Loss Of Bladder And Bowel Control
Bowel incontinence means you lose control over passing stool, whereas urinary incontinence refers to a condition that involves unwanted passage of urine. When you have bowel or bladder dysfunction, you are likely to experience other problems as well with voluntary urination and bowel movements. Not only can these problems cause pain and discomfort, they can be a source of embarrassment as well. While you may not feel comfortable with the idea of seeking medical help, you should not waste time and talk to your healthcare provider to find a treatment option to deal with loss of bladder or bowel control.
Neural Control Of The Lower Urinary Tract
The lower urinary tract is innervated by 3 sets of peripheral nerves involving the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous systems:
- Pelvic parasympathetic nerves: arise at the sacral level of the spinal cord, excite the bladder, and relax the urethra
- Lumbar sympathetic nerves: inhibit the bladder body and excite the bladder base and urethra
- Pudendal nerves: excite the external urethral sphincter
These nerves contain afferent as well as efferent motor axons.5
Basic Structure Of The Urinary System And Terminal Bowel
The bladder and bowel consist of smooth muscle with an inner lining of specialised and functionally important epithelial cells, with additional cell types that include nervous and vascular supplies, connective tissue cells, interstitial cells and immune system cells but the properties and arrangement of the cells in these organ systems is very different. Here the main focus of this review is on the neuronal control of the bladder, bowel and lower urinary tract structures and a detailed discussion of other cell types is not included.
Read Also: Treatment After Bladder Tumor Removal
Loss Of Bowel Control
Bowel incontinence the inability to control bowel movements can occur when you are unaware that your rectum is full. If you cant feel the sensation that you need to empty the bowel, you may pass stool without knowing it.
Sometimes a bulge in an intervertebral disc in the lower back irritates a nerve. When this happens, bladder and/or bowel dysfunction can occur along with pain depending on which nerve a herniated disc irritates.
Why Might A Person With Cauda Equina Syndrome Become Incontinent
The cauda equina nerves supply muscle sensation to the bladder, bowel and legs. When these nerves become suppressed from Cauda Equina Syndrome then muscle sensation becomes lost which can result in loss of bladder and/ or bowel control.
Common incontinence conditions include
- Urinary retention
- Loss of bladder and bowel sensation
Most cases of Cauda Equina Syndrome require emergency surgery to decompress the nerves and prevent permanent damage and loss of sensation to the bladder and bowel.
If you are experiencing symptoms of Cauda Equina Syndrome it is important to seek help straight away in order to receive treatment as soon as possible. It has been proven that if surgery takes places within 48 hours of symptoms that for many sensation and bladder and bowel control can be restored.
Further information and downloads can be found in the help & information section. Living with a bladder or bowel condition or caring for someone with a bladder and bowel condition can affect you emotionally and socially sometimes it can help to speak to others who understand your situation.
There are many ways you can find help on this site, including our which is a moderated space for peer support and discussion.
You May Like: Treatment For Overactive Bladder In Males
Bladder And Bowel Control
Home » Bladder and Bowel Control
Because the nerves controlling the bladder attach to the very base of the spinal cord, bladder function is almost always affected by spinal cord injury, regardless of the level at which the injury occurred. When messages can no longer be passed from the bladder muscles to the brain, the bladder is affected in one of two ways:
- Spastic bladder. This is when the bladder fills with urine, and a reflex causes it to suddenly empty. Spastic bladder usually occurs with the injury is above the T-12 level.
- Flaccid bladder. The bladder muscles dont work or become sluggish. Instead of emptying, urine backs up into the kidneys. Treatments include surgery and medications. Flaccid bladder usually occurs with injuries below the T-12 level.
Bladder And Bowel Incontinence
Incontinence is a loss of control of a person’s bowels or bladder which can cause accidental leakage of body fluids and waste. Incontinence can be more than a physical problem. It can disrupt your quality of life if its not managed well.
Fear, anxiety, and anger are common feelings for people dealing with incontinence. You may avoid being intimate or having sex because you are afraid of urine, gas, or stool leakage. Fear of having an accident may keep you from being physically active, enjoying hobbies, or spending extended time outside your home.
Anyone can have incontinence during and after surgery or some other treatments for cancer. Incontinence can also occur because of other non-cancer medical conditions. Be sure to talk to your health care team if you have difficulty controlling urination or bowels. Talking about incontinence can be embarrassing, but being open and honest with your health care team can help manage it.
