What Are Some Common Treatments For Disorders Of The Urethra
If you do have a disorder involving the urethra, the treatment will depend on the disorder. Possible therapies include:
Medications
If you have an infection, your provider will put you on anti-infective medications, such as antibiotics. If you have something like urethral cancer, your provider may suggest chemotherapeutic drugs.
Procedures
Many urethral conditions require treatments as therapies. These treatments may include:
- Dilation: Your provider will try to expand the urethra by using cystoscopy and instruments like a balloon.
- Urethrotomy: Your provider will use cystoscopy and a cutting instrument to remove the ring of scar tissue.
- Urethroplasty or urethral reconstruction: Your provider will use tissue from elsewhere in your body to build or rebuild a urethra.
- Surgery to remove tumors.
What Does The Bladder Do
How much attention do you pay to your bladder? Most of us only think of the bladder when its full and gives that sensation of needing to urinate. But there are likely things about the bladder you dont know, like why its so important and what can happen if something goes wrong? Can we live without a bladder and, if so, how? Learn more about normal bladder function, what the bladder does, and some of the things that can go wrong with this part of the body.
Understanding The The Urinary System
The bodys urinary system is also called the renal system, and it is made up of several different organs.1-3 The urinary systems job is to filter out waste and extra water from the blood and remove it from the body in the form of urine. The major organs that make up the urinary system are:
- Two kidneys
- One urethra
Read Also: Treatment Of Overactive Bladder In Females
The Urinary Bladder Is A Reservoir For Urine
Urine flows through the ureters into the urinary bladder. In women, the bladder is located in front of the vagina and below the uterus. In men, the bladder sits in front of the rectum and above the prostate gland. The wall of the bladder contains folds called rugae, and a layer of smooth muscle called the detrusor muscle. As urine fills the bladder, the rugae smooth out to accommodate the volume. The detrusor relaxes to hold the urine, then contracts for urination. An adult bladder is full at about half a liter, or about two cups.
Pain Where Bladder Is Located Other Possible Causes
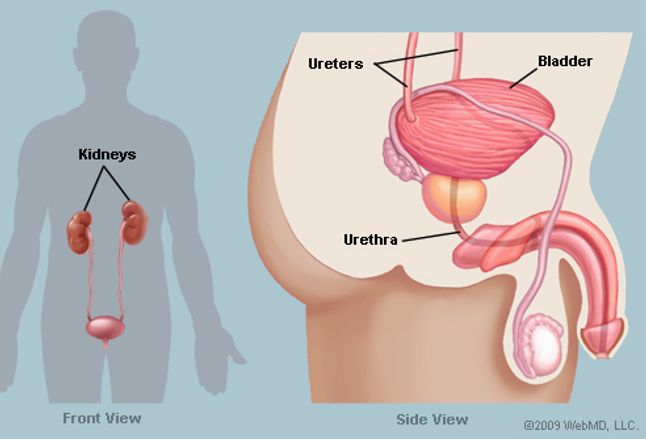
Some of the other reasons you may have pain where the bladder is located are a damaged urethra and a weak and neurogenic bladder.
If pain where bladder is located is an issue for you, seek help immediately or start using the associated treatments. Dont allow the problem to get any worse.
Medical Disclaimer
The information contained in this post is for general information purposes only. The information is provided by PainBalance.org and while we endeavor to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the post for any purpose.
As noted, you should always consult with your doctor for medical advice to be sure of the issue you are experiencing.
You May Like: All Symptoms Of Bladder Infection
S Of The Urinary Bladder
The apex of the bladder points forward towards the pubic symphysis, while the base lies posteriorly, against the rectum in males or vagina in females. The neck of the bladder is the inferior aspect where the bladder walls narrow and converge towards the urethra like a funnel. This directs urine into the urethra.
The body of the bladder is the largest part lying between the apex, fundus and neck of the bladder. The trigone of the bladder is a triangle region on the posterior wall. The two ureteric orifices and internal urethral orifice mark the three points of the trigone. It has a slight elevation known as the uvula of the bladder.
The parts of the detrusor muscle towards the neck of the bladder form the internal urethral sphincter. Some fibers run around the neck for better bladder control. This sphincter closes during ejaculation to prevent backward flow of semen into the bladder in men. The internal urethral sphincter is under involuntary control. The external urethral sphincter which is under voluntary control is formed by the urogenital diaphragm.
- Vesical venous plexus > > internal iliac veins or into the internal vertebral venous plexus
- Males vesical plexus communicates with the prostatic plexus
- Females vesical plexus communicates with the vaginal/uterovaginal plexus
Also Check: What Vitamins Are Good For Bladder Health
What Are The Parts Of The Urinary System
The kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra make up the urinary system. They all work together to filter, store and remove liquid waste from your body. Heres what each organ does:
- Kidneys: These organs work constantly. They filter your blood and make urine, which your body eliminates. You have two kidneys, one on either side of the back of your abdomen, just below your rib cage. Each kidney is about as big as your fist.
