Almost Everyone Diagnosed With Bladder Cancer Will Undergo Bladder Tumor Biopsy And Resection
A person with a tumor in the bladder may have blood in his urine, and when he has to urinate, he may feel an urgent. Malignant tumors are cancerous tumors, they have the tendency to end up being gradually worse, and can potentially lead to death. Common types of benign tumors. A biopsy is a procedure in which a doctor takes a tissue sample from the area where cancer may exist.
Occurrence In The United States
The American Cancer Society estimates that 83,730 new cases of bladder cancer will be diagnosed in the United States in 2021 and that 17,200 people will die of the disease. The incidence of bladder cancer increases with age, with the median age at diagnosis being 73 years bladder cancer is rarely diagnosed before age 40 years.
Bladder cancer is about 3 times more common in men than in women. Over the past 2 decades, however, the rate of bladder cancer has been stable in men but has increased in women by 0.2% annually. The male predominance in bladder cancer in the United States reflects the prevalence of transitional cell carcinoma . With small cell carcinomain contrast to TCCthe male-to-female incidence ratio is 1:2.
Bladder cancer is the fourth most common cancer in men in the United States, after prostate, lung, and colorectal cancer, but it is not among the top 10 cancers in women. Accordingly, more men than women are expected to die of bladder cancer in 2021, with 12,260 deaths in men versus 4940 in women. Nevertheless, women generally have a worse prognosis than men.
The incidence of bladder cancer is twice as high in white men as in black men in the United States. However, blacks have a worse prognosis than whites.
Limited data indicate that small cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder probably has the same epidemiologic characteristics as urothelial carcinoma. Patients are more likely to be male and older than 50 years.
Treating Stage Iii Bladder Cancer
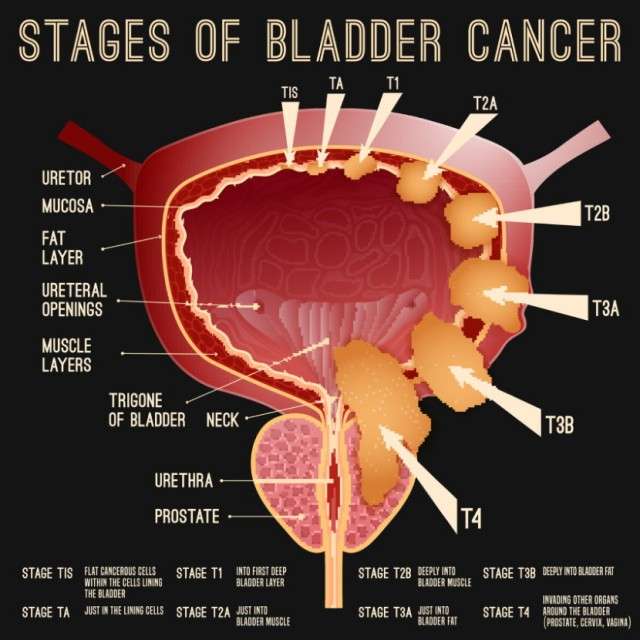
These cancers have reached the outside of the bladder and might have grown into nearby tissues or organs and/or lymph nodes . They have not spread to distant parts of the body.
Transurethral resection is often done first to find out how far the cancer has grown into the bladder wall. Chemotherapy followed by radical cystectomy is then the standard treatment.Partial cystectomy is rarely an option for stage III cancers.
Chemotherapy before surgery can shrink the tumor, which may make surgery easier. Chemo can also kill any cancer cells that could already have spread to other areas of the body and help people live longer. It can be especially useful for T4 tumors, which have spread outside the bladder. When chemo is given first, surgery to remove the bladder is delayed. The delay is not a problem if the chemo shrinks the cancer, but it can be harmful if it continues to grow during chemo. Sometimes the chemo shrinks the tumor enough that intravesical therapy or chemo with radiation is possible instead of surgery.
Some patients get chemo after surgery to kill any cancer cells left after surgery that are too small to see. Chemo given after cystectomy may help patients stay cancer-free longer, but so far its not clear if it helps them live longer. If cancer is found in nearby lymph nodes, radiation may be needed after surgery. Another option is chemo, but only if it wasn’t given before surgery.