Read Also: First Signs Of Bladder Infection
How Common Is Neurogenic Bladder
Neurogenic bladder dysfunction is very common among people with spinal cord injuries, affecting more than 90% of them. About 95% of people with spina bifida have neurogenic bladder dysfunction. The condition also affects 50% to 80% of people who have multiple sclerosis. Neurogenic bladder affects people with stroke and Parkinsons disease and many other types of nervous system conditions. Conditions that damage nerves like advanced diabetes can also cause neurogenic bladder.
Consequences Of Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction
People with Neurogenic Bowel Dysfunction commonly have the following consequences in life.
- Loss of Independence
- Social Isolation
Proper examination of the body and organs also gives a brief idea for diagnosis. The bowel sounds should be auscultated and the abdomen should be properly palpated and check for distention.
Rectal examination should also be performed as it gives the idea about sphincter innervation and the amount and consistency of stool present in the rectal vault, the presence of hemorrhoids or masses, and in males the size of the prostate gland. Rectal examination should also determine the rectal angle and tone or spasticity of the puborectalis muscle. When the examining finger is inserted, it should be directed towards the umbilicus to check the rectal angle, and to check for puborectalis tone, gentle pressure is applied towards the sacrum. The strength and endurance of the voluntary muscles should also be assessed. These findings will also help to differentiate whether the injury is UMN or LMN type.
Colostomy
Don’t Miss: Used Bladder Scanner For Sale
Nerve Stimulation To Treat Urinary Incontinence
Topics in this Post
Many people have heard of pacemakers and how they can be used to treat heart conditions. But did you know a similar implantable device is available to treat urinary incontinence?
Urinary incontinence, or the loss of bladder control, is common. One of the most common types is urge incontinence, which is distinguished by a sudden, intense urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine. About 17% of women and 3% to 11% of men experience urge incontinence at some point in their lives.
Symptoms of incontinence can cause people to feel socially isolated, experience sexual inhibition, or become afraid to make social or travel plans. Careers and personal relationships are often affected.
Fortunately, many treatment options can help, including sacral neuromodulation.
What Complications Are Related To Neurogenic Bladder
People who have neurogenic bladder are at higher risk for other urological problems, including repeated infections, kidney damage, vesicoureteral reflux and stones that form in the urinary tract.
People with bladder control conditions such as neurogenic bladder may experience quality of life issues. Its important to recognize these issues and get help with them.
You May Like: What Is T1 High Grade Bladder Cancer
Innervation Of The Bladder And Urethral Sphincters
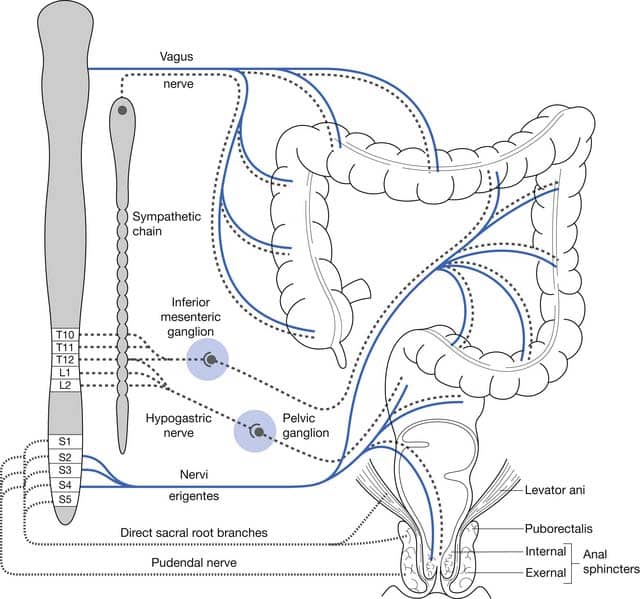
The bladder receives indirect innervation from parasympathetic autonomic neurons in the sacral parasympathetic nucleus of the spinal cord, which project via the pelvic nerve to the pelvic ganglia. Sympathetic innervation is also indirect and arises from neurons in the thoracolumbar spinal cord, which project via the hypogastric and pelvic nerves to the hypogastric ganglia/pelvic ganglia and ganglia of the lumbosacral sympathetic chain. Hence the body of the bladder is directly innervated by efferent fibres that arise from parasympathetic postganglionic neurons in the pelvic ganglia and intramural ganglia and by efferent fibres that arise from sympathetic postganglionic neurons in lumbosacral sympathetic chain and hypogastric ganglia/pelvic ganglia . The internal urethral sphincter receives innervation from the hypogastric and pelvic ganglia as described above for the bladder detrusor muscle. The external urethral sphincter is directly innervated by motor neurons in the sacral segments of the spinal cord .
