urinate, or both. Although IC cannot be cured, it can be treated. Researchers have found there are dietary changes you can make to help manage and avoid IC flare-ups. Below are just a few examples of foods/beverages that are IC friendly and those that are not:
You May Like: Why Does My Bladder Hurt When I Pee
What To Have During An Ic Flare
If you are having an IC flare-up, its imperative to pay attention to the foods you eat. You want to avoid eating any foods that can exacerbate flare-ups, especially acidic foods, spicy foods, and carbonated drinks.
Instead, try to eat food that promotes bladder and urinary health. Eat a rainbow of fresh fruits and vegetables, avoiding high-acid fruits, tomatoes, and onions. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds in fruits and vegetables will help fight inflammation causing the flare-up.
What foods can be eaten during an IC flare-up? Foods that can be eaten during an IC flare-up include most vegetables , fruits with low citric acid, and lean meats. Some patients can also tolerate low-acid dairy .
Food is medicine. The foods you eat can be used to treat many chronic health issues, including irritable bowel syndrome, small intestinal bacterial overgrowth , and gut dysbiosis. Diet can even be used to treat cognitive decline. Interstitial cystitis is no different: diet helps treat IC.
Foods That Can Trigger An Ic Flare
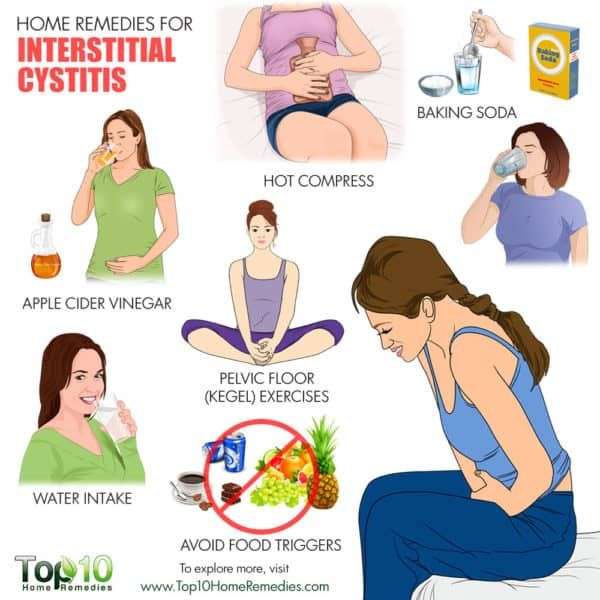
Many foods can trigger interstitial cystitis flare-ups. Some foods, like acidic fruits, spicy foods, and soy, cause more widespread symptoms, while others only affect some IC sufferers. Its essential to find the foods that have a negative effect on your unique symptoms.
What foods cause IC flare-ups? Some foods that cause IC flare-ups include:
- Acidic foods, including tomatoes and fruits high in citric acid like citrus fruits
- Acidic drinks and juices, including cranberry juice
- Artificial sweeteners like aspartame , saccharin, and acesulfame potassium
- Spicy foods and foods that contain hot peppers or horseradish
- Soy products, including dairy substitutes
- Onions
- Chocolate, particularly dark chocolate
- Gluten, which can cause inflammation if you have a sensitivity to it
One drink on the avoid list that might surprise you is cranberry juice. Most people think cranberry juice is bladder-friendly because of its reputation as a treatment for mild UTIs. But, its very acidic, which can exacerbate bladder symptoms in patients with interstitial cystitis.
Its important to read food labels carefully, particularly for additives and ingredients like artificial sweeteners, which frequently sneak into foods like salad dressings and low-calorie desserts.
Read Also: Best Product For Bladder Leakage
How Is Painful Bladder Syndrome Diagnosed
Your doctor will begin by getting a detailed description of your symptoms and medical history and performing a physical exam of the pelvic region. A urine test may be performed to rule out urinary tract infection.
A cystoscopy may be performed. A cystoscopy is a diagnostic procedure in which a slender tube with a camera is inserted through the urethra to examine the inside lining of the bladder. During this procedure, your doctor may inject liquid into the bladder to test its capacity, or remove tissue to examine for signs of bladder cancer.
