I Recommend Other Overactive Bladder Treatment Options
We want to move women away from overactive bladder treatments that have dementia and Alzheimers disease as side effects. As always at CU Urogynecology, we start with the simplest treatment options before moving to more complex ones. Women and their physicians should consider the following options.
Pelvic floor therapy can have good results on OAB. A recent study of 32 women who undertook 6-9 pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation therapy sessions over 2 weeks showed:
- 22.9 percent reduction in the number of urinations in a 24-hour period.
- 21.3 percent reduction during the day.
- 34.7 percent reduction at night.
- Improved quality of life and significant improvements lasting 6 months.
Non-anticholinergic medications are an option. Drugs known as beta-3 agonists, such as mirabegron can help. Beta-3 agonists are recommended for women at high risk for side effects of anticholinergic medications.
Botox injections can reduce OAB symptoms. It relaxes bladder muscles while increasing the bladders storage capacity. Bulking agents are injected into the area around the urethra or into the bladder.
Vaginal estrogen treatment in topical cream, tablet or ring application can reduce urinary frequency and urinary urgency in women with OAB. It should be discussed as an option, though studies on its effectiveness are inconclusive.
Availability Of Data And Materials
Access to anonymized individual participant-level data collected during the trial, in addition to supporting clinical documentation, is planned for trials conducted with approved product indications and formulations, as well as compounds terminated during development. Conditions and exceptions are described under the Sponsor Specific Details for Astellas on www.clinicalstudydatarequest.com. Study-related supporting documentation is redacted and provided if available, such as the protocol and amendments, statistical analysis plan and clinical study report. Access to participant-level data is offered to researchers after publication of the primary manuscript and is available as long as Astellas has legal authority to provide the data. Researchers must submit a proposal to conduct a scientifically relevant analysis of the study data. The research proposal is reviewed by an Independent Research Panel. If the proposal is approved, access to the study data is provided in a secure data sharing environment after receipt of a signed Data Sharing Agreement.
Third Line: Advanced Therapies
Unfortunately, despite advances in pharmacological therapy, many patients remain dissatisfied with conservative measures. Some will want to move on to more invasive treatment . Fortunately, significant advances have been made in this arena as well. As these treatments typically require referral to a specialist, only a brief overview of each of the three major treatment options will be provided here a review provides a more detailed analysis .
-
Neuromodulation: Neuromodulation therapies are incompletely understood but clearly involve activation of afferent inhibitory pathways. Studies show changes in cortical activity of areas involved in lower urinary tract function with neuromodulation.
Peripheral stimulation: Posterior tibial nerve stimulation has the strongest evidence base but vaginal, anal, and cutaneous stimulation have also been used. It is delivered in an office setting with stimulation of the nerve through an acupuncture type needle for 30 min weekly × 12 weeks. It has been proven to be superior to sham therapy , to have equal efficacy and better tolerability than antimuscarinics , and to have reasonably sustained long-term effect with maintenance therapy .
-
Botulinum toxin: Botulinum toxin binds to nerves using acetylcholine as a transmitter. On uptake into the cell, key proteins are cleaved, preventing the release of acetylcholine leading to muscle paralysis. The effect is reversed only with synthesis of new proteins and regrowth of axons.
Don’t Miss: Where Is Your Bladder Woman
Natural Treatment For Overactive Bladder
Bladder training and pelvic floor exercises are just two natural treatments for overactive bladder. Research suggests that these nondrug remedies can be very effective for many women, and they have almost no side effects.
But before starting any OAB treatment, itâs important to understand bladder function and what things may cause overactive bladder.
Another way to strengthen pelvic floor muscles is electrical stimulation, which sends a small electrical pulse to the area via electrodes placed in the vagina or rectum.
Until you get your overactive bladder under control, wearing absorbent pads can help hide any leakage.
Other lifestyle tips for preventing incontinence include:
Overactive Bladder In The Vulnerable Elderly

Accepted for publication 26 June 2014
3 October 2014Volume 2014:6 Pages 131138
Introduction
Urinary symptoms such as urgency/frequency and incontinence become increasingly prevalent with aging.1,2 A large multinational population-based survey estimated the prevalence of overactive bladder in Europe and Canada to be 12.8% in women and 10.8% in men.2 The NOBLE study showed similar trends in the USA, with OAB being twice as prevalent in individuals over 65 years of age than in those aged 45 years or younger.3 Urinary symptoms have a considerable negative impact on quality of life and health in the elderly,4,5 and have been shown to be associated with increased risk of falls and fractures.6,7 Costs associated with urinary symptoms in the aged are significant.8,9 With the aging of the population, it is estimated that by 2025 there will be 52 million adults in the USA with lower urinary tract symptoms.10 Thus, the burden of these symptoms on society is increasing.
