Malignant Neoplasm Of Urethra
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- C68.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C68.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C68.0 other international versions of ICD-10 C68.0 may differ.
type 1 excludes
How To Prevent Bladder Cancer
The study on bladder cancer is still going on. Moreover, the doctors do not know its causes so you can try out some of the common preventing ideas by professionals. You should avoid smoking as it can kill immunity and decreases the life of a person. Also, you should drink plenty of water every day so the system of your body works properly.
If you feel the symptoms of even slight pain, you should never take it lightly. Bladder cancer can be deadly for you and it can spread quickly if not taken care of.
Read Also: How To Stop An Overactive Bladder At Night
What Are The Risk Factors For Bladder Cancer
Some factors increase the risk of bladder cancer:
- Cigarette smoking is the biggest risk factor it more than doubles the risk. Pipe and cigar smoking and exposure to second-hand smoking may also increase ones risk.
- Prior radiation exposure is the next most common risk factor .
- Certain chemotherapy drugs also increase the risk of bladder cancer.
- Environmental exposures increase the risk of bladder cancer. People who work with chemicals, such as aromatic amines are at risk. Extensive exposure to rubber, leather, some textiles, paint, and hairdressing supplies, typically related to occupational exposure, also appears to increase the risk.
- Infection with a parasite known as Schistosoma haematobium, which is more common in developing countries and the Middle East.
- People who have frequent infections of the bladder, bladder stones, or other diseases of the urinary tract, or who have chronic need for a catheter in the bladder, may be at higher risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Patients with a previous bladder cancer are at increased risk to form new or recurrent bladder tumors.
Other risk factors include diets high in fried meats and animal fats, and older age. In addition, men have a three-fold higher risk than women.
Recommended Reading: What Is Urinary Bladder Cancer
Treating Stage 0 Bladder Cancer
Stage 0 bladder cancer includes non-invasive papillary carcinoma and flat non-invasive carcinoma . In either case, the cancer is only in the inner lining layer of the bladder. It has not invaded the bladder wall.
This early stage of bladder cancer is most often treated with transurethral resection with fulguration followed by intravesical therapy within 24 hours.
Recommended Reading: Florida Bladder Institute Patient Portal
Malignant Neoplasm Of Overlapping Sites Of Bladder
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- C67.8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C67.8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C67.8 â other international versions of ICD-10 C67.8 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
You May Like: Antibiotics Given For Bladder Infection
Recommended Reading: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation For Overactive Bladder
Specific Coding For Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder
Non-specific codes like C67 require more digits to indicate the appropriate level of specificity. Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for malignant neoplasm of bladder:
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.0 for Malignant neoplasm of trigone of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.1 for Malignant neoplasm of dome of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.2 for Malignant neoplasm of lateral wall of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.3 for Malignant neoplasm of anterior wall of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.4 for Malignant neoplasm of posterior wall of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.5 for Malignant neoplasm of bladder neck
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.6 for Malignant neoplasm of ureteric orifice
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.7 for Malignant neoplasm of urachus
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.8 for Malignant neoplasm of overlapping sites of bladder
- BILLABLE CODE Use C67.9 for Malignant neoplasm of bladder, unspecified
Drg Mapping Rules For C679
Diagnostic codes are the first step in the DRG mapping process.
The patients primary diagnostic code is the most important. Assuming the patients primary diagnostic code is C67.9, look in the list below to see which MDCs Assignment of Diagnosis Codes is first. That is the MDC that the patient will be grouped into.
From there, check the subsections of the MDC listed. The patient will be mapped into the first subsection for which the treatment performed on the patient meet the listed requirements of that subsection.
DRG grouping rules are adjusted each year, so make sure to check the rules for the fiscal year of the patients discharge date.
Don’t Miss: Can You Treat A Bladder Infection Without Antibiotics
Can I Prevent Malignant Neoplasm
Theres no way to prevent malignant neoplasms altogether, but there are certain things you can do to reduce your risk:
- Protect your skin when you go outside.
- Limit the amount of alcohol you drink.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating well and exercising often.
- Attend all routine cancer screenings, such as colonoscopies and mammograms.
How Is Malignant Neoplasm Treated
Treatment depends on the type and size of the tumor and whether it has spread to other areas of your body. If the malignant neoplasm is localized to one area, surgery may be an option. If the cancer has spread, then your healthcare provider may recommend chemotherapy, radiation therapy or targeted drug therapy.