Neuronal tracing and ultrastructural studies have shown that sensory nerve fibres originating in lumbosacral dorsal root ganglion , are present in the detrusor muscle, but there is also a significant innervation of the lamina propria lying next to the urothelium . These fibres express a number of different neurotransmitters including the neuropeptides substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide, CGRP .
Possible Mechanisms Underlying Recovery
Reorganization of the micturition reflex following spinal cord injury is dependent in part on the plasticity of bladder afferent pathways and the unmasking of reflexes triggered by unmyelinated, capsaicin-sensitive, C-fiber bladder afferent neurons. Plasticity of bladder afferent neurons is associated with morphologic, chemical, and electrical changes, which appears to be mediated in part by neurotrophic factors released at the level of spinal cord and the peripheral target organs . Upregulation of anti-inflammatory mediators and neuroprotective molecules is likely to play an important role in the plasticity of bladder afferent pathways as well as reorganization of synaptic connections in the spinal cord . In rats, poor voiding efficiency at 4 and 8 weeks after spinal cord injury was coincident with upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines , chemokines and downregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IL-13, whereas spontaneous recovery of voiding function at 12 weeks was associated with maximum expression of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1018, neurotrophin BDNF and CXCL-5 as well as the neuroprotective leptin19 in bladder .
Also Check: Small Cell Carcinoma Bladder Survival Rate
Pharmacological Interventions For Bladder Management
Pharmacological interventions will vary depending on the localization of the inciting injury and it is imperative to consider carefully the characteristics of the clinical signs when choosing medications. Table 2 present some possible medications for neurogenic bladder management.
Table 2. Possible drugs suggested to act on the lower urinary tract physiology during neurogenic dysfunction.
Terazosin, a long-acting selective -1 adrenoreceptor blocking molecule has been used to treat vesico-sphincter dyssynergia in spinal cord-injured male humans and reduced bladder outlet obstruction but causes side effects such as collapse and has not been reported in clinical papers since 2002. In dogs, terazosin has been used to treat vesico-urethral reflex dyssynergia but not in the context of spinal cord injury and showed side effects in 93% of the cases . Similarly, tamsulosin is also a -1 adrenoreceptor blocking molecule with higher affinity that terazosin but has not been trialed after spinal cord injury in dogs.
When faced with an atonic bladder , the clinician has few options and there is no clear pharmacological method to reduce constant urinary leakage, which is problematic. Bethanechol can be trialed to improve bladder contraction but there is no clinical evidence to back this and the efficacy is poor in the author’s experience.
Bladder And Bowel Management In Dogs With Spinal Cord Injury
- 1The Royal Veterinary College, University of London, Hertfordshire, United Kingdom
- 2CVS Referrals, Bristol Veterinary Specialists at Highcroft, Bristol, United Kingdom
- 3Department of Clinical Sciences, North Carolina State University College of Veterinary Medicine, Raleigh, NC, United States
- 4Department of Clinical Sciences, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, United States
Don’t Miss: Botox For Ms Bladder Problems
Urinary Incontinence And The Bladder
Spinal disorders or injuries that cause nerve compression or damage may cause Neurogenic Bladder Disorder also termed Bladder Dysfunction. NBD means the patient has problems with urination. The term neurogenic refers to the nerve tissues that supply and stimulate an organ or muscle to function properly. In the case of NBD, nerves that control the bladder and muscles involved in urination cause the bladder to be overactive or underactive.
NBD symptoms may include:
-
Limited or no voluntary control
-
Involuntary urination
-
Feel sudden urge to urinate
-
Frequent bathroom visits
-
Bladder does not completely empty
-
Bladder overfills and pressure causes accidental leakage of urine
-
Bladder is unable to hold urine
The brain and spinal cord are the central chains of command that transmit signals and messages to and from the bladder. Photo Source: 123RF.com.
