Prevention And Treatment Of Side Effects
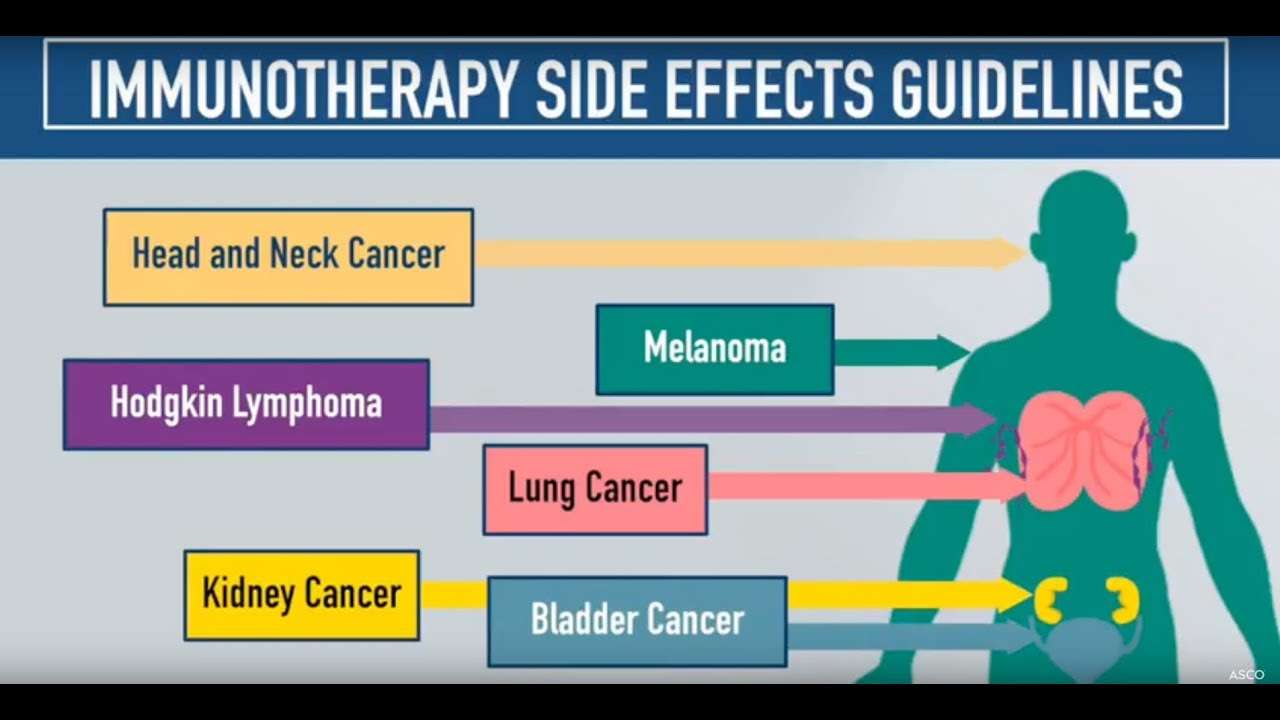
The side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors therapies are usually caused by the immune system attacking normal body parts in the same way it attacks cancer cells. Different types of immunotherapies can cause various side effects, many of which depend on the type of treatment, the tumor type and location, and the patients general health condition. Immunotherapy side effects can be mild, moderate, or even life-threatening. Some side effects can resolve on their own within a certain time frame while others persist and worsen. In such cases, it should be considered to taper the dosage, discontinue, or change the medication. Indeed, prevention of the occurrence or worsening of side effects is essential for effective treatment of these patients population. At the end of immunotherapy, it is important to observe side effects, some of which may occur months or years later . Side effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors therapies may affect the following parts of the body.
Table 2 List of serious complications and brief prevention methods for bladder cancer.
Sex After Bcg Treatment
Men should use a condom during sex for the first week after each BCG treatment. If you are a woman having the treatment, your partner should use a condom during this time. This protects your partner from any BCG that may be present in semen or vaginal fluid. Your doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about this.