Overactive bladder
Vulnerable or frail elderly
Evaluating OAB in the vulnerable elderly
|
Figure 1 Conceptual relationship of clinical factors.Notes: Symptoms, measurable function, and morbidity related pathophysiology, their evaluation and any treatments are related concerns which must be identified, clarified, and prioritized. While this sometimes-subtle distinction is always important, it assumes greater importance in the vulnerable elderly. |
Who is the patient?
What are feasible treatment options?
Antimuscarinics
Recommended Reading: Go Less Bladder Control Side Effects
Can Overactive Bladder Be Controlled
Overactive bladder therapy can be challenging to manage. However, many people are very satisfied with the treatment they receive and they often see a dramatic improvement in their quality of life. Your doctor will guide you to the best steps to begin with and give you options for any additional treatments you may need over time.
Types Of Urinary Incontinence
There are different types of incontinence:
- Stress incontinence occurs when urine leaks as pressure is put on the bladder, for example, during exercise, coughing, sneezing, laughing, or lifting heavy objects. Its the most common type of bladder control problem in younger and middle-age women. It may begin around the time of menopause.
- Urge incontinence happens when people have a sudden need to urinate and cannot hold their urine long enough to get to the toilet. It may be a problem for people who have diabetes, Alzheimers disease, Parkinsons disease, multiple sclerosis, or stroke.
- Overflow incontinence happens when small amounts of urine leak from a bladder that is always full. A man can have trouble emptying his bladder if an enlarged prostate is blocking the urethra. Diabetes and spinal cord injuries can also cause this type of incontinence.
- Functional incontinence occurs in many older people who have normal bladder control. They just have a problem getting to the toilet because of arthritis or other disorders that make it hard to move quickly.
You May Like: Not Being Able To Hold Bladder
Urinary Incontinence In Older Adults
Urinary incontinence means a person leaks urine by accident. While it may happen to anyone, urinary incontinence is more common in older people, especially women. Incontinence can often be cured or controlled. Talk to your healthcare provider about what you can do.
What happens in the body to cause bladder control problems? The body stores urine in the bladder. During urination, muscles in the bladder tighten to move urine into a tube called the urethra. At the same time, the muscles around the urethra relax and let the urine pass out of the body. When the muscles in and around the bladder dont work the way they should, urine can leak. Incontinence typically occurs if the muscles relax without warning.
Alternative Treatments For Nocturia
Many people turn to complementary and alternative medicine before seeking medical help. You may also be interested in alternative medications or treatments for nocturia, but there are few studies to support their use. These treatments may work for nocturia, but only if OAB is the cause.
For example, research has found that:
- herbal medications have a positive impact on symptoms of OAB and quality of life
- acupuncture provides short-term relief for OAB symptoms
- homeopathic remedies may have benefits, but need more studies
- alternative treatments have fewer side effects than medications
- saw palmetto berry extract has no benefit for nocturia
But more research is needed to confirm if CAM works for OAB.
Always talk to your doctor before trying a supplement or alternative treatment. Certain CAM treatments can cause unintended side effects, especially if youre already taking medication.
Read Also: Frequent Bladder Infections In Females
What Are The Specific Symptoms Of Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder represents a collection of symptoms that can include:
- Urinary urgency: This is a failure to be able to postpone the need to urinate. When you feel you need to urinate, you have a limited amount of time to get to a bathroom.
- Frequency of urination: People who experience this symptom need to urinate very often. Typically its an increase in the number of times you urinate compared to what you previously experienced.
- Urge incontinence: In this case, there can be a leakage of urine when you get the urge to urinate.
- Nocturia: This symptom is characterized by the need to get up and urinate at least two times each night.
Medical Treatments For Nocturia
Your doctor may prescribe medications when preventive measures and lifestyle changes fail to reduce the frequency of your nighttime urination. Doctors prescribe a class of drugs called anticholinergics to treat symptoms of OAB, if thats the cause of your nocturia. They reduce bladder spasms that create the urge to go.
