What Is A Ct Urogram With Contrast
CT urogramCTcontrastCT
What is involved in a ct urogram?
During a CT urogram, an X-ray dye is injected into a vein in your hand or arm. X-ray pictures are taken at specific times during the exam, so your doctor can clearly see your urinary tract and assess how well its working or look for any abnormalities.
Contents
What Will I Experience During And After The Procedure
CT exams are generally painless, fast, and easy. Multidetector CT reduces the amount of time that the patient needs to lie still.
Though the scan is painless, you may have some discomfort from remaining still for several minutes or from placement of an IV. If you have a hard time staying still, are very nervous, anxious, or in pain, you may find a CT exam stressful. The technologist or nurse, under the direction of a doctor, may offer you some medication to help you tolerate the CT exam.
If the exam uses iodinated contrast material, your doctor will screen you for chronic or acute kidney disease. The doctor may administer contrast material intravenously , so you will feel a pin prick when the nurse inserts the needle into your vein. You may feel warm or flushed as the contrast is injected. You also may have a metallic taste in your mouth. This will pass. You may feel a need to urinate. However, these are only side effects of the contrast injection, and they subside quickly.
If you swallow oral contrast material, you may find the taste mildly unpleasant. However, most patients can easily tolerate it. If you receive an enema, you can expect to experience a sense of abdominal fullness. You may also feel an increasing need to expel the liquid. If so, be patient the mild discomfort will not last long.
Many patients also receive an iodine-based contrast material intravenously to help evaluate blood vessels and organs such as the liver, kidneys, and pancreas.
What To Expect When Having A Ct Scan
A CT scan is a painless procedure that is typically performed on an outpatient basis, taking about 1030 minutes to complete.
The patient may be told not to eat or drink before the test, and a laxative or enema may be used to clear the bowels so the images are clearer. Some CT scans may be performed using special contrast dyes, which may be swallowed as a liquid, delivered intravenously, or administered with an enema. These contrast agents can help improve the quality of the CT image.
For the test, the individual lies on a flat table that slides through the middle of the scanner. Buzzing and clicking noises may be heard within the scanner. During the test, the patient may have to stay still for several minutes or to briefly hold his/her breath.
You May Like: Muscularis Propria Invasion Bladder Cancer
Nephrogenic Phase And Excretory Phase Images
A contrast medium was injected through an upper extremity vein at a flow rate of 2.0 mL/s. Scanning was performed 100 s and 15 min after injection of contrast material is started as a nephrogenic phase and excretory phase, respectively. To clearly depict BC by expanding the bladder at the excretory phase, patients were given 500 mL of fresh water before CT examination. The scan range of DE-CT included from the upper margin of the liver to the lower margin of the ischium. The excretory phases were scanned from the upper renal margin to the lower urethral margin.
What Is A Urologic Test For Cancer
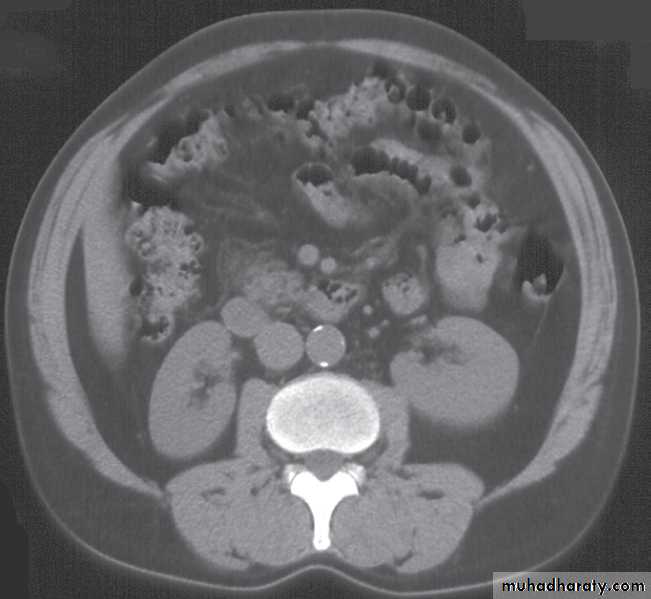
This test is good at finding tumors of the kidney, renal pelvis, and ureter, as well as other urologic abnormalities. It may identify kidney stones and hydronephrosis . In addition, the entire abdomen and pelvis is also imaged. This allows a radiologist to identify other abnormalities in these parts of the body. In patients with cancer, it will help identify signs of spread to lymph nodes or other organs like the liver.
