Nonsurgical Treatment Options For Ui
Fortunately, there are several nonsurgical treatments for urinary incontinence. From training your bladder and pelvic floor exercises to using a urethral support device, there are different options you can try to manage your symptoms. We recommend discussing your options with a doctor before deciding on the best course of action.
In some cases, your doctor might recommend lifestyle changes to help manage and prevent the symptoms of urinary incontinence. These range from adjustments to your diet, to exercise habits to management techniques between bathroom breaks. Common nonsurgical treatments for urinary incontinence are:
Caring For Someone With Incontinence
So far, weve covered managing your own incontinence, but what if youre caring for an older adult? Incontinence is a common issue faced by dementia caregivers, and can be one of the most challenging parts of providing care. Research shows that:
- Those with dementia have a 2-3-fold increased chance of urinary incontinence
- The more severe the dementia, the more likely that there will be incontinence
- Urinary incontinence contributes to caregiver burden and increases the risk that someone will be admitted to a nursing home.
Steps to take
Dementia may not be the only cause of incontinence, so the first step is to look for other causes, like those reversible ones mentioned earlier .
If there doesnt seem to be any of those issues going on, then managed continence is the approach that is most likely to help. Rather than using the bladder medications, which can worsen confusion and dampen alertness, managed continence includes the use of continence products and a schedule of timed toileting .
In some cases, environmental adjustments and equipment, like bedside commodes, catheters, and urinals, can make frequent toileting easier and less disruptive, especially overnight.
Managing Bladder Or Urinary Incontinence
Sometimes urinary incontinence can last a short time, depending on whats causing it. But sometimes incontinence can be long-term and uncomfortable, making some everyday activities difficult to manage.
Your health care team will ask you questions to determine the type of bladder incontinence you might have. Then, you might need tests to verify the type and learn the cause of it which will help them know the best way to manage it.
- Pelvic floor muscle strengthening may be recommended. A physical therapist that specializes in pelvic floor muscle exercises can help. This might help muscle strength and bladder control get better by doing exercises that tighten and relax muscles that control the flow of urine.
- Bladder training canhelp manage how often you need to urinate throughout the day, by assigning certain time intervals to empty your bladder.
Read Also: Bladder Tumor Removal Surgery Recovery
What To Expect At Your Appointment
During your appointment, your healthcare professional will likely ask questions about your symptoms. Theyll probably want to know how long youve been incontinent, which types of incontinence youve experienced, and other details.
They may also ask about your daily habits, including your typical diet and any medications or supplements that you take.
Depending on your symptoms and medical history, they may also order additional tests, including:
- Collecting a sample of urine for analysis. Laboratory staff can check the urine sample for signs of infection or other problems.
- Measuring the amount of urine that you release when urinating, the amount left over in your bladder, and the pressure in your bladder. This information is gathered by inserting a catheter, or a small tube, into your urethra and your bladder.
- Conducting a cystoscopy. During this test, theyll insert a small camera into your bladder to examine it up close.
