Try To Keep Bowel Movements Regular
- As your bladder and bowel are next to each other, a full bowel affects bladder function.
- Many people find their bladder control problems are worse if they are constipated , which can happen if you dont empty your bowel regularly or dont eat enough fibre.
- Avoid straining while emptying your bowels as this can overstretch the muscles of your pelvic floor and may lead to weakness developing.
What Are The Symptoms Of Bladder Control Problems
Signs and symptoms of urinary incontinence can include
- leaking urine during everyday activities, such as lifting, bending, coughing, or exercising
- being unable to hold in urine after feeling a sudden, strong urge to urinate
- leaking urine without any warning or urge
- being unable to reach a toilet in time
- wetting your bed during sleep
- leaking during sexual activity
What Can Cause Trouble With Emptying Your Bladder
Chronic urinary retention can be caused by a wide variety of factors. They all boil down to either a blockage or an obstruction , or the bladder not being strong enough to allow all the urine to be voided.
The causes of urinary retention include:
- Urinary tract infection.
- Other infections, including sexually transmitted diseases.
- In men, an enlarged prostate which is very common with advanced age, especially after 80.
- Pelvic organ prolapse, when the uterus, bladder, bowel, or other internal organs move from their intended place.
- Urinary tract stones.
- Physical blockages like urethral strictures.
- An underactive bladder, in which the bladder muscles are the problem, is associated with conditions that include Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, diabetes, and pelvic injuries , among other conditions.
Recommended Reading: Does Medicare Cover Bladder Control Pads
You Have A Nerve Issue
Neurological problems can prevent normal signaling between the brain and the bladder and urethra, which could lead to trouble with bladder emptying. These include Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, diabetes or birth defects like spina bifida, according to the NIDDK.
Injuries that occur from a stroke or vaginal birth, as well as spinal cord injuries, pelvic injuries or brain injuries can also cause nerve damage that may lead to bladder problems.
Correct Function Of The Bladder Muscles Prevents Residual Urine
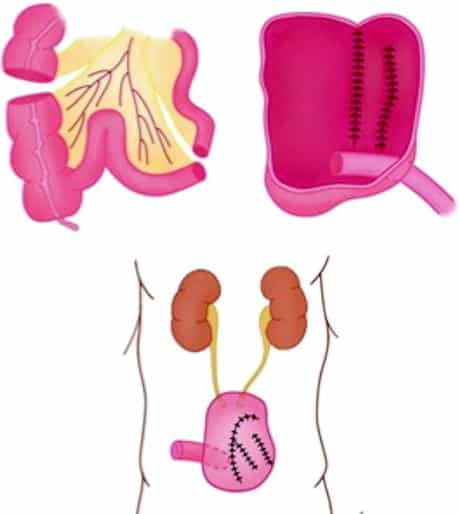
The urinary bladder fulfils two important tasks. It stores the urine until it receives the command to empty. The bladder also drains the urine. Disorders in bladder function can therefore be due to impaired storage function and impaired emptying capability.
The urethra is enclosed by two circular muscles, the sphincters. The two sphincters and the bladder muscle work together to empty the bladder. The inner and outer sphincters open. Shortly after, the bladder muscle contracts. In a healthy urinary tract, this mechanism ensures that the bladder completely empties with little pressure and that no residual urine remains in the bladder.
In addition to good interaction between the sphincter and bladder muscles, the nervous system must also be intact for the urinary tract to function properly. The nerve fibres and nerve impulses coordinate how the muscles interact.
Recommended Reading: Difference Between Uti And Overactive Bladder
Anxiety : : Bladder Not Emptying Completely / Frequent Restroom Trips
I have been dealing with anxiety my whole life and have had off and issues with emptying my bladder. I will use the restroom and will either feel like i need to go again right after or will experience burning then I know that it didnt completely empty, will go back and be able to go a little more then the burning will fade. I have had this for a long time and wonder if I could have possibly been born with a minor abnormality causing it or the chronic anxiety not letting the muscles relax enough to empty my bladder. I am constantly told I have a bladder infection by doctors and think this might be the reason. I do experience a tiny burn at the end of the stream but no other bladder infection symptoms. Unless they are diagnosing it solely because of hematuria, which i do have a minor kidney issue that causes microscopic blood in my urine. Does anyone else with anxiety suffer from this? Could it just be the muscles too tense to let the bladder empty?
Urinary Retention At A Glance
- Urinary retention, either acute or chronic, is the problem of being unable to empty the bladder properly.
- Urinary retention occurs most frequently in older men, but it can affect women and men of any age.
- Chronic urinary retention may cause few symptoms and sometimes people dont know they have it until urinary incontinence causes them to seek treatment.
- Acute urinary retention is a medical emergency and may involve complete inability to urinate and painful, urgent need to urinate.
- Surgical and other treatments are available to resolve urinary retention.
Recommended Reading: Icd 9 Code For Overactive Bladder
Bladder Not Emptying All The Way Here’s What Might Be Going On
When your bladder doesn’t feel empty after using the bathroom, you may be dealing with urinary retention. The condition, which is marked by an inability to fully empty the bladder, can be a side effect of numerous health problems.