Surgery
If the tumor is small and still contained to one area, surgical removal may be possible. Your surgeon will remove the entire mass, as well as some healthy tissue around it. Surgery usually isnt an option if the cancer has spread to other areas of your body.
Chemotherapy
Cancer-killing drugs are given, either in pill form or through an IV line in your arm or hand. Chemotherapy destroys cancer cells and keeps them from multiplying. Its used to treat both primary cancer and metastatic cancer . Chemotherapy may be used alone or in conjunction with other treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses strong beams of energy to destroy cancer cells. During this procedure, high-energy radiation is directed at the tumor and the machine can be repositioned to aim at different levels. Sometimes, radiation therapy is used before surgery to shrink a tumor. It can also be used after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells.
Targeted drug therapy
What are the complications of treatment for malignant neoplasm?
- Loss of appetite.
Also Check: What Do They Give You For Bladder Infection
Genetic Factors In Pathogenesis
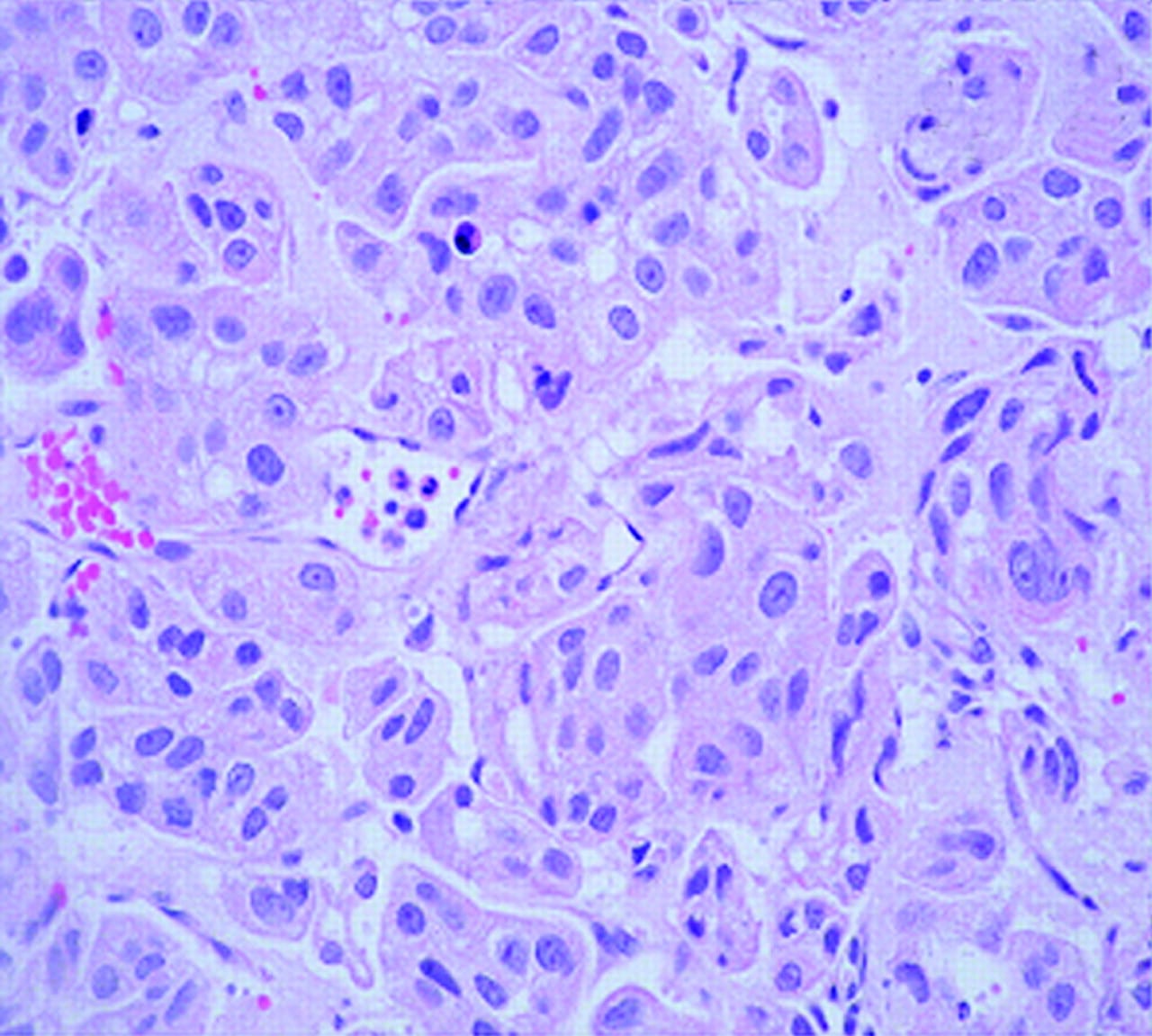
Divergent, yet interconnected and overlapping, molecular pathways are likely responsible for the development of noninvasive and invasive bladder tumors. Somatic mutations in fibroblast growth receptor3 and tumor protein p53 in tumor cells appear to be important early molecular events in the noninvasive and invasive pathways, respectively.