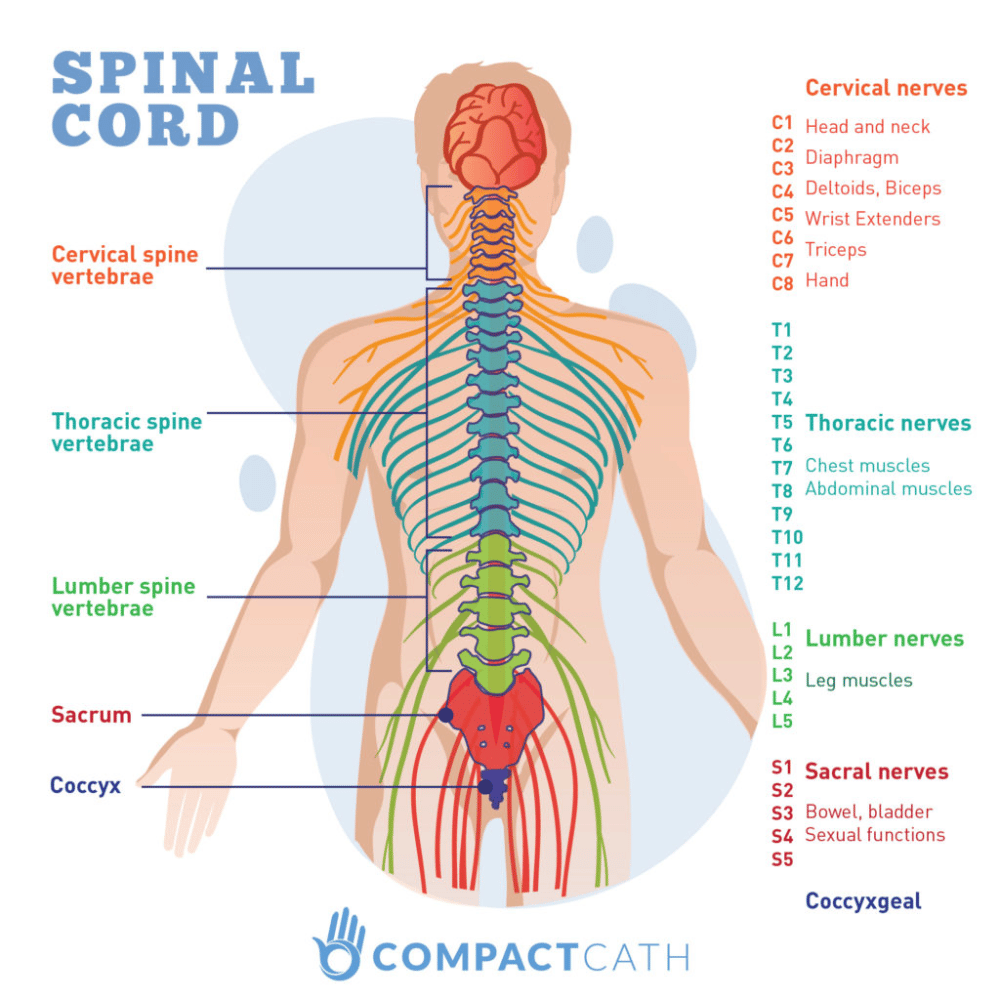
Which Nerves Control What
A complex series of nerves control your bowel.
- parasympathetic nerves from the S2, S3 and S4 levels of the spinal cord, called thepelvic splanchnic nerve
- sympathetic nerves from the T11-L2 levels of your spinal cord, which form a nerve called thehypogastric nerve .
- parasympathetic nerves from the S2, S3 and S4 levels of the spinal cord
- sympathetic nerves from the T11-L2 levels of the spinal cord .
- spinal nerves from the S2, S3 and S4 levels of your spinal cord, which form the pudendal nerve.
- skeletal muscle, which can be voluntarily controlled.
Become a member
- Get active on the forum
- Upload videos and images
Don’t Miss: Icd 10 Code For Urothelial Carcinoma Of Bladder
Mechanical Techniques To Manage Bladder Emptying
There are three proposed methods employed to empty the bladder in dogs following spinal cord injury: manual emptying intermittent aseptic catheterization and placement of a indwelling catheter.
Intermittent sterile catheterization is also simple, guarantees an almost complete bladder emptying. But it is more invasive, carries a risk of introducing an infection in the bladder, can potentially cause urethral inflammation and stricture if done frequently, and might also appear challenging to untrained staff in particular in female dogs. In female dogs, the clinicians’ preference might also often be to leave indwelling catheter in place rather than repeating sterile catheterization.
