Common Causes Of Excess Weight And Tips To Address
2. Hormonal imbalances – Menopause, endometriosis, or possibly elevated cortisol due to an acute or chronic stress, can cause weight gain.
3. Emotional eating – Identify if binge eating is occurring by discussion if possible . Refer client to their GP for a referral to a dietician or psychologist if client is agreeable.
4. Poor food choices – High fat & sugar diet, poor intake of fibre, fruits vegetables are identified during discussion, refer client to their GP for a referral to a dietician.
5. Reduced mobility or exercise – refer client to their GP for a referral to an exercise physiologist, physiotherapist, or a local rehabilitation program or starting with a walking program.
6. Psychological issues – There are many types of psychological factors that could impact a clients thinking and behaviour. Ascertain if your client would be open to a discussion with their GP about a referral to a psychologist or a psychiatrist.
7. Life circumstances and stages in life – These can dramatically affect ones weight. For example, irregular hours, night duty shifts, cost or time pressures. Many may be working full time and parenting or caring for elderly parents, affecting time and energy to eat well, exercise or find motivation.
Offering support, empathy, and non- judgement advice, may go a long way to helping someone start on a weight loss journey to improve their incontinence. Read more on how to discuss incontinence.
Association Between Obesity And Types Of Incontinence
There was also a difference in the kind of incontinence reported by patients:
- Stress incontinence: It is basically experiencing urinary leaks when you make intra abdominal pressure to laugh, cough, or lift weight. Most patients with overweight and obesity are affected by this type of incontinence, as noted in scientific studies.
- Urge incontinence: It is not related to abdominal pressure, and patients report sudden and unexpected urge to urinate, not associated with any coughing, laughing, or lifting weight. Patients with obesity are not particularly affected by this type of incontinence.
- Mixed incontinence: It is a type of incontinence that includes both stress and urge incontinence symptoms. Overweight and obese patients also suffer from this type.
By only looking at the trend, we can see that something is going on here. Obesity increases the risk of stress-predominant incontinence and not urge incontinence. Stress incontinence is triggered by abdominal pressure, where fat deposits are usually located. When obesity is extreme, the risk of urinary incontinence is very high.
In morbidly obese women who were about to undergo bariatric surgery , this symptom affected 60-70% of them. It was a prevalence of 28% stress incontinence, 4% urge incontinence, and 32% mixed incontinence. The association is clear, not only between obesity and incontinence but also regarding the type .
How Obesity & Urinary Incontinence Are Related
The prevalence of obesity is rising quickly Itâs estimated that
This means that the number of people experiencing urinary incontinence will likely be on the rise around the same time since it has been proven that obesity is a risk factor for urinary incontinence.
When you are obese, the extra fat on your bodyâ specifically in your midsectionâ places extra pressure on your bladder, urethra, and pelvic floor muscles. This is referred to as intra-abdominal pressure and can result in:
Whether you experience them alone or together, these results usually lead to stress urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, urge incontinence, or mixed incontinence. This is because:
1. Bladder contractions are part of what makes you feel the urge to urinate. When your bladder is contracting more than expected due to extra pressure, you may feel the need to void more frequently.
2. A mobile urethra helps you have urinary continence by opening and closing your urethral sphincter when peeing or holding your pee. When pressure is placed on your pelvic floor muscles, it damages the urethra, making it less able to do its job correctly, leading to unintentional urine leakage.
You May Like: How To Deal With A Bladder Infection At Home
Impact Of Obesity On Long
Urinary incontinence is not very common in men. It is more prevalent in women. But one of the triggers of incontinence in men is radical prostatectomy. This procedure is usually done to take out prostate cancer. It is also helpful if you have benign prostate hyperplasia and very severe urinary symptoms. However, some patients end up with urinary incontinence shortly after surgery.
The prostate is located in the bladder neck. Thus, by removing the prostate, your surgeon will also stretch the bladder. If you have additional risk factors for urinary incontinence, it could be triggered. One of these risk factors is being obese.
Obese patients are at a higher risk to suffer from urinary incontinence after prostate surgery. They also have a higher incidence and severity of lower urinary tract symptoms . Urinary incontinence is usually a temporary problem after surgery, but obese men take more time to recover. They sometimes have long-term urinary incontinence and may not fully recover at all. According to a recent meta-analysis, this association was made evident in 1 and 2 years after prostate surgery. BMI changes did not alter Early-onset urinary incontinence. In other words, men will have a similar risk of urinary incontinence, but when they are obese, this problem will be maintained for a very long time.