Diet Modification Can Reduce Bladder Symptoms & Pain
When researchers Robert Moldwin Md, Barbara Shorter RD & colleagues at Long Island University published the results of the first formal research study exploring the role of diet and interstitial cystitis , their results validated what thousands of patients have known for decades, that certain foods can and do trigger bladder frequency, urgency, pressure and/or pain. Ninety percent of the patients who participated in that ground breaking study reported food sensitivities, a number which has since been replicated in several IC studies. In 2013, the same research team demonstrated that men with chronic prostatitis share similar food sensitivities. There is no doubt that some foods hurt the bladder.
The excessive intake of caffeine is a strong risk factor. Researchers in Massachusetts found that men who drank an average of 2 cups of coffee per day were more likely to develop lower urinary tract symptoms and difficulty with urine storage while women developed progressively worse symptoms of urgency.
Diet modification is a cornerstone of bladder management and is recommended as a first line intervention in the AUA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of IC/BPS . Please note, however, that patients often have unique and individualized food tolerances.
Don’t Miss: Will Overactive Bladder Go Away
How Can I Manage Bladder Irritation
You can manage discomfort by avoiding foods you have identified as bladder irritants. But removing foods from your diet doesnt mean you can never have them again. You might be able to enjoy them in moderation . Drinking plenty of water will help reduce pain from any bladder-irritating foods you might ingest, in moderation or accidentally.
Tips For Handling Specific Ic Triggers
- Sexual Intercourse Flares Unfortunately, for some people, interstitial cystitis and sex are connected. Sexual intercourse can lead to interstitial cystitis flares. To prevent flares from intimacy, try taking pain-reducing and anti-spasmodic medications prior to sex, use lubricant during intercourse, and after sex take a sitz bath or ice your perineum.
- Clothing Flares If you feel a flare coming on while youre wearing athletic pants, pantyhose, tight jeans, or slimming undergarments, remove them immediately. Opt for clothing that is not constrictive and fits loosely around the waist and pelvic region.
- Diet flares While research consistently shows no links between certain foods or drinks to IC, there is a strong relationship between diet and painful bladder syndrome. Dietary modification can lessen the severity of your symptoms. Coffee, soda, caffeinated beverages, tomatoes, spicy foods, high-acid foods, citrus, and MSG can all trigger IC symptoms. If you have a flare, journal what you ate prior to it. This will help you identify foods that could be causing your IC flares and allow you to avoid these in the future.
Don’t Miss: What Is Aggressive Bladder Cancer
What Can I Do If I Have Bladder Pain From Foods
Living with bladder irritation can be uncomfortable. But you can take steps to remove irritants from your diet and reduce pain. Avoid foods that irritate your bladder, and remember that water is important. Drinking enough water helps you feel more comfortable after you eat foods that irritate your bladder.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Bladder discomfort can be frustrating and even embarrassing. Conditions like IC can make you feel like you need to pee even after youve already gone to the bathroom, and your bladder can hurt a lot. But you can get help to reduce irritation. Talk to your healthcare provider about your bladder irritation and possible food and drink causes.
The Role Of The Urologist
Given the multidisciplinary approach, which is recommended in the management of BPS, the urologist is often in a unique position to act as the vehicle to coordinate such efforts and establish a local network of health professionals with relevant expertise. This is enhanced if individual departments can develop a treatment algorithm, which is tailored to the services they can offer. Having a nominated urologist to champion and lead such an initiative can complement this. Where local services for treatment services do not exist, e.g., urinary diversion or nerve stimulation, developing a referral pathway to a specialist centre is recommended. Maintaining communication with primary care teams is also valuable to update referral criteria, support for patient care, and provide educational events.