Video of the Day
As a result, figuring out the underlying culprit is a must for feeling better.
Urinary retention becomes more common with age, and people assigned male at birth are significantly more likely to be affected than those assigned female at birth , according to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive Kidney Diseases .
In most instances, “a person will have a constant urge to urinate without being able to,” explains S. Adam Ramin, MD, a urologic surgeon and medical director of Urology Cancer Specialists in Los Angeles. “It is a very uncomfortable sensation. The urge becomes stronger and stronger, but no matter what a person tries, they will not be able to urinate.”
This can lead to bladder damage, incontinence, urinary tract infections and even kidney damage.
Here’s a look at some of the most common causes and the best way to manage the condition.
When To Seek Medical Care
A person who has any of the following symptoms should see a health care provider right away:
- complete inability to urinate
- electromyography
Physical Exam
A health care provider may suspect urinary retention because of a patients symptoms and, therefore, perform a physical exam of the lower abdomen. The health care provider may be able to feel a distended bladder by lightly tapping on the lower belly.
Postvoid Residual Measurement
This test measures the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination. The remaining urine is called the postvoid residual. A specially trained technician performs an ultrasound, which uses harmless sound waves to create a picture of the bladder, to measure the postvoid residual. The technician performs the bladder ultrasound in a health care providers office, a radiology center, or a hospital, and a radiologist a doctor who specializes in medical imaging interprets the images. The patient does not need anesthesia.
A health care provider may use a catheter a thin, flexible tube to measure postvoid residual. The health care provider inserts the catheter through the urethra into the bladder, a procedure called catheterization, to drain and measure the amount of remaining urine. A postvoid residual of 100 mL or more indicates the bladder does not empty completely. A health care provider performs this test during an office visit. The patient often receives local anesthesia.
Medical Tests
Also Check: Kegel Exercise Weights For Bladder Control
What Are The Complications Of Treatments For Urinary Retention
UTI from Catheter Use
Incontinence and Erectile Dysfunction After Prostate Surgery
Transurethral surgery to treat an enlarged prostate may result in loss of bladder control or erection problems in some men. These problems are usually temporary. Most men recover their bladder control in a few weeks or months, and most recover their sexual function within 1 year after the operation.
Hope through Research
The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases has many research programs aimed at finding and improving treatments for urinary disorders. Researchers supported by the NIDDK are working to develop methods for preventing UTIs in patients who must use urinary catheters. One team of researchers is developing a catheter that gradually releases an antiseptic agent while it stays in the urinary tract. Another team is studying the use of benign bacteria on a catheter to inhibit the growth of disease-causing bacteria.
How Is Urinary Retention Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will ask about your health history and the medicines you take. He will press or tap on your lower abdomen. You may need any of the following tests:
- A digital rectal exam is when healthcare providers carefully feel the size of your prostate.
- A post void residual test will show how much urine is left in your bladder after you urinate. You will be asked to urinate and then healthcare providers will use a small ultrasound machine to check how much urine is left in your bladder.
- Blood or urine tests may show infection or prostate specific antigen levels. PSA may be elevated in prostate cancer.
- An ultrasound uses sound waves to show pictures on a monitor. An ultrasound may be done to show bladder stones, infection, or other problems.
- A CT scan , or CAT scan, is a type of x-ray that is taken of your prostate, kidneys, and bladder. The pictures may show what is causing your urinary retention. You may be given a dye before the pictures are taken to help healthcare providers see the pictures better. Tell the healthcare provider if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast dye.
Read Also: What Happens When You Remove Your Bladder
How Can Urinary Retention Be Prevented
For men:
If you have an enlarged prostate, be sure to take prostate medications as prescribed by your doctor and avoid medications associated with urinary retention, such as over-the-counter cold and allergy medications that contain decongestants.
For women:
If you have mild cystocele or rectocele, you may be able to prevent urinary retention by doing exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles.
Kimberly-Clark Australia makes no warranties or representations regarding the completeness or accuracy of the information. This information should be used only as a guide and should not be relied upon as a substitute for professional medical or other health professional advice.
Healthdirect.gov.au, . Urinary retention. Available at: .
http://www.health.qld.gov.au, . Adult Urinary Obstruction, Retention and Bladder Scanning. Available at: .
John P. Cunha, F. . Urinary Retention: Get the Facts on Causes and Treatment. MedicineNet. Available at: .
Kidney.niddk.nih.gov, . Urinary Retention National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse. Available at: .
Knott, MD, L. . Acute Urinary Retention. Information about AUR. Patient | Patient.co.uk. Patient.co.uk. Available at: .
Urinary Retention: Does Drinking Water Really Help
Urinary retention is a condition characterized by an inability to fully empty the bladder. The bladder serves as a storage tank for urine, a substance made by the kidneys after they have filtered out waste and extra water from your blood. Once made, the urine travels to the bladder where it will stay until a person is ready to urinate. In a healthy individual, the bladder can hold up to two cups of urine comfortably for up to five hours.