Doctors do not yet know how BCG may affect an unborn baby. They will recommend you do not become pregnant or make someone pregnant while having it. You should use effective contraception during treatment. Your doctor or specialist nurse can give you more information about this.
Immunotherapy For Bladder Cancer
Some people with bladder cancer have immunotherapy. Immunotherapy helps to strengthen or restore the immune systems ability to fight cancer.
You may have immunotherapy to:
- kill bladder cancer cells
- stop bladder cancer cells from growing and spreading
- lower the risk that the cancer will come back
- help keep the cancer from coming back after it has already been treated
- control symptoms of bladder cancer
Your healthcare team will consider your personal needs to plan the drugs, doses and schedules of immunotherapy. You may also receive other treatments.
You May Like: Bladder Cancer Spread To Liver
What Are The Side Effects Of Immunotherapy For Bladder Cancershare
- View Ovarian Cancer Main Page
Discover Local Ovarian Cancer resources:
SurvivorNet Fact Checking and Medical Review Standards:
The SurvivorNet News Team creates high quality medical information that complies with our industry leading standards for factual accuracy and sourcing from leading experts at academic medical institutions. Every news article is thoroughly fact-checked by our physician collaborators. We vet each piece of work for factual integrity, impartiality, and clearly label any professional conflicts.
All SurvivorNet articles adhere to the following standards:
- Save This Video
Outstanding Questions And Future Prospects
The success of cancer immunotherapy has prompted intensified interest in defining the specific effector immune cells and fundamental mechanisms responsible for anti-tumor immunity. In addition, certain oncogenic pathways and transcriptional programs in malignant cells are associated with intrinsic sensitivity or resistance to immunotherapeutics . These cumulative findings hold enormous promise to facilitate biomarker identification that can predict or monitor which patients would benefit from immunotherapy. The treatment stratification and surveillance are of paramount importance for UBC as ICI therapy is being aggressively advanced into the neoadjuvant and bladder-sparing settings, where inappropriate regimens could be potentially detrimental. Unfortunately, individual parameters have been proved unreliable and such a model has to take different elements that affect tumor-host interactions into account . Thus, taking advantage of cutting-edge approaches such as single-cell sequencing and mass cytometry, which enable high-dimensional molecular analyses during the whole course of ICI treatment, will be valuable to simultaneously probe a wide range of immune subsets and regulators, and systemically nominate biomarker candidates for further detailed investigations.
You May Like: How To Help Overactive Bladder
What Is The Immune System And How Does It Work With Cancer
The immune system is a natural part of our body. Its role is to get rid of foreign or damaged material and cells before they cause trouble.
Most of the time, our immune system can find foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses, and destroy them. The immune system uses signals to attack them while leaving healthy cells alone.
Cancer is different from an illness caused by a bacteria or virus. It involves the uncontrolled growth of normal body cells. In other words, cancer cells may not be found by the immune system. Though they look different under the microscope, cancer cells can hide and grow. One way cancer cells hide is to express proteins on their surface to turn-on a “checkpoint” to stop an immune system attack.
The National Cancer Institute studied common tumors in its Cancer Genome Atlas project. The research showed that bladder cancer, skin cancer and lung cancer have the most cellular changes . These types of cancer may be more likely to respond to treatments that help the immune system find cancer cells, called “immunotherapies”.
What is Immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy is any treatment that makes the immune system stronger. For cancer, it helps the body find and attack cancer cells. The field of immuno-oncology studies how the immune system interacts with cancer. It uses that information to make new treatments.
What Happens Under Normal Conditions?
What Happens When Cancer Cells Grow and Hide?