Don’t Miss: How To Prevent Bladder Leakage
Bladder Pain Syndrome And Interstitial Cystitis Beyond Horizon: Reports From The Global Interstitial Cystitis/bladder Pain Society Meeting 2019 Mumbai India
Mohammad Sajjad Rahnama’i1 , 2 , * ,
how to cite: Rahnama’i M S , Javan A, Vyas N , Lovasz S , Singh N, et al. Bladder Pain Syndrome and Interstitial Cystitis Beyond Horizon: Reports from the Global Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Society Meeting 2019 Mumbai â India. Anesth Pain Med. 2020 10:e101848. doi: 10.5812/aapm.101848.
What Is The Outlook For People Sensitive To Bladder Irritation

If foods irritate your bladder, you may worry about finding enough to eat. SOME people with IC are able to eat and drink these foods:
- Alcohol or wines .
- Almonds.
- Coffee or highly roasted.
- Extracts .
- Nuts almonds, cashews and peanuts.
- Onions .
- Sun tea .
- Tomatoes .
- Zest of orange or limes.
- Other foods not listed.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Best Pads For Bladder Leakage
Summary Of Presented Findings
2.1. Diagnosis of IC/BPS
In daily clinical practice, the diagnosis of BPS/IC is difficult to make. Patients present with a variety of complaints, signs, and clinical test results. Hence, these patients are often misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed . A good history and physical examination along with cystoscopy is a must for the diagnosis of IC/BPS .
Many patients have a history of mental trauma and stress, which needs to be dealt with. In addition, pain management needs to focus on the character, intensity, duration, and radiation of the pain. The pain score is important in determining the treatment strategy. On the examination, one can find palpable âMyofascial Bandsâ in addition to undefined nodules in the perineum, suprapubic region, thigh, and even back, of unknown origin. Assurance is very important at each step and the patient should be educated about the disease, and the goals of management should be discussed. Patients and their families should also be told that it takes time for the pain to be controlled, and there is a stepwise approach.
Pictorial Representation of Therapeutic Modalities Linked to the Clinical Scores of BPS/IC
2.2. Treatment
Today, the BPS/IC diet is no longer a restrictive one, but a modified, personalized version of a diet composed of natural and minimally processed foods from all essential food groups.
Algorithm for pain management in patients with BPS/IC
Interstitial Cystitis Foods To Avoid
The Interstitial Cystitis Association suggests that the following foods should be avoided:
- Aged cheese
- Processed, smoked or cured meats
- MSG
- Some fruits banana, strawberry, pineapple, grapes, cantaloupe, plums
- Onions
- Tomatoes
- Yogurt
Every individual is different so it is best to first try an elimination diet and then slowly test foods by adding them back to the diet one by one to see what is a trigger for each individual.
Recommended Reading: Icd 10 Code For Overactive Bladder
Tip : Make The Most Of Each Visit
As mentioned in the previously featured section on evaluation, all other causes of pelvic pain must be ruled out before addressing a management plan. Patients with chronic pain conditions take a long time to accurately assess. In general, a urologist can predict this will be the case based on the referral. Therefore, it is important to book the initial time up front. Having booked the time upfront may decrease the stress of trying to rush these patients. Upon receiving the diagnosis of IC/BPS, patients are certain to have multiple questions.
Importantly, have the patient provide as much information prior to coming into the office or clinic room. This may include: health questionnaires, medication lists/allergies, lists of previous treatments, frequency voiding charts , survey scores , urinalysis, and culture results. This objective information can then be reviewed before your interview to save time for the physical exam and treatment plan.
Lastly, to help make the most of the initial visit and subsequent visits, find a method to objectify the patients symptoms in terms of the most bothersome issue and the degree of bother. It is helpful to ask:
Foods That Can Alleviate Ic Symptoms
While the list above can aggravate symptoms of interstitial cystitis, some foods can improve them. Its often harder for IC patients to tell which foods positively affect their symptoms, but a few foods are consistently used to promote bladder health.
The best diet to promote bladder health and improve IC symptoms will include:
- Water: Drinking enough water helps you void your bladder regularly.
- Chamomile and peppermint tea: Chamomile tea and peppermint tea promote bladder health.