Also Check: Can A Bladder Sling Be Removed
Papillary Or Flat Tumors
Papillary tumors grow out from the inner lining toward the hollow center of the bladder, in slim finger-shaped growths. These are often non-invasive, because they grow outward from the bladder lining rather than inward deeper into the bladder walls. One type of slow growing, non-invasive papillary bladder cancer is called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential .
Flat bladder tumors do not grow into the hollow part of bladder, but grows in a flat shape instead. If a flat tumor has not grown outside of the urothelium layer of cells, then it is non-invasive. If it has grown deeper into the bladder wall, then it is called invasive.
Sex After Bladder Cancer Treatment
Surgery can damage sensitive nerves, making sex more difficult. Some men may have trouble having an erection, though for younger patients, this often improves over time. When the prostate gland and seminal vesicles are removed, semen can no longer be made. Women may also have trouble with orgasm, and may find sex less comfortable. Be sure to discuss treatment options with your doctor.
Recommended Reading: How To Stop A Leaky Bladder Without Surgery
Smoking Can Affect The Risk Of Bladder Cancer
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk to your doctor if you think you may be at risk for bladder cancer.
Risk factors for bladder cancer include the following:
- Using tobacco, especially smoking cigarettes.
- Having a family history of bladder cancer.
- Having certain changes in the genes that are linked to bladder cancer.
- Being exposed to paints, dyes, metals, or petroleum products in the workplace.
- Past treatment with radiation therapy to the pelvis or with certain anticancer drugs, such as cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
- Taking Aristolochia fangchi, a Chinese herb.
- Drinking water from a well that has high levels of arsenic.
- Drinking water that has been treated with chlorine.
- Having a history of bladder infections, including bladder infections caused by Schistosoma haematobium.
- Using urinarycatheters for a long time.
Older age is a risk factor for most cancers. The chance of getting cancer increases as you get older.
About The Bladder Renal Pelvis And Ureter
The bladder is a hollow organ in the pelvis that stores urine before it leaves the body during urination. This function makes the bladder an important part of the urinary tract. The urinary tract is also made up of the kidneys, ureters, and urethra. The renal pelvis is a funnel-like part of the kidney that collects urine and sends it into the ureter. The ureter is a tube that runs from each kidney into the bladder. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body. The prostate gland is also part of the urinary tract.
The bladder, like other parts of the urinary tract, is lined with a layer of cells called the urothelium. This layer of cells is separated from the bladder wall muscles, called the muscularis propria, by a thin, fibrous band called the lamina propria.
Also Check: Causes Of Weak Bladder Muscles
What Is Bladder Cancer
Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the bladder is called bladder cancer. It starts when cells in the bladder grow out of control and crowd out normal cells. This makes it hard for the body to work the way it should.
Cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body. For instance, cancer cells in the bladder can travel to the bone and grow there. When cancer cells spread, its called metastasis.
Cancer is always named for the place where it starts. So when bladder cancer spreads to the bone , it’s still called bladder cancer. Its not called bone cancer unless it starts in the bone.
Surgical Removal Of Bladder Tumors
The main option is to perform surgery to remove the cancerous bladder tumors along the bladder wall of your cat. Surgical removal is used on a case-by-case basis, so it’s hard to say if your cat will need to go under anesthesia and endure surgery. The decision to surgically remove the cancer is less likely to be made for elderly cats and incredibly young kittens alike because the operation is risky for cats at both ends of the age spectrum.
You May Like: How To Control My Bladder
Cystoscopy With Cautery Destruction Of The Bladder Tumor
Cystoscopy is an outpatient procedure during which a thin, lighted tube with a camera is passed through the urethra into the bladder, allowing your doctor to see the inside of the bladder.
Most modern cystoscopes are also equipped with channels that permit small instruments to be passed into the bladder. During a cystoscopy, your doctor may use these instruments to remove tissue, stop bleeding with a special electrical device called an electrocautery or even perform laser treatment. If the bladder cancer tumor is small enough, this cautery may be used to remove the cancer.