Three things help cancers hide from the immune system:
Side Effects Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
Along with its needed effects, bcg may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor as soon as possible if any of the following side effects occur while taking bcg:
More common
- painful urination
Rare
Also Check: Does Lemon Water Help Bladder Infections
More Serious Side Effects
Treatment with a PD-1 inhibitor such as pembrolizumab can help a patients immune system to fight cancer cells, but it can also cause the immune system to attack healthy cells. This can cause very serious side effects in some patients. Before starting treatment with pembrolizumab, healthcare providers will speak with patients about the relative benefits and risks of treatment. If a patient chooses to begin treatment with pembrolizumab, healthcare providers will explain the signs and symptoms of serious side effects so that the patient can recognize them quickly and seek treatment. Such serious side effects can include:
- Lung problems
Adverse Effects Of Bcg
Common adverse effects include cystitis, dysuria, malaise, fatigue, and a low fever . These can be managed by NSAIDS, phenazopyridine, and anticholinergics. If symptoms become intense or last longer than 24 hours, consider either delaying additional instillations until symptoms improve or reducing the dose.
In a review including 2602 patients treated with intravesical BCG instillation , the most common side effects were fever > 103ºF, hematuria, granulomatous prostatitis, pneumonitis and/or hepatitis, arthralgia, epididymitis, sepsis, rash, ureteral obstruction, bladder contracture, renal abscess, and cytopenia.
Early-onset BCG infection often presents as systemic manifestations. In contrast, delayed-onset infection presents as localized disease. Manifestations are as follows:
- Systemic manifestations occur when BCG disseminates outside of the genitourinary tract. They include sepsis syndrome, pulmonary issues from dyspnea, granulomatous hepatitis, osteomyelitis, reactive arthritis, monoarthritis, psoas abscess, and vascular complications due to mycotic aneurysms.
- Localized manifestations include cystitis, bladder contracture, granulomatous prostatitis, prostate abscess, epididymo-orchitis, testicular abscess, pyelonephritis, renal abscess, urethral stricture, and balanitis.
The AUA has noted the following with regard to BCG2:
Contributor Information and Disclosures
Fellow in Urologic Oncology and Minimally Invasive Surgery, University of Chicago Medical Center
Also Check: What Causes An Overactive Bladder At Night
What Happens During Bcg Cancer Treatment
Before beginning BCG treatment, local anesthesia is given to numb the area and keep you comfortable. Next, your healthcare provider will place a catheter into your urethra and inject the liquid BCG solution into your bladder.
The BCG solution needs to come in contact with cancer cells to kill them. So, once the medication is injected, your healthcare provider will remove the catheter and ask you to lie on your back, stomach and both sides for 15 minutes each.
When the process is complete, youre free to leave your appointment. However, you should avoid peeing for at least one more hour.
How long do you hold BCG in your bladder?
Once the BCG solution is injected into your bladder, youll hold it for a total of two hours. After this point, youll be able to pee.
What does BCG do to the bladder?
When the BCG solution enters your bladder, your immune system cells begin to attack the cancer cells in your bladder.
BCG treatment schedule
The initial BCG cancer treatment occurs weekly for six weeks. This is called induction therapy.
If the treatment is working, your doctor may prescribe BCG maintenance therapy. Maintenance therapy is given once a week for three weeks at the three-, six- and 12-month marks. For some people, this may be continued up to three years.
Mechanism Of Action Of Bcg
The mechanism of action of bacillus Calmette-Guérin therapy is incompletely understood. Some early studies purported that an immune response against BCG surface antigens cross-reacted with putative bladder tumor antigens, and this was proposed as the mechanism for the therapeutic effect of BCG however, multiple subsequent studies refute this claim.
The most likely mechanism of action of BCG immunotherapy involves a combination of its direct effect on tumor cells along with the patients immune response to the therapy. These effects are summarized by Kawai et al into three categories: infection of cancer cells, induction of immune response, and antitumor effects.
The infection of cancer cells is mediated by the glycoprotein fibronectin, which allows the internalization of BCG, breakdown of proteins, and cellular changes that trigger the immune system. This is similar to the immunologic reaction that occurs in patients with tuberculosis. This immune response comprises specific cellular changes including surface receptor changes and release of various cytokines. Interferon is considered to be an important part of this process and has been used in the past to determine appropriate response to treatment. The immune response crescendos to antitumor activity in which cells recognize the cancer cells, target them for destruction, and subsequently decrease cancer burden.
