Preventing And Fixing An Overactive Bladder
Prevention is always the best medicine. With this in mind, lets first talk about some lifestyle choices that lower your risk of an overactive bladder.
The most important factors to preventing OAB are maintaining a healthy weight and getting regular exercise. A healthy body optimizes the functioning of the urinary tract and other vital organs. Further, an active lifestyle is the best way to counteract diabetes and obesity. Other prevention measures include limiting alcohol and caffeine, quitting smoking, and managing any known medical conditions.
Now lets say youre struggling with a bit of OAB. Are there measures you can take to counteract it? Many signs point to yes. One noteworthy finding reported by Harvard University showed that 70 percent of women who used alternative remedies reported being satisfied with the treatment. These treatments might include supplements, herbs, and therapies.
While research is still a bit sparse , here are three that have shown promise.
Beta Agonists For Bladder Problems
This class of medication, mirabegron , works by relaxing the bladder muscle during the storage phase, thus increasing the capacity of bladder to hold more urine. They can be used for the treatment of overactive bladder . Mirabegron is the first drug in this category.
- How beta-agonist drugs work: They work by relaxing the bladder muscles and reducing bladder overactivity.
- Who should not use this medication: Individuals with the following conditions should not use mirabegron or a similar class of drugs:
- Allergy to this drug
- Advanced kidney disease
Also Check: Chronic Bladder Infection In Men
How Do Health Care Professionals Diagnose Overactive Bladder
The diagnosis of overactive bladder is based on the presence of symptoms, while excluding other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. This is based on history, physical examination, and a urine test. Waking up to urinate one or more times at night, urinary frequency , urinary urgency, and urinary incontinence are all important clues in evaluating someone suspected of having overactive bladder.
In addition to a general physical examination, a pelvic exam in women and a prostate examination in men are helpful in excluding other contributing conditions.
Urine analysis to assess for infection, blood cells in the urine, and high levels of glucose in the urine is recommended. Occasionally, urine cytology is sometimes advised in individuals undergoing evaluation of urinary incontinence and overactive bladder, particularly individuals with blood cells in the urine . Bladder ultrasound measurement of the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination may also provide additional information about the cause of urinary incontinence but is not needed in all individuals with OAB symptoms.
Also Check: What Do They Do For Bladder Cancer
Common Questions About Mirabegron
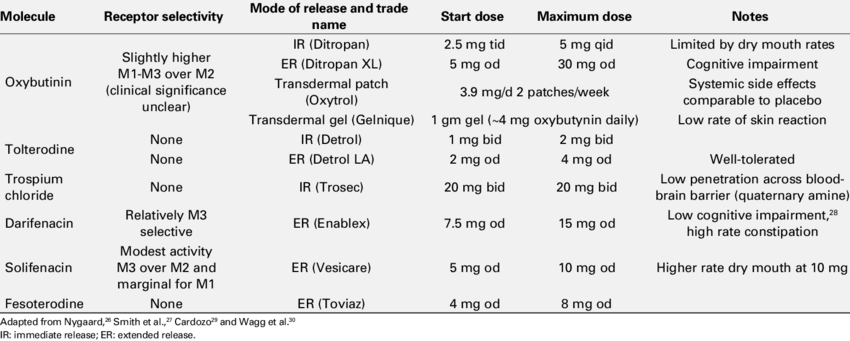
Mirabegron is a type of medicine called a beta-3-adrenergic-receptor agonist.
It works by relaxing the muscles around your bladder. This increases the amount of pee that your bladder can hold and reduces your need to pee as frequently or as urgently.
Mirabegron starts to work after about 3 to 4 hours to relax the muscle surrounding your bladder.
However, it can take up to 4 to 8 weeks for you to notice any improvements in your symptoms.
Usually, treatment with mirabegron is long term.
However, if you no longer have bladder problems, your doctor will advise you to stop taking mirabegron.
Mirabegron is generally safe to take long term, as long as you’re not bothered by side effects.
Many people take it for several months or even years without any problems.
It is safe to take mirabegron with everyday painkillers like paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Do not stop taking mirabegron without talking to your doctor first.
If you stop taking this medicine, it will take about 10 days for it to be completely out of your body.
Your symptoms of overactive bladder may come back or get worse.
Mirabegron is not usually the first choice of treatment for an overactive bladder.
Your doctor will usually try you on a type of medicine called an antimuscarinic first.