Living With Advanced Cancer
Advanced cancer usually means cancer that is unlikely to be cured. Some people can live for many months or years with advanced cancer. During this time palliative care services can help.
Most people continue to have treatment for advanced cancer as part of palliative care, as it helps manage the cancer and improve their day-to-day lives. Many people think that palliative care is for people who are dying but palliative care is for any stage of advanced cancer. There are doctors, nurses and other people who specialise in palliative care.
Treatment may include chemotherapy, radiation therapy or another type of treatment. It can help in these ways:
- slow down how fast the cancer is growing
- shrink the cancer
- help you to live more comfortably by managing symptoms, like pain.
Treatment depends on:
- how far it has spread
- your general health
You May Like: Antibiotics Given For Bladder Infection
What Tests Will I Have If My Doctor Suspects Bladder Cancer Or Another Urinary Problem
Your doctor will want to analyze your urine to determine if an infection could be a cause of your symptoms. A microscopic examination of the urine, called cytology, will look for cancer cells.
A cystoscopy is the main procedure to identify and diagnose bladder cancer. In this procedure, a lighted telescope is inserted into your bladder from the urethra to view the inside of the bladder and, when done under anesthesia, take tissue samples , which are later examined under a microscope for signs of cancer. When this procedure is done in the doctors office, local anesthesia gel is placed into the urethra prior to the procedure to minimize the discomfort.
If the diagnosis of bladder cancer is made, then the next step is to remove the tumor for detailed staging and diagnosis.
Transurethral resection is a procedure done under general or spinal anesthesia in the operating room. A telescope is inserted into the bladder and the tumor is removed by scraping it from the bladder wall , using a special cystoscope . This procedure is diagnostic as well as therapeutic.
This often can be done as an outpatient procedure, with patients discharged from hospital the same day. After removal, the tumor is analyzed by a pathologist, who will determine the type of tumor, the tumor grade and the depth of invasion. The purpose of the procedure is to remove the tumor and obtain important staging information .
What Are The Symptoms Of Bladder Cancer
You probably cant detect a bladder mass on your own, so its beneficial to be familiar with the potential symptoms of bladder cancer and seek medical care if they occur. Some of the most common signs of this condition include:
- Blood in the urine
- Burning sensations or pain while urinating
- Difficulty emptying the bladder
- An unusually weak urine stream
- A frequent urge to urinate, even when the bladder is empty
- Low back pain on one side
Its important to note that bladder cancer shares many symptoms with urinary tract infections and other benign conditions. If you notice changes in your urination or have any symptoms that concern you, be sure to promptly speak with a physician. Its also a good idea to let your physician know if anyone in your family has been diagnosed with bladder cancer or if you have experienced bladder problems before.
You May Like: What Causes Overactive Bladder In Women
What Is A Urinary Tract Tumor
A urinary tract tumor is a type of cancer that develops from the disorganized uncontrolled growth of cells that make up the urinary system. A tumor of the urinary tract could involve the kidneys, ureters , urinary bladder, prostate gland , and urethra .
Bladder tumors are by far the most common type of urinary tract tumor. Of these, transitional cell carcinoma is the most common. This type of tumor originates from the cells that line the bladder. Bladder tumors need to be distinguished from benign conditions such as inflammatory masses or polyps and noncancerous diseases that cause thickening of the bladder wall.
Primary kidney tumors are relatively rare in both cats and dogs and are almost always malignant. About 50% of these tumors arise from the cells that line the kidney tubules . These are called renal carcinomas. While renal carcinoma is the most common kidney cancer in dogs, renal lymphoma is the most common kidney cancer in cats.
Primary tumors of the urethra or ureter are also rare in cats and dogs. These types of tumors develop from the cells that line the ureter and urethra.
Tumors can also develop in the prostate gland in male dogs.
Treating Stage I Bladder Cancer
Stage I bladder cancers have grown into the connective tissue layer of the bladder wall , but have not reached the muscle layer.