- Ureters: These two thin tubes inside your pelvis carry urine from your kidneys to your bladder.
- Bladder: Your bladder holds urine until youre ready to empty it . Its hollow, made of muscle, and shaped like a balloon. Your bladder expands as it fills up. Most bladders can hold up to 2 cups of urine.
- Urethra: This tube carries urine from your bladder out of your body. It ends in an opening to the outside of your body in the penis or in front of the vagina .
Read Also: Can Soda Cause Bladder Infection
Interstitial Cystitis/painful Bladder Syndrome
Interstitial cystitis, also referred to as bladder pain syndrome, is a chronic condition that causes painful urinary symptoms. It affects mostly women, according to the . The cause of the condition is currently unknown, but certain factors may trigger symptoms, such as infections, physical or emotional stress, diet, bladder injury, or certain medications.
Symptoms of interstitial cystitis
The symptoms can range from mild to severe and vary from person to person. Symptoms can include:
- urinalysis to check for infection
- cystoscopy to view the lining of your bladder
- urinary function tests
- potassium sensitivity test
Your doctor may also perform other tests to help rule out cancer as the cause of your symptoms, such as a biopsy, which is usually performed during cystoscopy or urine cytology to check for cancer cells in your urine.
Treatments for interstitial cystitis
There is no one specific treatment for interstitial cystitis. Your doctor will recommend treatments for your individual symptoms, which may include:
What The Liver Does
Your liver helps the body break down and digest food by producing bile. Doctors from Stanford Childrens Health say that bile from the liver breaks down fats from your food so that it can be digested properly and your body absorbs all the necessary nutrients.
One very important function of the liver is to keep your blood clean and free of toxins. The liver also creates nutrients for the body and provides proteins for blood plasma. Good liver health also helps to keep your immune system strong.2
Taking into consideration the important work your liver does, its important to keep your liver healthy. Before we look at ways to boost the health of your liver and keep it functioning properly, lets look at the main reasons for liver pain.
Dont Miss: How Do Doctors Test For Bladder Infection
You May Like: Poise Impressa Incontinence Bladder Supports
Where Is The Urethra Located
The urethra is a passageway located in your bodys pelvic region. The walls of the tube are thin and made up of epithelial tissue, smooth muscle cells and connective tissue.
The urethra has two different types of sphincters, or muscles that act as valves that open or close. There is an internal urethral sphincter, which is located at the point where the urethra leaves the bladder. Theres also an external urethral sphincter located in the pelvic floor. These muscles work together with the bladder to get urine out of your body.
Your Urinary Bladder Has One Role
The urinary bladder is part of your urinary tract. The urinary tract includes the:
- Ureters, the tubes that go from your kidneys to your bladder
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra, the tube that drains the bladder and allows you to urinate
Your bladder acts as a reservoir to store urine until you are ready to eliminate it. A healthy bladder can hold between 1.5 to 2 cups of urine. Your kidneys produce the urine, which flows from the ureters to your bladder. Urinating helps your body stay healthy, allowing your body to balance fluid loads and rid itself of the toxins.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Pain But No Infection
Pain Where Bladder Is Located
If you have pain where bladder is located, it could come from various medical issues. You will learn some of the most common causes of bladder pain.
The information is helpful, but we always recommend seeing a doctor first if you can, Rather than seeking to do your self-help program.
We understand that not everyone may have access to medical care, free or otherwise. This information will have value for such persons.
Firstly, it is essential to follow the guidelines and not cut corners. Your health matters you shouldnt take unnecessary chances.
The first rule is to compare your symptoms with the signs of each disease we share. Eliminate any that dont apply.
Once you have finished that process, compare the remaining results for the treatments available.
The remedies that match would be the starting point of your treatment to a better you. This method will never fail if you follow it correctly.
First and foremost, you should still try to get medical advice and attention.
Here are the conditions that cause pain where bladder is located for those unable to do so.