Your doctor may suggest you take a diuretic for regular urine production. A diuretic can itself cause nocturia. But if you take it early enough in the day, it may help you get rid of excess fluid while youre awake. This should decrease your urine production at night.
Other drugs that may help are:
- desmopression in cases of diabetes insipidus to cause the kidneys to produce less urine
- tamsulosin , finasteride , or dutasteride to treat prostate enlargement
- antibiotics if you have a urinary tract infection
Your doctor may also adjust your diabetic medications to lower your blood sugar if theyre causing nocturia.
Read Also: What Antibiotic Do You Take For A Bladder Infection
Survey Methods And Participants
The study was conducted from April 2012 to July 2014 in compliance with Good Post-Marketing Study Practice . The primary findings of the study together with the methodology have been published elsewhere. Briefly, patients who were prescribed mirabegron for OAB with symptoms of urgency, urinary frequency and urge incontinence, and who had not been previously treated with mirabegron, were eligible for inclusion in the study. Data were collected via the internet-based post-marketing survey data collection system. Physicians registered each patient within 14days of the start of mirabegron treatment and entered data for all registered patients at the end of the 12-week observation period or at discontinuation.
Behavioral Modification For The Treatment Of Overactive Bladder
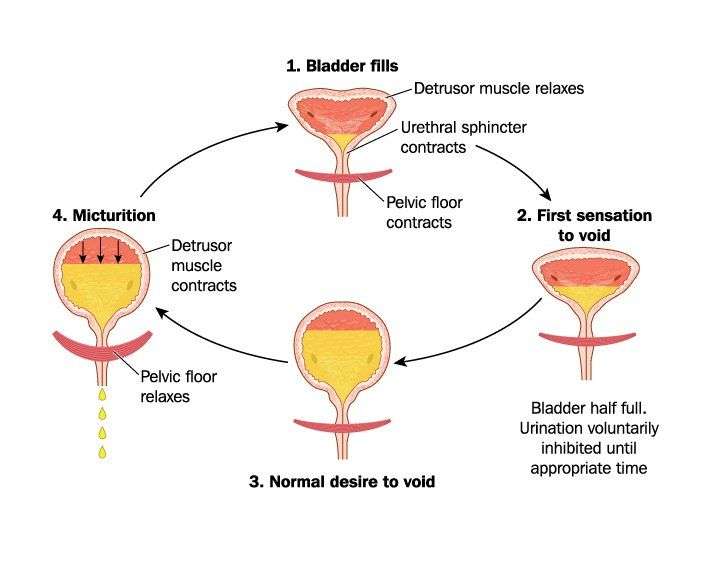
Various types of behavioral modifications may also be recommended for the treatment of overactive bladder. Examples include:
- Dietary Changes: Decreasing water consumption throughout the day can help reduce leakage, as can avoiding substances that irritate the bladder, such as caffeine, fruit juices, and spicy foods.
- Bladder Retraining: This method uses a set schedule for urination throughout the day. Between these times, no urination is allowed, even if leaks occur. The goal is to increase the time between bathroom visits to three to four hours.
- Electrical Stimulation and Biofeedback: This technique provides information about when a patient is squeezing the muscles of her pelvic floor. A sensor is placed in the vagina or anus so that pelvic floor muscle contractions can be recorded. Exercises can help strengthen weak pelvic floor muscles, and if they don’t respond, electrical stimulation can activate the appropriate muscles.
Also Check: What Is A Sling For The Bladder
Seven Effective Treatments For Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder occurs when sudden or frequent urges to urinate become hard to control, and can often lead to leakage .
In order to best treat overactive bladder, a urologist must pinpoint the underlying cause. Treatment will depend on symptom severity and the degree to which they impact someone’s quality of life. In general, there are three approaches to treatment: medication, behavioral interventions, and surgery.
Surgical Treatment For Overactive Bladder
Surgery may recommended for severe cases. The two most-commonly used procedures are:
- increases bladder size by removing a section of the bowel and adding it to the bladder. Increased bladder size allows someone to store more urine, reducing the urge to urinate. Possible complications include infection, blood clots, bowel obstruction, urinary fistula, and an increased risk of bladder tumors .
- Sacral Nerve Stimulation is a newer surgical technique that involves placing a small electrical device in the lower back. The device sends electrical impulses to the sacral nerve, which improves control of the muscles in the bladder and pelvic floor.