Transurethral resection with fulguration is usually the first treatment for these cancers. But it’s done to help determine the extent of the cancer rather than to try to cure it. If no other treatment is given, many people will later get a new bladder cancer, which often will be more advanced. This is more likely to happen if the first cancer is high-grade .
Even if the cancer is found to be low grade , a second TURBT is often recommended several weeks later. If the doctor then feels that all of the cancer has been removed, intravesical BCG or intravesical chemo is usually given. If all of the cancer wasn’t removed, options are intravesical BCG or cystectomy .
If the cancer is high grade, if many tumors are present, or if the tumor is very large when it’s first found, radical cystectomy may be recommended.
For people who arent healthy enough for a cystectomy, radiation therapy might be an option, but the chances for cure are not as good.
Recommended Reading: Botox For Overactive Bladder Cost
Papillary Vs Flat Cancer
Bladder cancers are also divided into 2 subtypes, papillary and flat, based on how they grow .
- Papillary carcinomas grow in slender, finger-like projections from the inner surface of the bladder toward the hollow center. Papillary tumors often grow toward the center of the bladder without growing into the deeper bladder layers. These tumors are called non-invasive papillary cancers. Very low-grade , non-invasive papillary cancer is sometimes called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low-malignant potential and tends to have a very good outcome.
- Flat carcinomas do not grow toward the hollow part of the bladder at all. If a flat tumor is only in the inner layer of bladder cells, it’s known as a non-invasive flat carcinoma or a flat carcinoma in situ .
If either a papillary or flat tumor grows into deeper layers of the bladder, it’s called an invasive urothelial carcinoma.
What Is Meant By Staging And Grading A Tumor
If bladder cancer is diagnosed, the doctor needs to know the stage, or extent, of the disease to plan the best treatment. Staging is a careful attempt to find out whether the cancer has invaded the bladder wall, whether the disease has spread, and if so, to what parts of the body. Grade refers to what the cancer cells look like, and how many cells are multiplying. The higher the grade, the more uneven the cells are and the more cells are multiplying. Knowing the grade can help your doctor predict how fast the cancer will grow and spread.
Urologists typically send a sample of the cancer tissue to a pathologist, a doctor who specializes in examining tissue to determine the stage and grade of the cancer. The pathologist writes a report with a diagnosis, and then sends it to your urologist.
Recommended Reading: Foods Good For Bladder Control
What Is Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
While the majority of bladder cancers arise in the bladder, the urothelial cells that line the bladder are found in other locations in the urinary system. Sometimes these urothelial cancers can occur in the lining of the kidney or in the ureter that connects the kidney to the bladder. This is known as upper tract urothelial cancer correspond to a subset of urothelial cancers that arise in the urothelial cells in the lining of the kidney or the ureter . Learn more about UTUC here.
Bladder Cancer Clinical Trials
What about Clinical Trials?
You may hear about clinical trials for your bladder cancer. Clinical trials are research studies that test if a new treatment or procedure is safe and effective.
Through clinical trials, doctors find new ways to improve treatments and the quality of life for people with disease. Trials are available for all stages of cancer. The results of a clinical trial can make a major difference to patients and their families. Please visit our clinical trials research webpage to learn more.
You May Like: How Do You Treat A Bladder Infection
What Causes This Cancer
The reason why a particular pet may develop this, or any tumor or cancer, is not straightforward. Very few tumors and cancers have a single known cause. Most seem to be caused by a complex mix of risk factors, some environmental and some genetic or hereditary.
Urinary tract tumors are most common in middle-aged to older animals. However, a rare form of primary kidney cancer called a nephroblastoma usually occurs in dogs less than 1 year of age and young cats. Its cause is related to genetic changes that occur early in life. In German Shepherds, a mutation of a specific gene is associated with renal carcinoma and the development of a nodular skin condition called dermatofibrosis.
Bladder tumors in dogs have been linked to being overweight and to exposure to certain insecticides. It has also been proposed that chronic bladder infections and inflammation may increase the risk of developing bladder cancers. Certain breeds of dogs are more likely to develop bladder tumors, including the Scottish Terrier.