Urinary Incontinence In Women: Causes And Treatment
Urinary incontinence is twice as common in women than in men, and it’s especially common in older women. Among women ages 65 and older, 4 in 10 experience some loss of bladder control.The three main types of urinary incontinence are:
- Stress urinary incontinence, when you experience leakage or loss of urine when you laugh, sneeze, run or make some other sudden movement
- Urge incontinence, when you have a frequent or sudden urge to urinate
- Mixed, in which women experience symptoms of both types
When either form of urinary incontinence affects your quality of life, seek a medical professional’s help. Beaufort Memorial has a team of women’s health specialists trained in the latest treatments for this medical condition.
Request an appointment with an OB-GYN or gynecologist.
What Are Some Of The Different Types Of Urinary Incontinence
The following are some of the different types of urinary incontinence:
-
Urgency incontinence: This is the inability to hold urine long enough to reach a restroom. It can be associated with having to urinate often and feeling a strong, sudden urge to urinate. It can be a separate condition, but it may also be an indication of other diseases or conditions that would also warrant medical attention.
-
Stress incontinence: This is the leakage of urine during exercise, coughing, sneezing, laughing, lifting heavy objects or performing other body movements that put pressure on the bladder.
-
Functional incontinence: This is urine leakage due to a difficulty reaching a restroom in time because of physical conditions, such as arthritis, injury or other disabilities.
-
Overflow incontinence. Leakage occurs when the quantity of urine produced exceeds the bladders capacity to hold it.
When To Seek Medical Help
Any instance of incontinence is reason to seek medical help. It may be a symptom of a more serious condition that needs to be treated.
Even if the underlying cause isnt serious, incontinence can be a major disruption in your life. Its important to get an accurate diagnosis and discuss treatment options with a healthcare professional.
In some cases, incontinence can be a sign of a medical emergency.
You should seek immediate medical attention if you lose control of your bladder and experience any of the following symptoms:
- trouble speaking or walking
Urinary incontinence and treatment for urinary incontinence may result in complications, depending on the cause.
These complications may include:
- Urinary tract infections. UTIs can be caused by wet undergarments against the skin. This may create an environment where bacteria can grow.
- Kidney damage. In some cases where the flow of urine is obstructed, you may experience kidney trouble or kidney failure.
- Cellulitis. This skin infection is caused by bacteria and may cause swelling and pain.
- Medication side effects. Medications used to control urinary incontinence may cause side effects, depending on the medication. Side effects may include dry mouth, nausea, hypertension, or others.
- Catheter side effects. If you have a catheter placed, you may experience side effects such as infection and trauma.
- Mental health side effects. Urinary incontinence may cause feelings of anxiety, depression, or social isolation.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Bladder Incontinence In Young Adults
What Happens To The Urinary System With Aging
The urinary system includes:
- the muscles of the pelvic floor.
There are sphincters that open or close the urethra, and nerves that run to the bladder muscles and sphincters which helps to control urinary release and flow. The brain and legs are also part of the urinary system: a person has to be able to decide when its time to go to the toilet, and have the ability to get to one when the time is right.
In this article, well focus mainly on the bladder and urethra, and the bladder outlet.