Also Check: How Do You Get Rid Of Overactive Bladder
Can A Ct Scan Show Bladder Inflammation
Both MRI and CT provide high image quality, allowing easy diagnosis of urinary tract infections. CT is usually readily available than MRI , however both modalities allow comprehensive evaluation of the renal parenchyma, surrounding structures and spaces, and better evaluation of the urothelial wall .
What Is The Best Test For Cancer
MR Urogram. Another option for imaging is MRI of the abdomen and pelvis or MR Urogram. This test is also effective at finding tumors in the kidney and ureters and evidence of spread of cancer. It may be used to avoid radiation or in patients with contrast dye allergies or borderline kidney function.
Recommended Reading: Best Supplement For Overactive Bladder
What Could Come Next
If you do have bladder cancer, at this stage, the medical team will not yet have all the information they need to be able to decide which treatment is best for you.
In order to do this, they may take a sample of cells from your bladder known as a biopsy to examine in the pathology laboratory. This sample will be taken during a second cystoscopy, usually a rigid cystoscopy.
Full details are in our What is a TURBT booklet .
After all the various tests have been completed, you will be offered another appointment with your urologist, at which they will explain their findings and what they propose to do in terms of treatment.
How Long Does It Take For A Cystoscopy To Go Away
Patients will go home after the cystoscopy if it is done in the doctors office. There may be some bleeding and irritating bladder symptoms following the cystoscopy for a day or two. If the symptoms do not improve within 3-5 days, notify your urologist. Seeing blood in the urine can be very troubling, even small amounts of blood can change the color of the urine dramatically. This should resolve on its own. Make sure to stay hydrated to help keep your urine diluted.
Recommended Reading: Pro Source Steel Pressure Tank Replacement Bladder
Is Bladder Cancer A Complex Disease
Conclusion: Bladder cancer is a complex disease, and its management is evolving. Advances in therapy, understanding of the disease, and advanced imaging have ushered in a period of rapid change in the care of bladder cancer patients. Keywords: bladder cancer, urothelial carcinoma, imaging, management, CT, MRI, urography.
What Is Nci Doing To Improve Ct Imaging
Researchers funded by NCI are studying ways to improve the use of CT in cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment. NCI also conducts and sponsors clinical trials that are testing ways to improve CT or new uses of CT imaging technology. Some of these clinical trials are run by the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group, one of five groups in NCIs National Clinical Trials Network. The American College of Radiology Imaging Network, which is now part of ECOG-ACRIN, performed the National CT Colonography Trial, which tested the use of CT for colorectal cancer screening, and participated in the NLST, which tested the use of CT for lung cancer screening in high-risk individuals
NCIs Cancer Imaging Program , part of the Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis , funds cancer-related basic, translational, and clinical research in imaging sciences and technology. CIP supports the development of novel imaging agents for CT and other types of imaging procedures to help doctors better locate cancer cells in the body. In addition, CIP maintains the Cancer Imaging Archive, which is a library of medical images of cancer, including low-dose CT images, that are accessible for public download. This library has been used extensively by outside researchers in developing computer-aided diagnosis to help radiologists interpret CT images, for example, in lung cancer screening.
Also Check: Stage 3 Bladder Cancer Symptoms
Coronavirus : Insight And Considerations For The Hospital Environment
Diatrizoic Acid
- Diatrizoic acid is used in place of barium when a patient is allergic to barium or when there is a chance the intestines or stomach have been perforated. It is not as thick as barium sulfate, but it has an unpleasant taste that may be slightly masked with flavoring.
- Gastrografin will be given a few hours before the exam or, if delivered rectally, right before the exam.