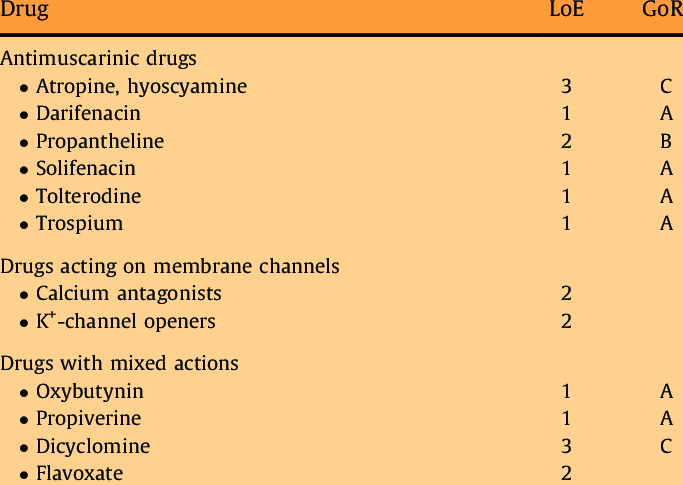
Antimuscarinics include:
There’s no clear evidence to suggest that taking mirabegron will reduce fertility in men or women.
Yes, you can usually drive or cycle while taking mirabegron.
Consider Alternative Treatment Options
In addition to the established treatment options for OAB, a variety of alternative treatments may help reduce symptom-related anxiety and stress.
The results of a 2020 randomized controlled trial involving 27 females revealed that laser acupuncture led to significant improvements in OAB symptoms and quality of life.
Researchers have also investigated electrical stimulation, which sends targeted electrical pulses to the muscles that control and support the bladder, for use in OAB treatment. A found that electrical stimulation, in combination with bladder training and biofeedback, significantly reduced the symptoms of OAB and improved quality of life.
Recommended Reading: Does Botox Help Overactive Bladder
Tests Of Bladder Function
Your doctor may order tests to assess how well your bladder is functioning and its ability to empty steadily and completely . These tests usually require a referral to a specialist and may not be necessary to make a diagnosis or begin treatment. Urodynamic tests include:
Your doctor will review the results of any tests with you and suggest a treatment strategy.
Does Drinking Water Help With Overactive Bladder
A note on overactive bladder and water intake: An understandable reaction to overactive bladder is to reduce your fluid intake. However, you need plenty of water for your bodys other systems to function properly. Consequently, you should talk with your doctor about how much water consumption is right for you.
You May Like: Over The Counter Bladder Control Meds
Cautions With Other Medicines
Mirabegron may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how mirabegron works.
Tell your pharmacist or doctor if you’re taking:
- digoxin, a medicine for heart failure or abnormal heart rhythm
- imipramine or desipramine, medicines for urinary incontinence or nerve pain
- dabigatran, a blood thinner
- ketoconazole or itraconazole, medicines used to treat fungal infections
- ritonavir, a medicine used to treat HIV
Who Can And Cannot Take Mirabegron
Mirabegron can be taken by adults .
It is not suitable for everyone. To make sure it’s safe for you, tell your doctor or pharmacist before starting mirabegron if you:
- have had an allergic reaction to mirabegron or any other medicines in the past
- have liver or kidney problems
- have high blood pressure
- are not able to pee or empty your bladder completely
- have a blockage in your bladder
- have a heart problem called QT prolongation
- are pregnant, trying to get pregnant or breastfeeding
Recommended Reading: What Are The Chances Of Surviving Bladder Cancer
What Are Overactive Bladder Symptoms
The symptoms of an overactive bladder include frequent urination , urgency of urination with or without urgency urinary incontinence, and nocturia . Overactive bladder may cause significant social, psychological, occupational, domestic, physical, sexual, and financial problems. Again, these symptoms should not be considered a normal part of aging.
What Medications Cause Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder involves an uncontrolled urge or sudden need to urinate. Most of us have increased our fluid intake at some point, which led to more trips to the bathroom. But an overactive bladder is different. It does not occur due to an increase in fluids. Although, some medications can cause this. So, what medications cause overactive bladder? We will take a look shortly.
An overactive bladder is not the same thing as urinary incontinence. Urinary incontinence occurs when urine leaks out involuntary. Either condition can develop on its own, but they can also occur together. An overactive bladder can often lead to urinary incontinence.
Also Check: How To Fix Bladder Leakage Naturally
Some Medications For Type 2 Diabetes
The newer medications for type 2 diabetes, a class called sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors work by increasing the amount of glucose or blood sugar your kidneys excrete and pass through urine, which takes fluid with it, says Varin. Some good news: There was a concern that SGLT2 inhibitors would also increase the risk of urinary tract infection , but newer research has failed to find that connection, suggests the February 2020 issue of Clinical Kidney Journal.