Normal Aging
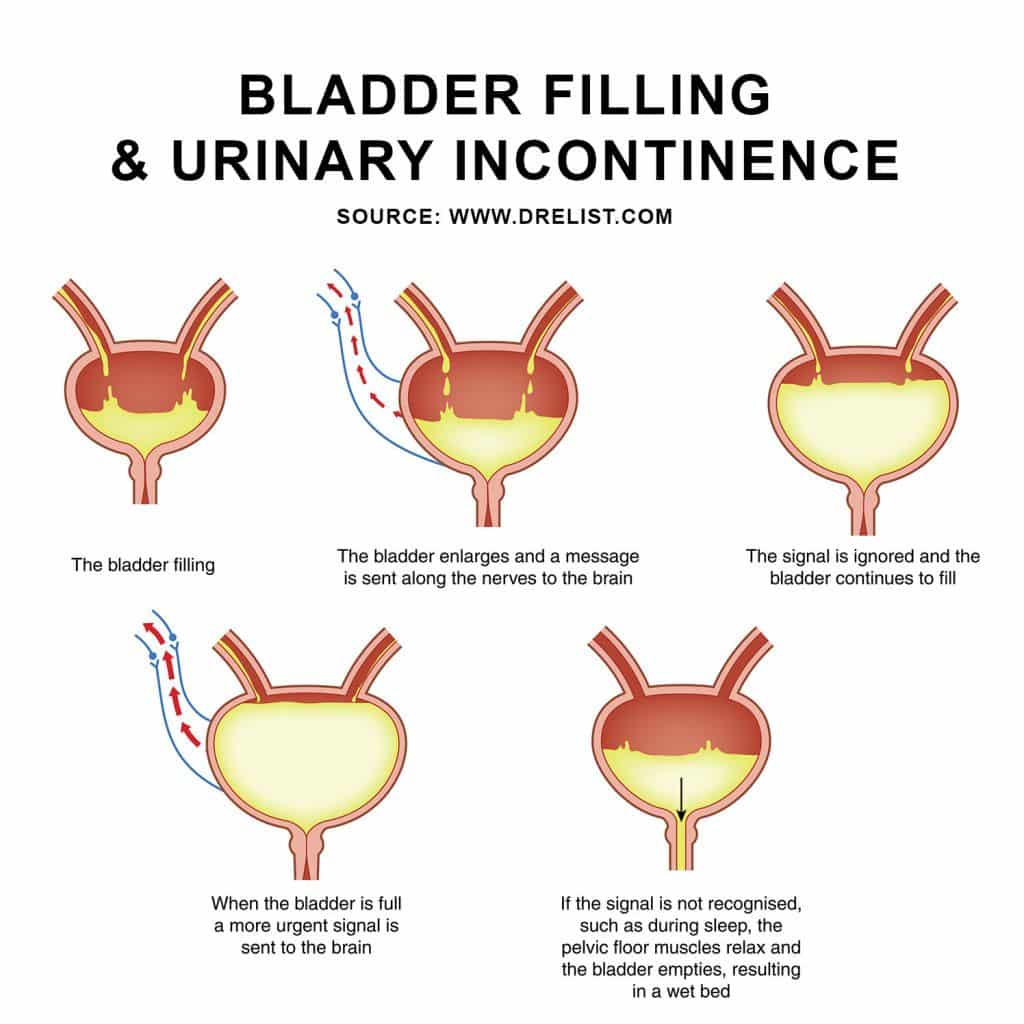
With age, some of the muscle fibers in the bladder are replaced with stiffer, fibrotic tissue, and the neurological responses that we rely on to maintain normal urinary function decline slightly.
In practical terms, this means that:
- The sensation that the bladder needs to be emptied happens when the bladder is fuller than in a younger person
- The bladder muscle contracts less forcefully
- The urethral sphincter is looser in older women
- The larger prostate gland can obstruct the urethra in men
- Theres a more frequent need to pass urine
- 80% of those over 80 get up at least once in the night to pass urine
Nighttime urination or nocturia is a urinary symptom thats hard to ignore, or cope with. As Dr. Wagg told me: The magic number for nighttime frequency where it has an effect on your quality of life is two and more. And intriguingly, daytime frequency. If you look at peoples self reported quality of life and daytime frequency, the unlucky number is indeed 13.
When To See A Health Care Provider And What To Expect

Talk to your health care provider if you have urinary incontinence or any signs of a bladder problem, such as:
- Needing to urinate more frequently or suddenly
- Urinating eight or more times in one day
- Passing only small amounts of urine after strong urges to urinate
- Trouble starting or having a weak stream while urinating
Your doctor may recommend urodynamic testing and perform the following to try to figure out what might be causing your bladder problem:
- Give you a physical exam and take your medical history.
- Ask about your symptoms and the medications you take.
- Take urine and blood samples.
- Examine the inside of your bladder using a cystoscope a long, thin tube that slides up into the bladder through the urethra. This is usually done by a urinary specialist.
- Fill the bladder with warm fluid and use a cystoscope to check how much fluid your bladder can hold before leaking.
- Order or perform a bladder ultrasound to see if you are fully emptying your bladder with each void.
- Ask you to keep a daily diary of when you urinate and when you leak urine. Your primary care doctor may also send you to a urologist, a doctor who specializes in urinary tract problems.
Also Check: Does Overactive Bladder Come And Go
When Should I See A Health Care Professional
See a health care professional if you have symptoms of a bladder problem, such as trouble urinating, a loss of bladder control, waking to use the bathroom, pelvic pain, or leaking urine.