How Bladder Cancer Is Diagnosed
There are many tests used for diagnosing bladder cancer. Not all tests described here will be used for every person. Your doctor may consider these factors when choosing a diagnostic test:
-
The type of cancer suspected
-
Your signs and symptoms
-
Your age and general health
-
The results of earlier medical tests
The earlier bladder cancer is found, the better the chance for successful treatment and cure. However, there is not yet a test accurate enough to screen the general population for bladder cancer, so most people are diagnosed with bladder cancer once they have symptoms. As a result, some people have more advanced disease when the cancer is found. Still, most people are usually diagnosed with noninvasive bladder cancer .
The following tests may be used to diagnose and learn more about bladder cancer:
The following imaging tests may be used to find out if the bladder cancer has spread and to help with staging. Imaging tests show pictures of the inside of the body.
After diagnostic tests are done, your doctor will review the results with you. If the diagnosis is cancer, these results also help the doctor describe the cancer. This is called staging and grading.
The next section in this guide is Stages and Grades. It explains the systems doctors use to describe the extent of the disease and the way cancer cells look under a microscope. Use the menu to choose a different section to read in this guide.
You May Like: Can Bladder Infection Clear Up On Its Own
What Are The Risks Of Ct Scans For Children
Radiation exposure from CT scans affects adults and children differently. Children are considerably more sensitive to radiation than adults because of their growing bodies and the rapid pace at which the cells in their bodies divide. In addition, children have a longer life expectancy than adults, providing a larger window of opportunity for radiation-related cancers to develop .
Individuals who have had multiple CT scans before the age of 15 were found to have an increased risk of developing leukemia, brain tumors , and other cancers in the decade following their first scan. However, the lifetime risk of cancer from a single CT scan was smallabout one case of cancer for every 10,000 scans performed on children.
In talking with health care providers, three key questions that the parents can ask are: why is the test needed? Will the results change the treatment decisions? Is there an alternative test that doesnt involve radiation? If the test is clinically justified, then the parents can be reassured that the benefits will outweigh the small long-term risks.
How Long Does A Ct Scan Take
A CT scan can take anywhere from 10 to 30 minutes, depending on what part of the body is being scanned. It also depends on how much of your body the doctors want to look at and whether contrast dye is used. It often takes more time to get you into position and give the contrast dye than to take the pictures. After the test, you may be asked to wait while the pictures are checked to make sure they are clear and show all of the body part. If not, more pictures may be needed.
You May Like: Intravesical Treatments Of Bladder Cancer Review
Bladder Cancer Screening And Diagnosis
If doctors suspect that a patient has bladder cancer because of the presence of blood in the urine or an urgency to urinate, burning with urination, or unexplained increased frequency of urination, they may use several methods to confirm the diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease. Doctors at Columbia University Department of Urology at NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital use the latest laboratory testing and diagnostic technologies including:
Can A Urine Culture Show Cancer
If youre having urinary symptoms, this test may be done to see if an infection is the cause. Urinary tract infections and bladder cancers can cause the same symptoms. For a urine culture, a sample of urine is put into a dish in the lab to allow any bacteria that are present to grow. It can take time for the bacteria to grow, so it may take a few days to get the results of this test.
You May Like: Can A Hernia Affect Your Bladder
What Is The Best Scan To Detect Bladder Cancer
Cystoscopy. Cystoscopy is the key diagnostic procedure for bladder cancer. It allows the doctor to see inside the body with a thin, lighted, flexible tube called a cystoscope. Flexible cystoscopy is performed in a doctors office and does not require anesthesia, which is medication that blocks the awareness of pain.
Is Cystoscopy More Sensitive Than Urography
Although there is little doubt that cystoscopy is the most sensitive, specific, and reproducible method for identification of bladder malignancies, the diagnostic performance of CT is better than is commonly thought: In a study by Turney et al. , 200 patients with hematuria underwent both cystoscopy and CT urography. Bladder malignancy was found in 24% of the patients, and the sensitivity and specificity of CT urography were 0.93 and 0.99 . Similarly, Sadow et al. conducted a study that included 838 patients who had undergone CT urography and cystoscopy within 6 months of each another and found that CT urography had a sensitivity and specificity of 79% and 94% . In another study, Kim et al. found CT urography effective in the diagnosis of recurrent tumors in patients who had previously undergone transurethral resection of a bladder tumor. It is undoubtedly true that the diagnostic performance of CT will vary dramatically depending on the technique used and degree of bladder distention, thus explaining the variable diagnostic performance from one study to another. A dedicated CT urography technique with multiphase protocol will clearly be more sensitive for a subtle tumor than a routine screening examination performed in the emergency department for suspected abdominal pain. Nevertheless, the results of these studies suggest that if technique is optimized, subtle malignancies can be identified reasonably accurately at imaging.