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation
This procedure uses a thin needle that is placed through the skin near your ankle to send electrical stimulation from a nerve in your leg to your spine, where it connects with the nerves that control the bladder.
PTNS treatments are delivered once a week for 12 weeks to help treat symptoms of overactive bladder. You will likely need maintenance treatments every three to four weeks to keep symptoms under control.
Don’t Miss: Can You Have A Bladder Infection Without Symptoms
What Measures Can Be Taken At Home To Prevent Overactive Bladder Symptoms
The exact cause of overactive bladder syndrome is not known, thus preventative strategies are not established. However, the following options can avoid exacerbating symptoms in some individuals.
Caffeine may exacerbate urinary urgency, and it is potentially an irritant to the bladder. Eliminating caffeine intake can diminish some of the symptoms of overactive bladder.
Some experts suggest that avoidance of certain foods, such as chocolate, spicy foods, alcohol, carbonated beverages, and nuts, can be beneficial in preventing symptoms of overactive bladder. Others encourage increasing the amount of dietary fiber for people with overactive bladder. Limiting fluid intake can also help to reduce urinary frequency.
Excess weight can put more pressure on the bladder, causing urinary incontinence. Therefore, weight loss can also help with urinary incontinence in general.
How To Recover From A Loss Of Bladder Control
This type of response tends to only occur in those that are faced with extreme fear. Its unfortunately not something you can control if you still experience that level of fear. You cannot tell your limbic system to control your bladder because its reacting to what it perceives as a dangerous threat, and if you ever were in danger you would want your limbic system to act the same way.
There are two important factors for overcoming the loss of bladder control:
- Preventing yourself from experiencing any shame or embarrassment.
- Controlling anxiety from becoming that severe.
Your anxiety is going to make it very hard for you to not care about something like a loss of bladder control. You are going to need to do whatever it takes to remind yourself that no one is judging you no one cares that you lost control of your bladder from fear, and no one would care if it happened again in the future. Fear of losing control of your bladder contributes to further fears and anxiety. You have to make sure that you do whatever it takes to prevent it from affecting you further.
Youll also need to learn to control your anxiety so that it is not severe enough to cause that level of fear. Those with phobias should strongly consider desensitization therapy. Its an effective and widely used to way to reduce overall phobias.
Was this article helpful?
Don’t Miss: Overactive Bladder Only At Night
Causes Of Overactive Bladder
To understand the cause of Overactive Bladder, a basic understanding of how the urinary system operates is needed.
The kidneys produce the urine and send it to the bladder. The bladder expands to holds the urine while the sphincter muscle acts as a spiget and controls the flow of urine. Basically on or off. As soon as your bladder gets approximately half fullmost people can handle about 2 cups of urineyour brain is signaled that you need to empty it. The bladder muscles contract while the sphincter relaxes. When there is a coordination problem along this system, incontinence occurs.
With Overactive Bladder, a person may be suddenly aware of the urgency sensation but is unable to get to the toilet before losing control of his or her urine. Urine loss can be in large amounts that soak underwear and even outer clothing.
Common triggers like hearing running water or simply the anticipation of urinating can cause a bladder spasm. In some cases, people who have physical limitations may not be able to reach the toilet in time, causing an accident.
How Do Stress And Anxiety Impact The Bladder
Anxiety and an overactive bladder can occur simultaneously. Stress and anxiety affect the bladder in several ways. Both cause muscles in your body to tense up , and the bladder is essentially a muscular sac that also tightens with stress. Additionally, your pelvic floor is comprised of muscles that can tighten, compressing your bladder. Chances are that when your body tenses up, so does your pelvic floor and bladder. This triggers the need to urinate, and if youre anxious often, you might need to go too often.
Also Check: What To Take For Stress Relief
Don’t Miss: Does Oxybutynin Cure Overactive Bladder
Natural Remedies For An Overactive Bladder
1. Kegel Exercises
If a weak pelvic floor is at the root of your OAB then kegel exercises can help a lot. These pelvic floor exercises can be done anywhere at anytime and they benefit both men and women. When done regularly, they can really help an overactive bladder.
Melody Denson, MD, a board-certified urologist with the Urology Team in Austin, TX, recommends these exercises for OAB. She says, They will trigger a reflex mechanism to relax the bladder. If you feel a tremendous urge to urinate, doing a kegel before you run to the bathroom will help settle down the bladder spasm and help you hold it until you get there.