- Vegetables: Leafy green vegetables, cruciferous vegetables, root vegetables, gourds
- Low acid fruit: Pears, bananas, blueberries, melons
- Garlic and turmeric: Garlic and turmeric are anti-inflammatory spices that promote urinary health
These anti-inflammatory, bladder-friendly foods and beverages are typically safe bets for IC patients.
What are some IC diet tips? Some IC diet tips are keeping a food and symptom log , avoid foods and drinks that commonly cause IC symptoms, and trying an elimination diet to find the specific foods that worsen your symptoms.
You May Like: Medications That Cause Overactive Bladder
Recommended Supplements For Ic
For the treatment of interstitial cystitis, supplements are a good option and can be used with or without prescriptive medicine. They are considered effective alternative medicine for IC treatment. In both situations, supplements are effective and can boost the immune system. But we suggest consulting with your physician if you are taking the supplements with prescription medicines.
IC supplements are formulated with compounds that help in reducing the pain, frequency, and urgency associated with interstitial cystitis. These compounds can be antacids, anti-inflammatory essential amino acids, mucopolysaccharides, and bioflavonoids that promote interstitial cystitis treatment.
So, here are the best supplements for interstitial cystitis.
Complementary And Alternative Medical Therapies For Interstitial Cystitis: An Update From The United States
Megan Danielle Atchley1, Nima M. Shah2, Kristene E. Whitmore3
1 Pelvic and Sexual Health Institute, Philadelphia, PA 19107, USA 2 Division of Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA 19107, USA 3 Division of Female Pelvic Medicine and Reconstructive Surgery, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Drexel University College of Medicine, Pelvic and Sexual Health Institute, Philadelphia, PA 19107, USA
Contributions: Conception and design: All authors Administrative support: None Provision of study materials or patients: KE Whitmore Collection and assembly of data: MD Atchley Data analysis and interpretation: All authors Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Keywords: Interstitial cystitis bladder pain syndrome percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation complementary and alternative medicine
Submitted Jul 31, 2015. Accepted for publication Aug 09, 2015.
doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2223-4683.2015.08.08
Don’t Miss: Urinary Incontinence And Overactive Bladder
Percutaneous Nerve Stimulation /acupuncture
PTNS can also be used for treatment of IC/BPS. PTNS is used twice weekly in a study with a group of female Chinese patients who presented with IC symptoms of frequency, urgency, perineal pain or suprapubic pain. The patients experienced the IC symptoms of frequency, urgency, perineal pain or suprapubic pain for 3.4 years. The patients were part of a prospective study and participated in twice weekly 30-minute sessions for a total of ten sessions. In order to gauge their response to treatment, patients were given a VAS for pain, voiding diary, OLeary/Saint IC symptom and problem index, and a 36-item short-form health survey QOL questionnaire. At the end of their treatment, patients were then allowed to self evaluate with a rating of no effect, some effect, and significant effect. The end of treatment evaluation rating was completed using a self-evaluation table by answering yes or no questions. Very rare complications occurred with the PTNS procedure including localized tenderness or temporary pain at the needle insertion site, and minor bleeding immediately upon removal of the needle. Even though these minor complications were experienced, none of the 18 patients chose to discontinue treatment if they experienced this, and 4 of the 18 patients chose to continue further treatment courses after completion of the trial.
Men With Interstitial Cystitis

Men can get interstitial cystitis or painful bladder syndrome. Common symptoms of IC and BPS are urinary urgency, urinary frequency, nocturia , suprapubic or pelvic pain, the pain classically worsens with bladder filling and is relieved with urination, dysuria , and the sensation of incomplete evacuation of urine. If IC/BPS are present for many months or even years symptoms of pelvic pain and pelvic floor muscle spasm are seen. These include rectal spasms or rectal pain, pain with erection or ejaculation, soreness post erection or ejaculation, pain at the tip of the penis, groin or testes, prostate, bladder, epididymis, and testes tenderness. Treating the associated pelvic pain and pelvic floor spasm can help with symptoms of IC and BPS.
You May Like: How Does Botox Help Bladder Control