Bladder Leakage 3 Things Women Should Know About Urinary Incontinence
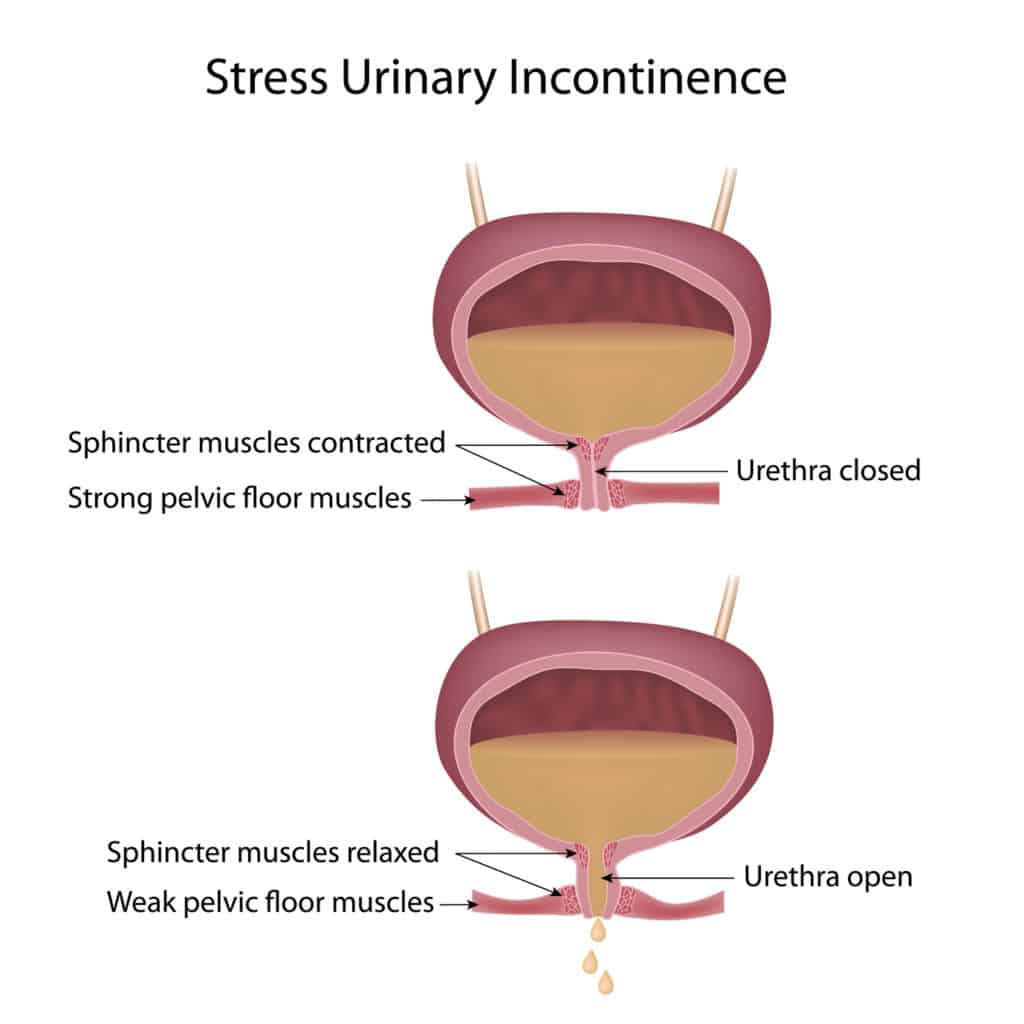
To dispel misconceptions, a urogynecologist discusses the surprisingly common, lingering issue many women experience.
Bladder leakage. For some women, the condition runs their life from the inside, preventing them from playing outside with their kids, going to a workout class or staying the night with family or friends.
And theyre not alone. Living with some degree of urinary incontinence, defined as an uncontrolled leakage of urine, is actually common, according to Pamela Fairchild, M.D., a urogynecologist at Von Voigtlander Womans Hospital at Michigan Medicine.
She says that approximately half of all women over the age of 20 experience some degree of incontinence. This means urinary incontinence isnt just an issue that affects elderly or postpartum women, although aging and childbirth are risk factors.
But if so many women experience it, then why does the topic still seem embarrassing?
Women get the sense that this is inevitable, that its a natural part of aging and they have to live with it, says Fairchild. This false perception leaves women feeling powerless, even though there are ways to greatly improve their quality of life.
To help overcome the stigma, Fairchild shared three facts about urinary incontinence that all women should know.
You May Like: What Can You Do At Home For A Bladder Infection
Keeping A Bathroom Journal
You may be asked to keep a bathroom journal before or after your appointment. In your journal, youll log all your bathroom trips and bladder leakage or issues. It can also be helpful to record what you eat and drink in your bladder journal. This record will help your doctor get a more accurate idea of your symptoms and how often they occur. Keeping a journal can also determine what triggers your need to pee or any accidents.
Treatment Options For Urgency Incontinence:
- Pelvic floor physical therapy This therapy helps to retrain the bladder.
- Medications A range of medications can help you hold your bladder for longer and decrease your urinary frequency symptoms.
- Botox injections in the bladder Botox relaxes the wall of your bladder in order to prevent it from contracting when it’s not supposed to.
- Peripheral nerve stimulation This treatment uses a needle to stimulate a nerve in your foot that travels up the leg to the spine, where it connects with the bladder and calms it down.