The overall response to BCG is limited if the patient is immunosuppressed.
Read Also: Symptoms Of Bladder Stones In Cats
What Is Bcg Treatment
Bacillus Calmette-Guerin treatment is a type of intravesical immunotherapy. This liquid drug is made from a strain of Mycobacterium bovis the same bacterium used to create the tuberculosis vaccine. When used in medicine, Mycobacterium bovis is weakened to reduce harm to your body.
BCG treatment is usually given after TURBT , which is a bladder surgery to remove any visible cancer.
How Does Immunotherapy Work
Pembrolizumab is a type of immunotherapy drug called a PD-1 inhibitor, that has been approved to treat various forms of bladder cancer and other types of cancers.1,2 The bodys immune system consists of a group of organs and cells that work to protect the body from diseases and infections. In a patient with cancer, immunotherapy drugs work by affecting the way the immune system functions to help it fight cancer cells more effectively.
Read Also: What Can Cause Uncontrollable Bladder
What Are Common Side Effects Of Immunotherapy
Side effects depend on the way you get immunotherapy.
Side effects of intravesical immunotherapy can include:
-
Discomfort or burning in your bladder
-
Feeling the need to urinate often
- Pain when you urinate
- Blood or clots in your urine
-
Flu-like symptoms, such as chills, fatigue, or fever
-
Serious infection if BCG spreads through your body
These side effects often go away within a few days after the treatment. Still, make sure you know what to watch for and when you need to contact your doctor.
Side effects of systemic immunotherapy can include:
- Skin changes, like itchy rashes, redness, blistering, cracking, and dryness
- Inflammation around finger and toe nails
- Fatigue
Treating Complications Of Bcg Therapy
If you do experience a problem from BCG infection, you may need to receive targeted antibiotics, such as isoniazid and rifampin.
Complications of BCG therapy sometimes dont occur until years later. That can happen if the BCG bacteria that spread in the body become reactivated. These complications can sometimes be tricky to diagnose. Medical imaging might first make your clinician concerned about cancer or about another type of bacterial infection.
Make sure that all your medical care providers know that you have had BCG therapy. That will help guide their diagnostic process and ensure you get the best possible care. In some cases, your clinician will want a tissue sample from the involved area to make sure that the problem is from a BCG infection and not from some other source.
Recommended Reading: Overactive Bladder Only At Night
Who Can Receive Pembrolizumab
Patients with certain forms of advanced or metastatic bladder cancer can be treated with pembrolizumab.1,4 Advanced or metastatic bladder cancer means that the cancer cells have spread beyond the bladder and/or to other parts of the body. Pembrolizumab is generally prescribed for patients who have already tried treatment with a chemotherapy that contains platinum, but the chemotherapy was not effective against the cancer or it was initially effective but has stopped working. Pembrolizumab may also be used for patients with advanced or metastatic bladder cancer who are unable to receive certain platinum-containing chemotherapy. If you have advanced or metastatic bladder cancer, your healthcare providers can discuss whether treatment with pembrolizumab may be suitable.
Pembrolizumab may also be used for patients with high-risk bladder cancer that has not grown into the bladder muscle and is not responding to Bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy. Additionally, these patients would have been unable to have bladder removal surgery or would have decided not to have this surgery.3
How Immunotherapy Affects Your Body
- Immunotherapy causes different side effects than chemotherapy because it revs up the immune system instead of attacking the cancer cells directly.
- Side effects depend on which part of the body immunotherapy affects, including the lungs, GI tract, skin, or heart.
- Steroid treatment can calm the overactive immune response and stop side effects.
Surgery and chemotherapy used to be the main treatments for bladder cancer. But chemotherapy causes a lot of side effects because it targets all quickly dividing cells. That includes cancer cells, as well as some healthy cells.