You May Like: Why Does My Bladder Leak When I Sleep
Why Won’t The Ct Tech Give Me The Results Of My Scan
Many patients get frustrated with x-ray, CT, and other technicians because the techs will not tell the patients what the images reveal. There is a reason for this. Technicians are not trained to diagnose medical diseases or conditions they are trained to use imaging equipment properly to obtain diagnostic-quality images.
While technicians are in fact able to identify many diseases and conditions, they are forbidden to discuss what they see with the patient. Only a doctor with many years of training should look at the images to make a diagnosis.
The images will be read by a radiologist, who will make a diagnosis. Your doctor will be notified, usually within 48 hours, and you will be contacted with the results. If the radiologist sees a condition that could be life-threatening, the reporting process will be much faster.
Transurethral Resection Of A Bladder Tumour

If abnormalities are found in your bladder during a cystoscopy, you should be offered an operation known as TURBT. This is so any abnormal areas of tissue can be removed and tested for cancer .
TURBT is carried out under general anaesthesia.
Sometimes, a sample of the muscle wall of your bladder is also taken to check whether the cancer has spread. This may be a separate operation within 6 weeks of the first biopsy.
You should also be offered a dose of chemotherapy after the operation. This may help to prevent the bladder cancer returning, if the removed cells are found to be cancerous.
See treating bladder cancer for more information about the TURBT procedure.
Recommended Reading: Do Bladder Infections Go Away
Why You Might Have A Ct Scan
You might have a CT scan:
- to diagnose a range of conditions including cancer
- to help work out where the cancer is, how close it is to nearby organs and how big it is this can help your doctors decide about whether you need further tests or what treatment you need
- to check how well treatment is working
- as part of your follow up after treatment
Screening For Bladder Cancer
Early-stage bladder cancer often shows no symptoms, or symptoms that are similar to those of benign conditions such as bladder stones, an enlarged prostate, or urinary tract infection. For this reason it is important to be examined regularly by a physician. If symptoms do appear they should be evaluated promptly so that bladder cancer can be detected in its earliest, most treatable stages.
Doctors may conduct some screening tests during an examination. During a urine cytology the doctor examines urine under a microscope to look for any cancerous or precancerous cells. During another test called a cystoscopy urologists place a cystocope, a flexible instrument consisting of a steerable slender tube with a camera or lens and a light, into the bladder through the urethra. They check the bladder and urethra for signs of cancer, remove any suspicious tissue, and check it under a microscope.
Also Check: Why Is Cell Type And Staging Of Bladder Cancer Important
What Is A Ct Scan Of The Abdomen Or Pelvis
The abdomen and pelvis contain the digestive organs as well as the urinary, endocrine, and reproductive systems.
A CT scan of this area may be done to look for abscesses, tumors, kidney stones, infections, or to try and uncover the cause of unexplained abdominal pain.
Abdominal scans can be used to help a doctor pinpoint the location of a tumor before a biopsy is performed.
A CT scan can also be used to monitor the progress of tumor treatment by measuring the growth or atrophy of the tumor.
Notice: This article is meant to give you a broad overview of what you might expect if you undergo a CT scan, with a definition and description of terms and procedures. Although I have an AD in radiography and a diploma in CT and MRI, which includes hands-on practical application in CT, I cannot give medical advice! If you have more questions about your procedure, please speak to your doctor or the technologists who will be performing the scan. I hope this is helpful!
Abdominal CT scan of an adult with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Extensive cyst formation is seen over both kidneys, with a few cysts in the liver as well.