- Sacral neural modulation In this outpatient surgical procedure, a bladder pacemaker is implanted to help control how the bladder is stimulated by the sacral nerve.
“Regardless of which type of incontinence you’re experiencing, it’s important to get evaluated simply because there are so many options for treating urinary incontinence,” says Dr. Lindo. “We always start with conservative treatment approaches, but if those don’t work, you don’t have to continue to suffer. We can help to improve your quality of life.”
Don’t Miss: Will Cranberry Juice Help A Bladder Infection
When To Seek Medical Help
Any instance of incontinence is reason to seek medical help. It may be a symptom of a more serious condition that needs to be treated.
Even if the underlying cause isnt serious, incontinence can be a major disruption in your life. Its important to get an accurate diagnosis and discuss treatment options with a healthcare professional.
In some cases, incontinence can be a sign of a medical emergency.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you lose control of your bladder and experience any of the following symptoms:
- trouble speaking or walking
Urinary incontinence and treatment for urinary incontinence may result in complications, depending on the cause.
These complications may include:
- Urinary tract infections. UTIs can be caused by wet undergarments against the skin. This may create an environment where bacteria can grow.
- Kidney damage. In some cases where the flow of urine is obstructed, you may experience kidney trouble or kidney failure.
- Cellulitis. This skin infection is caused by bacteria and may cause swelling and pain.
- Medication side effects. Medications used to control urinary incontinence may cause side effects, depending on the medication. Side effects may include dry mouth, nausea, hypertension, or others.
- Catheter side effects. If you have a catheter placed, you may experience side effects such as infection and trauma.
- Mental health side effects. Urinary incontinence may cause feelings of anxiety, depression, or social isolation.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose Bladder Control Issues
To confirm their diagnosis, your healthcare provider may order the following tests:
- Urinalysis. A urinalysis can screen for liver disease, kidney disease and diabetes. It can also diagnose UTIs.
- Kidney function tests. Kidney function tests are urine or blood tests that evaluate how well your kidneys are working.
- Post-void residual urine test. This test measures the amount of pee that stays in your bladder after youve gone to the bathroom.
- Urine culture. A urine culture checks your pee for germs that cause UTIs.
- Urodynamic testing. Urodynamic testing measures your nerve function, muscle function, pee stream strength and pressure around and in your bladder.
- Bladder diary. A bladder diary tracks how much fluid you drink, how much you pee, how long it takes you to pee and how often you pee.
Recommended Reading: Chemicals That Cause Bladder Cancer
Treating And Managing Urinary Incontinence
Today, there are more treatments and ways to manage urinary incontinence than ever before. The choice of treatment depends on the type of bladder control problem you have, how serious it is, and what best fits your lifestyle. As a general rule, the simplest and safest treatments should be tried first.
A combination of treatments may help you get better control of your bladder. Your doctor may suggest you try the following:
What Is Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the accidental loss of urine. According to the National Association for Continence, over 25 million adult Americans experience temporary or chronic urinary incontinence. UI can occur at any age, but it is more common among women over 50. Urinary incontinence may be a temporary condition that results from an underlying medical condition. It can range from the discomfort of slight losses of urine to severe, frequent wetting.
Read Also: Over The Counter Bladder Infection Medication
Signs Of Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is not a disease in itself, but it can be a symptom of an underlying problem. The kind of symptoms you have will help determine the type of urinary incontinence.
Some symptoms may include:
Many people live with urinary incontinence, but it may affect your quality of life. You may feel embarrassed or worried about being too far from a restroom. You may also feel like you cant do normal daily activities or enjoy life. These are common feelings, which may indicate its time to talk to your doctor about how to manage your symptoms.
You Have An Infection
UTIs are another common cause of urinary retention, says Dr. Ramin, because they can create bladder weakness or swelling in the urethra.
Prostate infections and some sexually transmitted infections can also cause bladder swelling, which can lead to problems with retention, the Cleveland Clinic notes.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Get Tested For Bladder Cancer
Don’t Miss: Can Bladder Cancer Be Seen On Ultrasound
What Are The Symptoms Of Incontinence
The main symptom of incontinence is a leakage of urine. This could be a constant dripping of urine or an occasional experience of leakage. If you have incontinence, you might have large amounts or small amounts of leaked urine. You might experience leakage for a wide variety of reasons often depending on the type of incontinence you have.