FGFR-3, Ras, and PIK3CA mutations occur with high frequency in noninvasive tumors, leading to upregulation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase . Loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 9 is among the most frequent genetic alterations in bladder tumors and is considered an early event.
Large numbers of genomic changes have been detected using karyotyping and comparative genomic hybridization analysis in urothelial carcinoma. Numerically common are losses of 2q, 5q, 8p, 9p, 10q, 18q, and Y. Gains of 1q, 5p, 8q, and 17q are frequently present, and high-level amplifications can be found however, the target genes in the regions of amplifications have not been conclusively identified.
Alterations in the TP53 gene are noted in approximately 60% of invasive bladder cancers. Progression-free survival is significantly shorter in patients with TP53 mutations and is an independent predictor of death among patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer.
Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder Unspecified
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- C67.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C67.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C67.9 – other international versions of ICD-10 C67.9 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
Don’t Miss: Causes Of Overactive Bladder In Males
Therapy: Treatment Options For Cancer Vary
Treatment options depend on the stage of the cancer and may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation.
Surgery may involve removing a small tumor or polyp only, or removing a tumor and a portion of the surrounding tissue, if the tumor is larger or has spread into nearby tissue. The surgeon may also remove some lymph nodes near the area of cancer if its known the cancer has spread to them, or to see if the cancer has spread to them.
Chemotherapy drug therapy may be used before surgery to shrink the size of tumors, or after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells that may have spread to other parts of the body.
Radiation therapy may similarly be given to shrink tumors before surgery or to kill any remaining cancer cells after surgery. It may also be used in place of surgery in some cases.
About The Bladder Renal Pelvis And Ureter
The bladder is a hollow organ in the pelvis that stores urine before it leaves the body during urination. This function makes the bladder an important part of the urinary tract. The urinary tract is also made up of the kidneys, ureters, and urethra. The renal pelvis is a funnel-like part of the kidney that collects urine and sends it into the ureter. The ureter is a tube that runs from each kidney into the bladder. The urethra is the tube that carries urine out of the body. The prostate gland is also part of the urinary tract.
The bladder, like other parts of the urinary tract, is lined with a layer of cells called the urothelium. This layer of cells is separated from the bladder wall muscles, called the muscularis propria, by a thin, fibrous band called the lamina propria.
Don’t Miss: Why Does My Bladder Leak So Much
Malignant Neoplasm Of Unspecified Lacrimal Gland And Duct
ICD-10 code C69.50 for Malignant neoplasm of unspecified lacrimal gland and duct
ICD-10
ICD-10 International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision
ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems , a medical classification list by the World Health Organization .
It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
ATC
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System is used for the classification of active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties.
It is controlled by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology .
DDD
The defined daily dose is a statistical measure of drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization .
It is used to standardize the comparison of drug usage between different drugs or between different health care environments.
How Are Multiple Neoplasms Coded In Icd 10
For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified .
Donât Miss: Hills Prescription Diet Urinary Care C D
Don’t Miss: Why Is My Bladder Burning
How A Lung Neoplasm Is Diagnosed
If you have ongoing respiratory symptoms that suggest a lung neoplasm, your healthcare provider may start by taking a detailed medical history.
Your healthcare provider will perform a focused physical exam, listening to the heart and lungs for sounds like wheezing and crackling that may be concerning for associated lung-related diseases, like COPD and emphysema, which increase ones chances of malignancy.
Imaging is usually ordered next. The following tests are initially performed to help provide more details on the lung neoplasm:
- Chest X-ray: This test is usually the quickest and least expensive imaging test, so it is used first. It is a painless scan that can show tumors 1 centimeter wide or larger.