2. Avoid Dietary Triggers
Significantly reduce the following foods and drinks that are known to contribute to overactive bladder:
- Alcohol
- Soda and other carbonated beverages
- Spicy foods
- Artificial sweeteners
- Milk and milk products
- Sugar and high sugar foods
Caffeine, alcohol and certain medications like diuretics are known to be major causes of acute incontinence, especially in the elderly population. Cranberry juice is surprisingly another thing to avoid if you have OAB. Although cranberry juice is often recommend for bladder health, it actually acts as an irritant if you have OAB.
3. Watch Fluid Intake
4. Double-Void
5. Schedule bathroom trips
6. Delay Urination
7. Try Acupuncture
8. Stop Smoking
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Simulation
A less invasive option called percutaneous tibial nerve stimulation is also available. It only takes about half an hour per session to perform and is usually done in a doctors office.
In PNTS, a needle electrode is inserted near the ankle that delivers electrical pulses to the tibial nerve. This nerve is linked directly to the sacral nerve.
As in SNS, these electrical pulses help block inappropriate bladder signaling.
Also Check: Bladder Problems After Endometrial Ablation
What Are Treatments For The Chronically Incontinent
Although many people will improve their continence through medications, pelvic-muscle exercises, and bladder training, some will never achieve complete dryness. Sometimes treatment failures are due to concurrent use of other necessary medications, such as diuretics , that actually can cause incontinence. Others may have dementia or other physical impairments that keep them from being able to perform pelvic-muscle exercises or retrain their bladders. Many will be cared for in long-term care facilities or at home. The following recommendations can help keep the chronically incontinent drier and reduce their cost of care:
- Scheduled toileting : Take people to the toilet every two to four hours or according to their toilet habits.
- Prompted voiding: Check for dryness and encourage use of the toilet.
- Improved access to toilets: Use equipment such as canes, walkers, wheelchairs, and devices that raise the seating level of toilets to make toileting easier.
- Managing fluids and diet: Behavioral modifications can directly impact symptoms of OAB. These include eliminating dietary caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods and encourage adequate fiber in the diet.
- Disposable absorbent garments: Use these to keep people dry.
- Avoid indwelling catheters as much as possible, as these are associated with a risk of urinary tract infection, stones, and urethral and bladder irritation.
What Is Overactive Bladder Or Urge Incontinence
Overactive bladder, which is sometimes called urge urinary incontinence though that is really the most common symptom of OAB, is a complex of urinary symptoms:
- The urgent and uncontrollable need to urinate often with leaking urine at these times .
- The ongoing need to frequently urinate .
- Waking up in the middle of the night specifically to pee .
OAB makes people feel like they gotta go suddenly and much too often.
Its a common and frustrating part of life for many men and women: About 40% of women and 30% of men have OAB symptoms, reports the Urology Care Foundation. Women over age 45 are more likely to have OAB, especially if they are entering menopause.
Many of these people dont talk about it, even with their doctor. We know that women often think OAB is uncommon and are embarrassed to discuss it, or they fear that the only treatment is surgery or there is no treatment. None of that is true.
Our physicians encourage women to seek medical attention for overactive bladder because it most often can be managed. Another reason is that it could be a symptom of another medical problem, like a UTI or diabetes.
Recommended Reading: Loss Of Bladder Control When Coughing
Hyperstimulation Can Cause Over Active Bladder
While not a disease, Over Active Bladder is the name of a group of symptoms that affect urinary function, such as the sudden urge to urinate that seems difficult to control, incontinence, and frequent urination. OAB affects approximately 30 40 percent of North Americans.
Research has found that emotional problems, such as anxiety disorder, can cause and aggravate over active bladder. For instance:
OAB patients reported higher anxiety symptoms compared to controls. OAB patients with anxiety reported more severe OAB/incontinence symptoms, worse quality of life, and more psychosocial difficulties compared to OAB patients without anxiety. There are positive correlations between the severity of anxiety symptoms and OAB/incontinence symptoms.
While the exact science isnt settled about the reasons why emotional problems can contribute to OAB, two theories suggest:
- The heightened autonomic nervous system activity can override normal nervous system communication between the bladder and brain causing the brain to generate a sense of urgency to urinate when the bladder isnt full, as we mentioned previously.
Any of the above reasons can cause a wide range of bladder and urination problems, including frequent urination.
Frequent urination during sleep hours is also common. Contributing factors include:
- Hyperstimulation can cause an increase in resting metabolism even when sleeping. An increase in resting metabolism will cause the body to produce more urine than normal.