Contents
Who To See For Bladder Problems
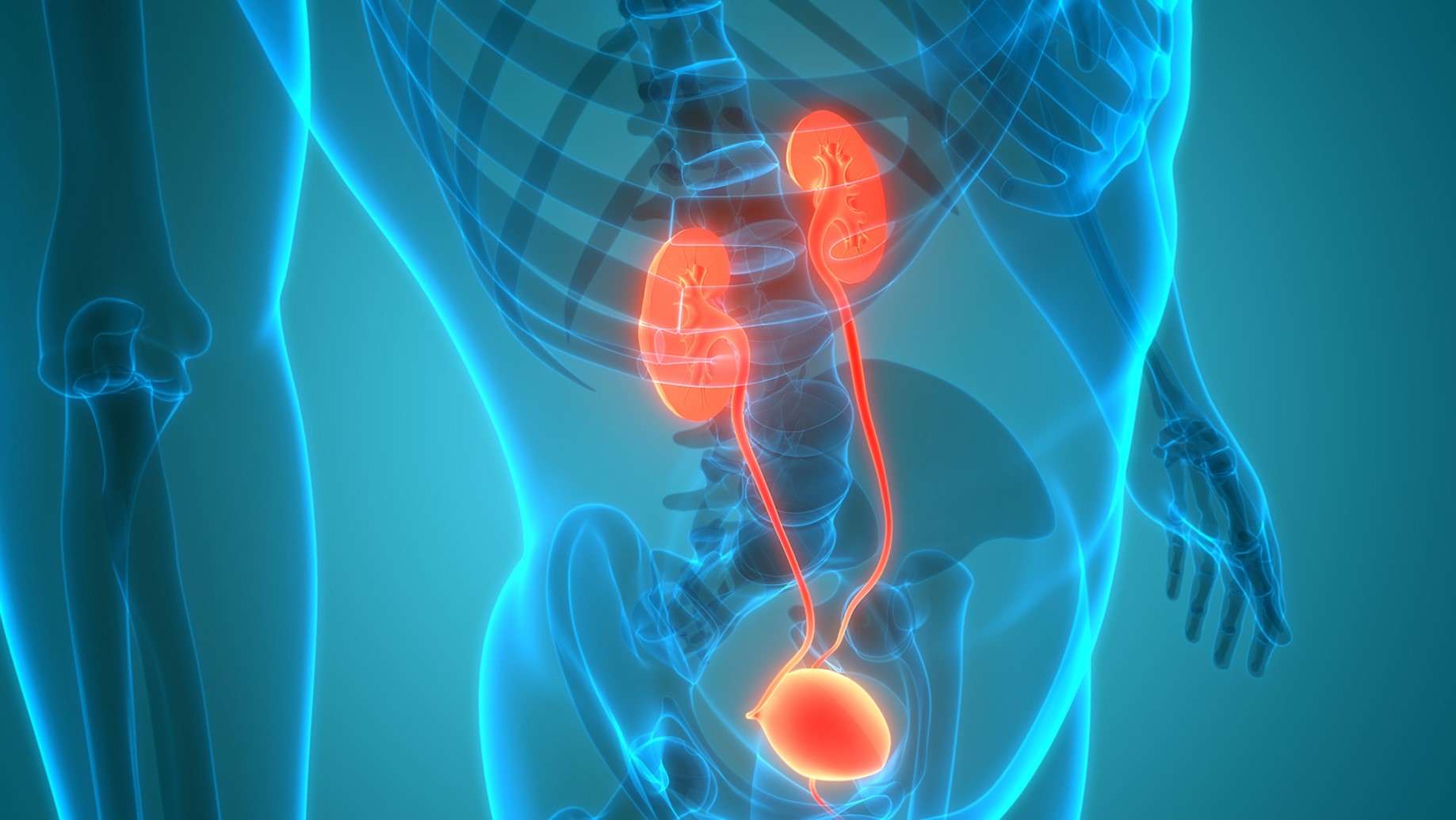
Bladder pain or discomfort, blood in urine, or urinary leaking are symptoms to report to a healthcare professional. They can help diagnose and treat any underlying condition causing bladder symptoms.
In many cases, a person may find going to their primary care doctor is a good place to start. Some insurances also require a referral to a specialist from a primary care doctor.
Some doctors specialize in bladder health. Specialists include:
- Urologists: Urologists specialize in treating urological conditions, such as UTIs, kidney stones, and other conditions of the urinary tract. They often form the head of a treatment team when a person has a condition affecting their urinary tract.
- Oncologist: A urologist or primary care doctor may refer a person to an oncologist to help with cancer detection and treatment.
- Gynecologist: A gynecologist specializes in female reproductive organs and may be able to help with certain issues that can affect the bladder.
- Urogynecologist: A urogynecologist specializes in female pelvic medicine and reproductive surgery, including surgery to treat stress urinary incontinence.
Also Check: T1 Bladder Cancer Life Expectancy
Tips To Keep Your Bladder Healthy
People rarely talk about bladder health, but everyone is affected by it. Located in the lower abdomen, the bladder is a hollow organ, much like a balloon, that stores urine. Urine contains waste and extra fluid left over after the body takes what it needs from what we eat and drink. Each day, adults pass about a quart and a half of urine through the bladder and out of the body.
As people get older, the bladder changes. The elastic bladder tissue may toughen and become less stretchy. A less flexible bladder cannot hold as much urine as before and might make you go to the bathroom more often. The bladder wall and pelvic floor muscles may weaken, making it harder to empty the bladder fully and causing urine to leak.