- CT scan: CT scans use low-radiation X-ray beams to take many pictures of the inside of your body. They can help detect smaller lung cancers and provide more details than an X-ray.
- Lung function test : Also known as spirometry, this test measures how much air the lungs can hold and how quickly the lungs can be filled with air and then emptied.
- Blood tests. A sample of your blood may be tested to check the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets , and to see how well your kidneys and liver are working. Because lung cancer can throw off these numbers, comparing your baseline numbers to your current numbers can help provide details on potential changes that have occurred as a result of your lung cancer.
Types Of Lung Neoplasms
Benign lung neoplasms are noncancerous and are usually classified by the tissues from which they arise. Benign lung neoplasms include:
- Hamartomas: Hamartomas are the most common type of benign lung nodule, accounting for about 55% of all benign lung tumors. They are unique in that these tumors consist of a variety of cell types, including muscle, fat, and cartilage. They are most often found on the periphery of the lung, along the outer edges. These coin-shaped tumors are usually small in size, oftentimes measuring 4 centimeters or less in diameter, and are commonly found accidentally on an X-ray.
- Bronchial adenomas: These neoplasms arise from the mucus glands or ducts of your windpipe or the large airways of the lungs. They are slow growing and rarely become malignant. Some types of bronchial adenomas are more common than others. For example, carcinoids account for 85% of bronchial adenomas .
- Papillomas: Arising from salivary glands, these are the least common type of benign lung neoplasm. They usually grow in the bronchial tubes. The two most common types of papillomas are squamous and glandular. Squamous papillomas are the result of the human papilloma virus . The cause of glandular papillomas remains a mystery.
Malignant lung neoplasms are cancerous and include three main types:
Other lung tumors that may affect the lungs include lymphomas, adenoid cystic carcinomas, and sarcomas. These types of cancer are treated differently than the more common lung cancers.
Also Check: How To Treat Overactive Bladder Naturally
Secondary Malignant Neoplasm Of Bladder
ICD-10 code C79.11 for Secondary malignant neoplasm of bladder
ICD-10
ICD-10 International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems 10th Revision
ICD-10
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems , a medical classification list by the World Health Organization .
It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
ATC
The Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System is used for the classification of active ingredients of drugs according to the organ or system on which they act and their therapeutic, pharmacological and chemical properties.
It is controlled by the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology .
DDD
The defined daily dose is a statistical measure of drug consumption, defined by the World Health Organization .
It is used to standardize the comparison of drug usage between different drugs or between different health care environments.
Papillary Vs Flat Cancer
Bladder cancers are also divided into 2 subtypes, papillary and flat, based on how they grow .
- Papillary carcinomas grow in slender, finger-like projections from the inner surface of the bladder toward the hollow center. Papillary tumors often grow toward the center of the bladder without growing into the deeper bladder layers. These tumors are called non-invasive papillary cancers. Very low-grade , non-invasive papillary cancer is sometimes called papillary urothelial neoplasm of low-malignant potential and tends to have a very good outcome.
- Flat carcinomas do not grow toward the hollow part of the bladder at all. If a flat tumor is only in the inner layer of bladder cells, itâs known as a non-invasive flat carcinoma or a flat carcinoma in situ .
If either a papillary or flat tumor grows into deeper layers of the bladder, itâs called an invasive urothelial carcinoma.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell If You Have Bladder Problems
Don’t Miss: Can Yeast Infection Cause Overactive Bladder
License For Use Of Current Dental Terminology
End User License Agreement:These materials contain Current Dental Terminology , copyright © 2021 American Dental Association . All rights reserved. CDT is a trademark of the ADA.
The license granted herein is expressly conditioned upon your acceptance of all terms and conditions contained in this agreement. By clicking below on the button labeled I accept, you hereby acknowledge that you have read, understood and agreed to all terms and conditions set forth in this agreement.
If you do not agree with all terms and conditions set forth herein, click below on the button labeled I do not acceptand exit from this computer screen.
If you are acting on behalf of an organization, you represent that you are authorized to act on behalf of such organization and that your acceptance of the terms of this agreement creates a legally enforceable obligation of the organization. As used herein, you and your refer to you and any organization on behalf of which you are acting.
Treatment Of Stage I Bladder Cancer

For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of stage I bladder cancer may include the following:
- Transurethral resection with fulguration. This may be followed by one of the following:
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Also Check: How Do You Fix Overactive Bladder