You might leak urine when you:
- Have an urge to urinate, but cant make it to the toilet on time.
- Have to get up in the middle of night to urinate .
Other Types Of Urinary Incontinence
- Overflow Incontinence This occurs when a person is unable to empty their bladder completely and it overflows as new urine is produced. Its often found in people with diabetes or spinal cord injuries.
- Functional Incontinence This type of incontinence has less to do with a bladder disorder and more to do with the logistics of getting to a bathroom in time. Its usually found in elderly or disabled people who have normal or near-normal bladder control but cannot get to the toilet in time because of mobility limitations or confusion.
- Nocturia The need to urinate twice or more during the night, usually affecting men and women over the age of 60. In men, nocturia can be a symptom of an enlarged prostate.
- Mixed Incontinence You show evidence of more than one type.
Don’t Miss: Overactive Bladder After Uti Treatment
How To Control Your Bladder
Bladder training is a preventive method that helps you retrain your bladder to hold more urine. This is a mind-body approach that helps your brain and bladder learn to tolerate the presence of more urine before creating the urge that you have to go right away.
The steps to bladder training include:
When Should I See A Health Care Professional
See a health care professional if you have symptoms of a bladder problem, such as trouble urinating, a loss of bladder control, waking to use the bathroom, pelvic pain, or leaking urine.
Bladder problems can affect your quality of life and cause other health problems. Your health care professional may be able to treat your UI by recommending lifestyle changes or a change in medicine.
Recommended Reading: Why Is My Bladder Constantly Leaking
What Are The Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
The signs can vary. Some people with the chronic form have a hard time starting the flow of urine. Some have a weak flow once they start. Others may feel the need to go but cant start. Others have to go a lot, while others still feel the need to go right after going. You may leak urine when you arent going because the bladder is full.
With the acute form, youre all of a sudden not able to go at all, or only able to go very small amounts. This occurs even though you have a full bladder. See a healthcare provider right away if this happens to you.
What Is The Urinary Tract
The urinary tract consists of the organs, tubes, and muscles that work together to make, move, store, and release urine. The upper urinary tract includes the kidneys, which filter wastes and extra fluid from the blood, and the ureters, which carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. The lower urinary tract includes the bladder, a balloon-shaped muscle that stores urine, and the urethra, a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body during urination. If the urinary system is healthy, the bladder can hold up to 16 ounces2 cupsof urine comfortably for 2 to 5 hours.
Muscles called sphincters squeeze shut the tubes from the bladder to help keep urine from leaking. The sphincter muscles close tightly like a rubber band around the opening of the bladder, which leads into the urethra.
Nerves in the bladder tell you when it is time to urinate. As the bladder first fills with urine, you may notice a feeling that you need to go. The sensation to urinate becomes stronger as the bladder continues to fill. As it reaches its limit, nerves from the bladder send a message to the brain that the bladder is full and the urge to empty your bladder intensifies.
Also Check: Does Baking Soda Help Overactive Bladder
Don’t Miss: Bladder Pacemaker For Urinary Retention
Doctors Notes On Inability To Urinate
An inability to urinate means that a person cannot pass urine out of the body through the urethra. Another broad term for inability to urinate is urinary retention, although urinary retention may be considered as either partial or complete. This is different from anuria, which means the persons body is not producing urine in the kidneys, because people who cannot acutely urinate still produce urine.
There are two types of urinary retention: acute and chronic. Acute may occur suddenly, and chronic may occur over a longer time span. Acute obstruction is a medical emergency and can be life-threatening. The causes of the inability to urinate can be either obstruction of the urethra or non-obstruction of the urethra but are due to muscle and/or nerve problems that interfere with normal signals between your brain and your bladder. The inability to urinate is a symptom itself of underlying medical problems that may affect the urinary tract.
Obstructive urinary retention or the inability to urinate are due to underlying causes. The causes include the following and frequently involve putting pressure on the urethra or obstruction of the urethral lumen that results in little or no ability for urine to pass out of the body.
- nerve disease, and
- An acute inability to urinate
- Urgent and painful feeling or need to urinate
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen
Chronic urinary retention symptoms and signs may include