Urinary retention can occur for a variety of reasons. Among men, an enlarged prostate is the most common cause. Among women, bladder muscle dysfunction and urinary stones are the typical culprits. Individuals with this condition may experience:
- Feeling the need to urinate right after using the bathroom
Recommended Reading: Women’s Bladder Control Medication
What Is Urinary Retention
Urinary retention is a condition where your bladder doesnt empty all the way or at all when you urinate. Your bladder is like a storage tank for urine. Urine is made up of waste thats filtered out of your blood by your kidneys. Once filtered, the urine moves to your bladder where it waits till its time to move through the urethra and out of the body.
When you have urinary retention, it can be acute or chronic . Acute means that it comes on quickly and it could be severe. Chronic urinary retention means that youve had the condition for a longer period of time.
The acute form of urinary retention is an emergency. In this case, youll need to see a healthcare provider right away. The chronic form happens most of the time in older men, but it can also occur in women.
Surgery May Cause Urinary Retention
Surgery is a common cause of urinary retention. Specifically, it’s the medication provided before and during surgery that is the culprit of urinary retention. During the surgery, patients will often be treated with intravenous fluid that replaces water, salts, and sugars you may lose during surgery, according to Healthline. This can cause a full bladder. Combined with anesthesia given to patients, which prevents any feeling in a localized area so there is little to no pain, this can prevent you from feeling like you need to pee, according to NIDDK.
Thankfully, if you are experiencing urinary retention after surgery, there is little reason to worry. It’s a very common side effect of surgery that should disappear once the anesthesia wears off and you can feel the need to pee again, according to Livestrong. Not all surgeries will cause urinary retention, however. The most common procedures to cause urinary retention are hip replacements and spinal, pelvic, and rectal surgeries, as well as hemorrhoid removal, according to Cleveland Clinic.
Read Also: How To Get A Healthy Bladder
How Is Chronic Urinary Retention Diagnosed
History and physical exam: During the diagnosis process, your healthcare provider will ask about your signs and symptoms and how long you have had them. He or she will also ask about your medical history and your drug use. A physical exam of the lower abdomen may show the cause or give your provider additional clues. After this, certain tests may be needed. Men may have a rectal exam to check the size of their prostate.
Your urine may be saved and checked to look for infection.
Ultrasound of the bladder: The amount of urine that stays in your bladder after urinating may be measured by doing an ultrasound test of the bladder. This test is called a postvoid residual or bladder scan.
Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is a test in which a thin tube with a tiny camera on one end is put into your urethra. This lets the doctor look at pictures of the lining of your urethra and bladder. This test may show a stricture of the urethra, blockage caused by a stone, an enlarged prostate or a tumor. It can also be used to remove stones, if found. A computed tomography scan may also help find stones or anything else blocking the flow of urine.
Urodynamic testing: Tests that use a catheter to record pressure within the bladder may be done to tell how well the bladder empties. The rate at which urine flows can also be measured by such tests. This is called urodynamic testing.
When To See A Doctor
Anyone experiencing symptoms of acute urinary retention should go to the emergency room.Chronic urinary retention is not a medical emergency, but it does usually indicate a potentially serious underlying problem.
A person should schedule an appointment with a doctor for urinary retention that lasts longer than a few days or that goes away and then returns.
People who experience temporary urinary retention due to medication or anesthesia may not need medical treatment if the symptoms disappear and do not return.
Although anyone can develop urinary retention, it is more common as a person ages. Males are also more likely than females to have urinary retention due to prostate issues and partial blockages of the urethra.
Some other risk factors include:
4 sourcescollapsed
- Carnevale, F. C., et al. . Quality of life and clinical symptom improvement support prostatic artery embolization for patients with acute urinary retention caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia.
You May Like: How To Treat Overactive Bladder Naturally
Urinary Retention: 5 Reasons You May Have Trouble Peeing
Did you know that we spend roughly 2,208 hours on the toilet in our lifetime? Thats a lot of time on the potty! And, if youre having trouble going No. 1, it could be costing you even more time than you like. Time spent anywhere else but a bathroom stall.
If you cant get the flow going when you feel you need to, and your bladder is full, you may have urinary retention. Urinary retention is the inability to pass urine in your bladder, and it can be acutea sudden inability to urinateor chronica gradual or slow inability to empty the bladder.
The difference can be from the cause and sometimes the symptoms, said James Wolach, MD, a urologist at Banner Health Clinic in Colorado. Acute is usually painful and they have the sensation to void but cant, whereas many people with chronic retention dont have any feeling they are not able to empty their bladders. While chronic may not seem as serious, it can lead to serious problems, so its important that both receive attention from your doctor.
There are many different causes for urinary retention, and much of your treatment will depend on the underlying cause. Here are five reasons you may be stuck and ways to improve your flow.
Also Check: Capsaicin Pills For Overactive Bladder
Less Common Causes Include:
- Some children are born with problems in the anatomy of their renal tract these are called congenital problems.
- Some children acquire problems in the anatomy of their urinary tract due to trauma or having a tumour.
- Some children have problems of the brain or spinal cord that affects the nerves that control bladder function.
- Occasionally, genetic diseases can affect the urinary tract.
Don’t Miss: Can Lower Back Pain Cause Bladder Problems