Also Check: How To Insert Catheter In Bladder
Medication For Incontinence In The Elderly
Anticholinergics. These medications can calm an overactive bladder and may be helpful for urge incontinence. Examples include oxybutynin , tolterodine , darifenacin , fesoterodine , solifenacin and trospium chloride. Mirabegron .Mar 9, 2021
Urinary incontinence medications for elderly
- TREATMENT OF URGE INCONTINENCE. The anticholinergic agents oxybutynin and tolterodine are used widely to treat urge incontinence. These medications are not, however, the most effective therapies. Behavior therapies are more effective, and theynot medicationsshould be first-line treatment.
Medication for incontinence in the elderly Medications are frequently used in combination with behavioral therapies. Here are some commonly prescribed options: Anticholinergic or antispasmodic drugs
Why Am I Leaking Urine All Of A Sudden
Incontinence can happen when the bladder muscles suddenly tighten and the sphincter muscles are not strong enough to pinch the urethra shut. This causes a sudden , strong urge to urinate that you may not be able to control. Pressure caused by laughing, sneezing, or exercising can cause you to leak urine .
Don’t Miss: I Feel A Lot Of Pressure On My Bladder
Treatment Options For Overactive Bladder
There are a number of treatment options available, but some are better for seniors than others. More times than not, a combination of different methods is the best treatment option. A lot depends on your physical and cognitive ability, so take that into consideration when determining the best choice for you. Speaking with your doctor, getting educated, and together working to find the best method can help with your OAB.
Behavior Intervention – Behavior intervention methods are typically the first choice for treating OAB because they have no side effects. Some of these options will not work for those that cannot control their muscles or cant maintain a mental state.
Kegel Exercises – Kegel exercises are used to strengthen your pelvic floor muscles and urinary sphincter. It is best to have someone teach you how to do them correctly, and with continued use throughout the day and for a few weeks, your symptoms should begin to reside.
Scheduled Toilet Trips – Scheduling trips to the bathroom during specific times of the day should help to reduce the sudden urge to urinate. Go at the same time every day even if you dont have to go.
Weight Loss – Losing weight can reduce the stress put on your bladder, therefore reducing your symptoms.
Double Voiding – Double voiding is a method used to hopefully completely void your bladder. This is done by using the bathroom, and then waiting a few minutes and trying again.
What Behavioral Changes Can I Make To Help With Overactive Bladder
There are many techniques and changes to your typical behavior that you can try to help with an overactive bladder. These can include:
Keeping a log: During a typical day, write down your fluid intake, the number of times you urinate, the number of accidents and when they occur. Make a note about what happened when the accident happened, like when you:
- Cough.
- Laugh.
- Were unable to reach the bathroom in time.
Monitoring your diet: Eliminate or decrease foods or beverages that may worsen your bladder symptoms. These could include:
- Tea.
- Spicy and acidic foods and drinks.
- Foods and drinks that contain artificial sweeteners.
Maintaining bowel regularity: Constipation can place added pressure on the bladder and have a negative effect on your bladder function. By keeping healthy bowel habits, you may be able to avoid constipation and help to lessen bladder symptoms. The following are some suggestions for maintaining bowel regularity:
- Increase your fiber intake by eating foods like beans, pasta, oatmeal, bran cereal, whole wheat bread, and fresh fruit and vegetables.
- Every morning, take 2 tablespoons of this mixture: 1 cup apple sauce, 1 cup unprocessed wheat bran, and ¾ cup prune juice.
- Exercise regularly to maintain regular bowel movements.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Being overweight can add pressure on your bladder, which may contribute to bladder control problems. If you are overweight, weight loss can reduce the pressure on your bladder.
You May Like: How Many Radiation Treatments For Bladder Cancer
Treatment Of Elderly Patients With Overactive Bladder: Has Mirabegron Come Of Age
- Tom MarcelissenCorrespondenceCorresponding author. Maastricht University Medical Center, Memorielaan 10, Maastricht 6226DB, The Netherlands. Tel. +31 62 4589283, Fax: +31 43 7865469.
- Chapple C.
- et al.
Eur Urol.
- Schermer C.
- et al.
BMJ Open.
- Nazir J.
- Freeman R.
Int J Urol.
- Kristy S.
- Schermer C.
Eur Urol.