Bladder problems can affect your quality of life and cause other health problems. Your health care professional may be able to treat your UI by recommending lifestyle changes or a change in medicine.
Help Fight The Frequent Urge To Urinate At Night
The good news is that there are ways to help fight occasional bladder control issues! Here are a few tips to help lower the risk of waking up in the middle of the night with occasional urinary urgency:
If these two tips help your occasional bladder issues but youre still having trouble sleeping, you could also help promote sleep by making sure your body is relaxed before bedtime. See below:
Dont Miss: Whats The Difference Between A Uti And A Bladder Infection
Don’t Miss: Bladder Neck Contracture After Prostatectomy
How Common Are Bladder Control Problems
Bladder control problems are common, especially in women. Researchers estimate that approximately half of all women experience UI.1 Women are more likely to develop UI during and after pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause. These events and how the female urinary tract is built make UI more common in women than men. Although UI is common, it is not a routine part of being a woman or getting older.
As many as 1 in 3 men over the age of 65 may lose urine by accident, and approximately half of men who seek treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms experience UI.2,3 A man is more likely to develop UI with age because prostate problems occur more often with age.
Does Menopause Cause Urinary Incontinence
Although women can experience urinary incontinence during their life, the frequency of UI tends to occur more often when you get older. This loss of bladder control stems from hormonal changes that affect muscle strength in your pelvic area. Women who are pregnant, giving birth, or going through menopause are all likely to have urinary incontinence. So, does menopause cause urinary incontinence? It is a contributing factor, but there is more to it.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Latest Treatment For Bladder Cancer
What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Neurogenic Bladder Unique
Patients can expect the most advanced treatment options available for neurogenic bladder, including sacral neuromodulation bladder injections and complex bladder reconstructive surgery.
Our goal is to provide a patient-centered approach, says Dr. Chai. So we work with your medical doctors including primary care physicians, neurologists, and specialists in physical medicine and rehabilitation to ensure that you are taken care of holistically.
Causes Of Loss Of Bladder And Bowel Control
Causes of Bowel Incontinence
Causes of Urine Incontinence
It is not always necessary to have a noticeable cause of loss of bladder and bowel control, but your doctor can help you identify the best treatment in this case. Certain conditions can cause urinary incontinence. For instance, it may happen due to poor overall health, vaginal childbirth, and any damage to the nervous system.
Recommended Reading: How To Fight A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
Also Check: Oxybutynin Dosage For Overactive Bladder
Managing Bladder Or Urinary Incontinence
Sometimes urinary incontinence can last a short time, depending on what’s causing it. But sometimes incontinence can be long-term and uncomfortable, making some everyday activities difficult to manage.
Your health care team will ask you questions to determine the type of bladder incontinence you might have. Then, you might need tests to verify the type and learn the cause of it which will help them know the best way to manage it.
- Pelvic floor muscle strengthening may be recommended. A physical therapist that specializes in pelvic floor muscle exercises can help. This might help muscle strength and bladder control get better by doing exercises that tighten and relax muscles that control the flow of urine.
- Bladder training canhelp manage how often you need to urinate throughout the day, by assigning certain time intervals to empty your bladder.
Treatments For Urinary Incontinence
Home treatments for urinary incontinence may help resolve the problem. For instance:
- Avoid caffeine, carbonated drinks and alcohol, but drink plenty of water.
- Do Kegel exercises, which strengthen the pelvic floor and bladder muscles.
- Eat more fiber if you’re constipated.
If home treatments don’t work, seek medical help. Medical treatments include:
- A bulking agent injected into the tissues around the bladder and urethra to help them control urine flow
- A midurethral sling, surgically implanted mesh or human tissue that acts like a hammock to support the urethra and bladder
- Biofeedback to improve control of the urethra and bladder muscles
- Botox injections into the bladder to increase capacity
- Colposuspension surgery to hold the bladder in place
- Medication to increase bladder capacity
- Nerve stimulation to increase blood flow to the bladder and strengthen surrounding muscles
- Surgery to increase bladder capacity
- Vaginal estrogen
- Vaginal pessaries to support the pelvic floor muscles
Our women’s health providers will work with you to find the most appropriate treatment for your condition. You can count on skilled, sensitive care every step of the way.