Placement of an indwelling catheter has similar advantages and disadvantages with the previous method but can lead to bladder mucosa minor trauma and bleeding , therefore blocking the catheter. It is usually used for a short time during hospitalization because it will be difficult for the owner to manage it at home. The use of a closed bag system and long-term placement of the catheter removes the need for repeated catheterization and is comfortable for the nursing team and the dog, also reducing the risk of urine scald especially for large dogs.
Changes To Extrinsic Nerve Fibres In The Gut
To our knowledge, detailed studies of changes in the extrinsic innervation of the most terminal bowel region during ageing have not yet been performed with work focusing mainly on the innervation of the stomach and small intestine, and to a lesser extent, on the colon. Here we briefly summarise the changes that have been reported in these areas, to highlight that this is likely to be an area of importance in the terminal bowel.
Analysis of changes in the density of extrinsic parasympathetic nerve fibres in the GI tract during ageing is difficult, because populations of intrinsic enteric neurons express the same markers as extrinsic parasympathetic nerves. A similar problem exists in many species for extrinsic afferent fibres. Studies of change to the extrinsic innervation have therefore involved anterograde tracing . Changes in the vagal innervation of the rat gut during have been studied in this way, but the vagus supplies only a minor part of the extrinsic innervation to the proximal parts of the large intestine, and no age-related changes were reported in this region or in the small intestine .
Recommended Reading: What Causes Your Bladder To Not Fully Empty
Early Symptoms Of Cauda Equina Syndrome: A Neurosurgeon Explains
Cauda equina syndrome is a potentially serious neurological disorder caused by pressure on the cauda equina, a collection of nerves at the base of the spine that govern sensation and function in the lower limbs, bladder and bowels. Cauda equina syndrome can have a rapid onset with sudden severe symptoms, but it can also develop slowly, with early symptoms that often mimic other conditions. Recognizing these early symptoms is essential for a prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment by experienced neurosurgeons in northern New Jersey.
Our Purpose Is To Transform Access To Education
We offer a diverse selection of courses from leading universities and cultural institutions from around the world. These are delivered one step at a time, and are accessible on mobile, tablet and desktop, so you can fit learning around your life.
We believe learning should be an enjoyable, social experience, so our courses offer the opportunity to discuss what youre learning with others as you go, helping you make fresh discoveries and form new ideas.You can unlock new opportunities with unlimited access to hundreds of online short courses for a year by subscribing to our Unlimited package. Build your knowledge with top universities and organisations.
Read Also: Pro Source Steel Pressure Tank Replacement Bladder
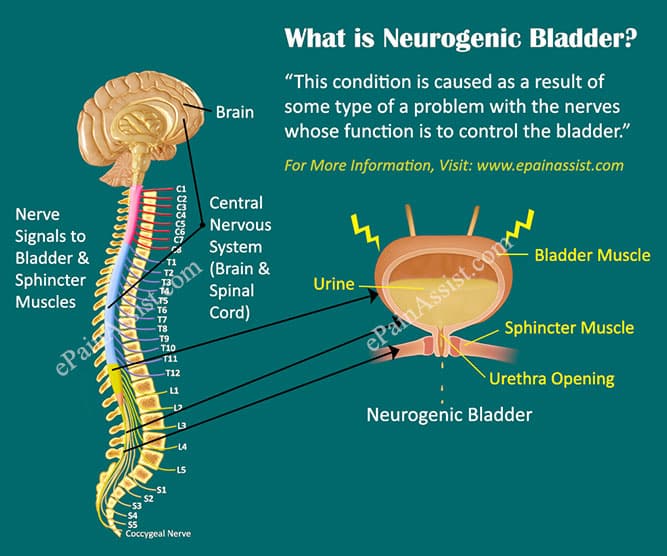
What Is Neurogenic Bladder
Neurogenic bladder is a spastic or flaccid dysfunction that affects part of the urinary system, which consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. This condition results from neurological damage caused by your spinal cord injury that prevents messages from being transmitted between the brain and bladder. The voiding function of the bladder, which is responsible for storing and excreting the liquid waste that is created by your kidneys, is controlled by the bodys nervous system.
An average bladder will need to empty four to eight times per day. However, for people with spinal cord injuries, bladder control is impeded because of the nerve damage. They may only be able to urine in little spurts or not at all.