Chemotherapy is hard. A lot of patients lose their hair. They get extremely tired and weak, Dr. Jay Shah, associate professor at Stanford University and a cancer surgeon at the Stanford Cancer Center, tells SurvivorNet.
Read Also: What Can I Drink For Overactive Bladder
Substantial Improvement In Survival
Dr. Powles and his colleagues enrolled 700 people with locally advanced or metastatic bladder cancer in the international JAVELIN Bladder 100 study, which was funded by Pfizer, the drug’s manufacturer.
All trial participants had already received chemotherapywith either cisplatin and gemcitabine or carboplatin and gemcitabine, if their health did not allow them to receive cisplatinand their disease had not worsened during chemotherapy.
Participants were then randomly assigned to receive either maintenance treatment with avelumab plus supportive care or supportive care alone. People in the maintenance group received infusions of avelumab every 2 weeks until their cancer started growing again or they left the study for other reasons. Supportive care for both groups included pain management, nutritional support, and treatment of infections.
People in the supportive care group whose cancer got worse did not receive avelumab as part of the trial. However, they could receive it or any other immunotherapy drug after leaving the study.
Maintenance treatment with avelumab after chemotherapy turned out to have substantial benefits. The median overall survival for people who received maintenance avelumab was more than 21 months, compared with about 14 months for people who received only supportive care until their cancer got worse.
Subtleties And Future Questions
Several factors have to be carefully considered in interpreting the trial results, explained Dr. Apolo.
A major one is that the study did not directly compare survival between people who got avelumab immediately versus when their cancer progressed. Only about half of the participants who initially received supportive care alone went on to receive immunotherapy after their cancer got worse. There could be many reasons for this, including lack of access to these drugs in different countries, Dr. Apolo said.
But it also might be that, for some people, the cancer was progressing too rapidly, she added. When these tumors start growing, they start growing very quickly. So if you wait to start at the time of progression, maybe its too late, added Dr. Apolo.
Not all patients will be caught by the second-line safety net, agreed Dr. Plimack.
So, for now, said Dr. Balar, the takeaway message from the JAVELIN study is after chemotherapy, dont wait to give immunotherapy.
But more and more, studies are looking at whether some patients should receive immunotherapy as first-line treatment, he continued. Immunotherapy is one of the most important advances weve made in the last 30 years, Dr. Balar said.
The JAVELIN results cant provide any insight into which patients benefit from first-line treatment with a platinum-based chemotherapy, he added. This trial wasnt designed to ask: Is chemotherapy necessarily the best choice for every patient? he explained.
Also Check: Bladder Infection From Hot Tub
Immunotherapy Side Effects: What To Know
If youve researched cancer treatment options, youve probably heard of immunotherapy, which trains the immune system to attack cancer, rather than attacking the cancer directly. You also might have heard that immunotherapy doesnt have side effects.
But thats not always the case. With the most common type of immunotherapy — immune checkpoint therapies — about 5-10% of patients experience side effects, and theyre life-threatening in about 1-2% of those cases, says Vivek Subbiah, M.D. Examples of immune checkpoint drugs include: pembrolizumab , nivolumab , atezolizumab , ipilimumab , avelumab and durvalumab .
Immunotherapy side effects often differ from those commonly seen with other types of cancer treatment. Heres what patients should know.
Fatigue, inflammation top common side effects
As with many cancer therapies, fatigue tends to be one of the most common, says Van Morris, M.D.
But immunotherapy drugs also can cause inflammation throughout the body. For example, patients may experience skin inflammation as pigment changes, a rash and feeling itchy, sometimes even without a rash. Inflammation in the lungs can cause a cough and chest pains. The colon may also become inflamed, causing abdominal pain and diarrhea.
Side effects often show up early in treatment or months or years later
Side effect management depends on the severity
Patients who develop diabetes may require insulin or a period of time off the immunotherapy.
Watch for changes in your body