While you cant control everything that affects your bladder, here are 15 steps you can take to keep it as healthy as possible:
What Are Common Tests To Check The Health Of The Urethra
If your healthcare provider suspects you have a disorder of the urethra, they may order these types of tests:
- Urine tests: These tests examine your urine in a lab.
- Cystoscopy: This test lets your provider look into your urethra and bladder with a cystoscope .
- X-rays and/or ultrasound: These imaging tests allow your provider to see bones and soft tissue. Ultrasound can help your provider see your kidneys and bladder.
- Retrograde urethrography: This test combines an X-ray with a contrast agent.
- Voiding cystourethrogram: This test also uses a contrast agent to show what happens when your bladder fills up and then when you void .
Don’t Miss: Herbal Remedies For Bladder Cancer
Is The Bladder Normal In Size
The bladder should fill and empty during the course of a scan. Always check the bladder at the beginning and end of the exam to make sure that the observation of a too big or too small bladder is persistent.
An absent bladder is most commonly due to failure of urine production in which case, look for bilateral renal anomalies. This can also occur with decreased renal perfusion . Some structural malformations prevent normal bladder development, including cloaca and bladder extrophy.
If the bladder is distended and fails to empty, posterior urethral valves and prune-belly syndrome should be considered. Demonstration of a dilated penile urethra in a male fetus with a large bladder differentiates prune-belly syndrome from PUV, in which the dilated posterior urethra creates the classic keyhole shape to the bladder. Amniotic fluid is usually decreased in these conditions.
In a female fetus, consider a cloacal malformation if there is a persistent fluid-filled structure in the pelvis. This should be a primary consideration if there is a fluid-debris level or a vertical septum. Ovarian cysts may be seen in the third trimester, beside or above the bladder.
Cynthia E. Neville, in, 2020
Location Of The Gallbladder
~ The gallbladder is located beneath the liver. Its location corresponds to the lowest ribs, on the right side of the rib cage.
~ The abdominal cavity in which the gallbladder is located, is termed as the gallbladder fossa, which is nothing but a depression on the undersurface of the liver, between the quadrate and the right lobes.
~ The organs that come in contact with the gallbladder, are the liver, the abdominal wall, the transverse colon, and the duodenum or small intestines.
~ The cystic artery, a branch of the right hepatic artery, supplies oxygenated blood to the gallbladder, while the deoxygenated blood is carried out by the cystic vein. The cystic vein drains the blood into the portal vein.
~ The gallbladder is supplied by nerves of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, which arise from the celiac plexus located in the abdomen. In addition to this, the gallbladder contracts in response to the hormone cholecystokinin secreted by the duodenum.
Read Also: Will A Bladder Infection Go Away On Its Own
Promoting Good Bladder Health
Sometimes, there is no choice but to hold urine, but it may not be good for the bladder. “Holding your urine for a short period of time, usually up to one hour, is typically okay,” Ramin said. “However, protracted and repeated holding of urine may cause over-expansion of bladder capacity, transmission of excess pressure into the kidneys, and the inability to completely empty the bladder. These problems in turn may lead to UTI , cystitis and deterioration of kidney function.”
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can also help prevent bladder stones by preventing the concentration of minerals that cause the stones. The Mayo Clinic suggests asking a medical profession about how much water the body needs according to age, size and activity level.
Editor’s Note: If you’d like more information on this topic, we recommend the following book:
S Of The Urinary System
The major organs of the urinary system are:
- Kidneys – filter the blood, keep the right balance of water in body tissues, and change liquid waste products into urine.
- Ureters – long narrow tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary bladder – a muscular pouch where urine collects and is stored until it is passed out of the body.
- Urethra – narrow tube that passes through the penis and carries urine from the bladder to the outside.
Also Check: How To Remove Bladder Cancer
Your Bladder And Its Neighbors
Learning a little about your anatomy will help you understand where your cancer is located and how it affects your body. The bladder is part of your urinary system which is responsible for collecting and removing liquid waste from the body. The term genitourinary system refers to your urinary and reproductive systems together, and bladder cancer may affect both these systems.
The kidneys are two organs located inside your belly, towards your back, one on either side of the spine. The kidneys remove toxins from the blood and regulate water content by making urine.
The ureters are two long tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder, entering the bladder through openings called uretic orifices.
The bladder is located in the pelvis between your hip bones. In women, its located in front of the uterus, and in men, its in front of the rectum. Urine is stored here until it can be passed out of your body. The bladder is made of three layers of tissue:
- Inner layer is made of cells called transitional cells. These stretch as the bladder fills with urine and shrink as the bladder empties.
- Middle layer is made of muscle tissue which contracts to squeeze urine out of the body.
- Outer layer consists of fat, fibrous tissue and blood vessels which cover the bladder.
Nine out of 10 Americans with bladder cancer have a cancer type that begins in the transitional cells of the bladders inner lining.