A Great Lack Of Information In The Medical Literature On The Association Between Bladder Problems And Metabolic Syndrome
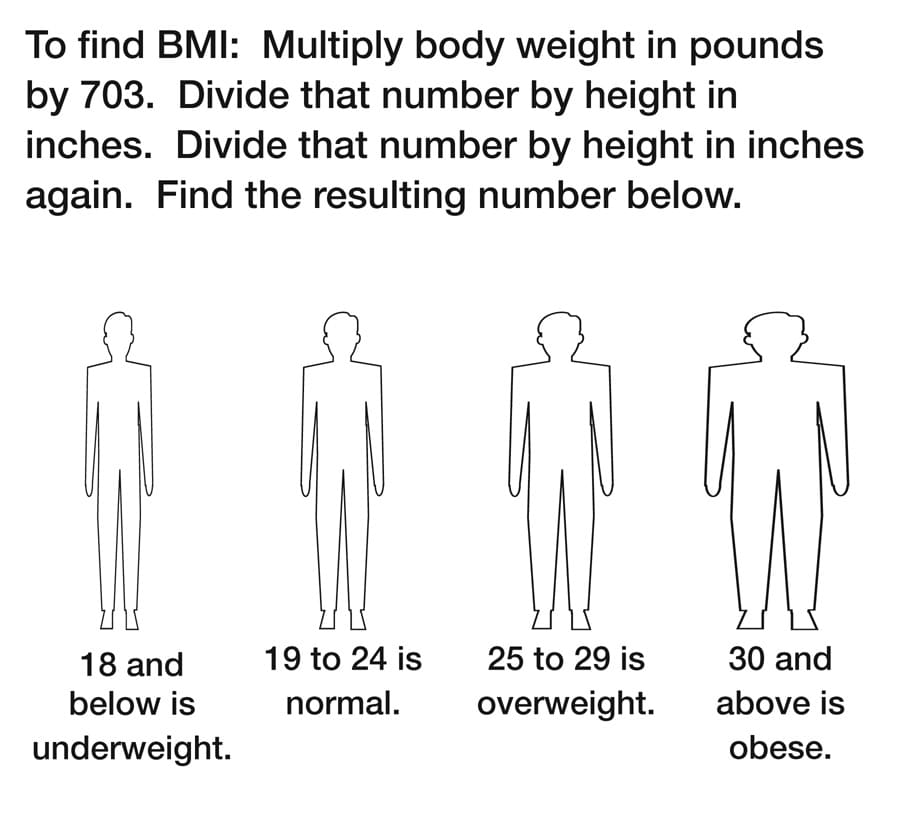
A recent study from the United Kingdom published in the International journal of clinical practice discusses the relationship between the problems of overactive bladder and the constellation of challenges associated with a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome.
Women not getting good information from doctors on overactive bladder
Here the researchers of this study noted that there is a great lack of information in the medical literature on the impact of metabolic syndrome on problems of overactive bladder especially in women. The research information that is available to doctors to help these women is usually of low quality, however, a doctor looking deep into the research can find evidence that obesity and other components of metabolic syndrome causes and can predict urinary problems.
Don’t Miss: Bladder Infection Keeps Coming Back
How Much Weight Do I Need To Lose To Have An Impact
Make an Appointment Catrina Crisp MD, MSc, FACOG513 463 4300
It doesnt have to be a drastic weight loss, but weight loss of around eight percent of a patients body weight, which is, on average, for a women, around 15 to 20 pounds, will reduce their weekly leakage whether its overactive bladder or stress incontinence by about 47 percent, Catrina Crisp MD MSc FACOG, of Cincinnati Urogynecology Associates, explains.
The less weight you lose, however, the less impact it will have on your incontinence, but regardless, studies show that weight loss does reduce urinary leakage. A 2009 study in the New England Journal of Medicine found that women who lost just two percent of their body weight had about a 28 percent reduction in their incontinence episodes.
Women Over 60 Who Are Not Active Have More Urgent Urinary Incontinence
A study from February 2020 points out the obvious, urinary incontinence is associated with age related problems of physical and cognitive impairments. But, urinary incontinence is made worse by sedentary behavior. What the study discovered was the longer the length of sedentary behavior the greater the urgent urinary incontinence. The simple solution? The best targeted intervention to treat this was to get the women more active.
You May Like: Hill’s Science Diet Bladder Stones
What You Can Do
Being overweight is only one risk factor for urinary incontinence. The condition can be caused by a number of medical issues, including:
- Urinary tract and bladder infections
- Pregnancy and childbirth
Your symptoms may be caused by a number of different reasons. It is important that you discuss your symptoms with your healthcare provider rather than attributing your symptoms solely to being overweight so any underlying problems are identified and/or eliminated.
Your healthcare provider may suggest you keep a bladder diary over the course of several days so you can track your symptoms. Some typical questions you may be asked to answer include:
- What happened immediately before the episode occurred? For example, did you cough or sneeze?
- Did you drink any beverages prior to the episode?
- Were you sedentary or active prior to the episode? If active, what exactly were you doing?