Read Also: I Have A Bladder Infection And My Back Hurts
Bladder Incontinence In Women
Bladder incontinence is more common in women than in men. Other than the possible causes listed above, some things that may increase risk of bladder incontinence in women are:
- Changes to urinary or vaginal tissue from hormone therapy, surgery, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy
- Hormonal changes from menopause
- Pelvic prolapse the bladder, uterus, and or rectum may slip backward or downward into the vaginal canal because of weak pelvic wall muscles
How Do I Do Kegel Exercises
To do Kegels:
If you are uncomfortable or uncertain about doing Kegel exercises on your own, a doctor or nurse can also teach you how to do Kegels. A pelvic floor physical therapist or other specialist may also be available in your area to help teach you how to strengthen these muscles.
You May Like: Bladder Infection That Won T Go Away
What Is Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence is the accidental loss of urine. According to the National Association for Continence, over 25 million adult Americans experience temporary or chronic urinary incontinence. UI can occur at any age, but it is more common among women over 50. Urinary incontinence may be a temporary condition that results from an underlying medical condition. It can range from the discomfort of slight losses of urine to severe, frequent wetting.
Forms Of Urinary Incontinence That Affect Men Only
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia affects about 50 percent of men over the age of 60, and 90 percent over the age of 85 an enlarged prostate can cause sudden and frequent urges to urinate.
- Peyronies disease is the result of injury or damage to penile tissue, causing an abnormal curvature.
Also Check: How To Relieve Bladder Infection Pain Fast
Read Also: Why Do I Get A Bladder Infection After Intercourse
Treatment For Different Types Of Urinary Incontinence
Lifestyle changes and treatments can help with symptoms. Your doctor can help you come up with a plan thatâs right for you.
For stress incontinence, treatments include:
Pads and Vaginal Inserts.
Pelvic floor exercises. If youve had a baby, chances are youve been told to do Kegel exercises. These help to strengthen the pelvic floor after childbirth. They also help prevent stress incontinence. Best of all, you can do Kegels anytime, anywhere.
Heres how:
Note: You can learn how to do Kegels by stopping your urine, but donât do this routinely. Stopping the flow of urine can lead to an infection.
Biofeedback. A probe is inserted to monitor when your bladder muscles squeeze. When youâre able to recognize it as its happening, you can start to gain control of it. Its often used in combination with Kegel exercises.
Pessary. For women, doctors may prescribe a device called a pessary that is inserted into the . It repositions the urethra to help reduce leakage.
Injections and surgery. Shots to bulk up your urethral area may help. In more extreme cases, you may need surgery. One procedure pulls the urethra back up to a more normal position, relieving the pressure and leakage. Another surgery involves securing the urethra with a sling, a piece of material that holds up the urethra to prevent leakage.
Pads.
What To Expect At Your Appointment
During your appointment, your healthcare professional will likely ask questions about your symptoms. Theyll probably want to know how long youve been incontinent, which types of incontinence youve experienced, and other details.
They may also ask about your daily habits, including your typical diet and any medications or supplements that you take.
Depending on your symptoms and medical history, they may also order additional tests, including:
- Collecting a sample of urine for analysis. Laboratory staff can check the urine sample for signs of infection or other problems.
- Measuring the amount of urine that you release when urinating, the amount left over in your bladder, and the pressure in your bladder. This information is gathered by inserting a catheter, or a small tube, into your urethra and your bladder.
- Conducting a cystoscopy. During this test, theyll insert a small camera into your bladder to examine it up close.
Recommended Reading: Panty Liners For Light Bladder Leakage
Try Simple Measures First Like Using A Fiber Supplement And Treating Underlying Conditions
Nobody wants to talk about or even imagine it. But loss of bowel control known as fecal incontinence is a problem for millions of adults in the United States, especially women.
It becomes more common with age. Its socially isolating and takes away your dignity. You live in fear that you have stool in your pants and people can smell it. Some people wont even tell their doctors about it, says Dr. Kyle Staller, a gastroenterologist at Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital.
Should I Drink Less Water Or Other Fluids If I Have Urinary Incontinence
No. Many people with urinary incontinence think they need to drink less to reduce how much urine leaks out. But you need fluids, especially water, for good health.
Women need 91 ounces of fluids a day from food and drinks.11 Getting enough fluids helps keep your kidneys and bladder healthy, prevents urinary tract infections, and prevents constipation, which may make urinary incontinence worse.
After age 60, people are less likely to get enough water, putting them at risk for dehydration and conditions that make urinary incontinence worse.12
Don’t Miss: How To Stop A Bladder Infection Fast