If there are no other underlying causes, losing weight may decrease your UI episodes. Overall health benefits can begin being seen in patients who lose just 5% of their current body weight, so you may see improvement by just losing a small amount of weight. Controlling your weight in the long-term may even completely eliminate your UI symptoms. The more weight you lose from your midsection, the less pressure is on your bladder.
Does Being Fat Affect Your Bladder
Being overweight or obese can affect the bladder in a number of ways. Being overweight and obese are risk factors for urinary incontinence, especially stress incontinence. Being overweight may also increase your risk of developing other types of urinary problems. For example, people who are overweight or obese have a higher incidence of kidney stones than people who are not overweight or obese. Kidney stones occur when salts and minerals build up in the kidneys and form crystals that block the outflow of urine from your kidneys into your bladder.
You May Like: My Dog Is Losing Control Of Her Bladder
Changes In The Insulin/igf
Insulin is one of the problems of overeating, eating sweets, and processed foods. When insulin levels increase after eating, they accelerate tumor growth. Many tumors have an insulin receptor that becomes activated every time we overeat or eat sweets. As such, insulin peaks become fuel for cancer. This phenomenon is evident in all types of cancer, including that of the prostate gland. Insulin level increase is associated with higher mortality for prostate cancer. In contrast, when type 2 diabetes patients use metformin, a drug that reduces their insulin levels, their risk of prostate cancer reduces dramatically. Similarly, when insulin levels decline in advanced diabetes, the risk of prostate cancer reduces as well. Another bioactive molecule is IGF-1 . This substance is similar to insulin and also stimulates growth in tissues. When elevated, IGF-1 stimulates tumors and promotes cancer in the prostate. Obese patients usually have an increase of IGF-1, and their risk of prostate cancer aggressiveness is higher. What IGF-1 does is taking prostate cancer cells and making them independent of androgens. They no longer need androgens to divide and keep on growing. Thus, they are more aggressive and turn into castrate-resistant prostate cancer.
What Is Overactive Bladder
Overactive bladder refers to a collection of urinary symptoms. The most prevalent symptom is an abrupt, uncontrolled desire or need to urinate. Some individuals will leak urine when they get this need. Another common symptom is the urge to urinate as many times as possible throughout the day and night. An individual with OAB may feel okay one instant and might immediately feel the need to pass urine the next.
Also Check: Bcg For Bladder Cancer Side Effects
Risk Factors For Oab And Ui
While the two conditions are different, the risk factors that may lead to both are very similar. The strongest risk factor for developing OAB or UI is being female. These problems affect women two times more than men, and roughly 17 percent of women between the ages of 40 to 59 experience some type of urological issue. Another risk factor is age. Especially for women, pelvic floor muscles weaken with age, which is a significant contributor to UI. Other age-related reasons include lack of mobility, infection, dementia or psychological disorders, and atrophy. Pregnancy is another top risk factor for developing OAB or UI, as is any previous gynecological or urological surgery. Obesity is also listed as a risk factor, and researchers are now claiming it is a leading contributor to developing OAB or UI.
How Extra Weight And Diet Can Affect Bladder Control
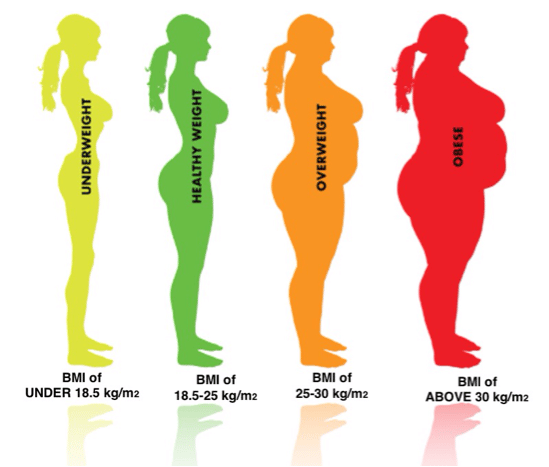
While scientists and researchers are still working out exactly to what extent being overweight and obese negatively affects health , the general consensus among medical professionals is that being overweight or obese contributes to a range of health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, prediabetes, and joint problems such as arthritis.5,6
Being overweight or obese can also reduce the quality of life in a number of waysby limiting a persons mobility, making things like air travel difficult and diminishing self-esteem.7
Carrying extra weight can also put pressure on the bladder causing urinary incontinence or make it worse8,9, which is a condition that one in three women will suffer with at some point in her life.
Diet can also affect bladder control. Well explore in more detail how weight and nutrition can contribute to urinary incontinence, and well look at ways to improve symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Nivolumab Fda Approval Bladder Cancer
The Dish On Nutrish: How Diet Can Affect Bladder Control
Many women who experience bladder leakage reduce their fluid intake to avoid experiencing leaks, but this can actually worsen the problem by creating highly concentrated urine that makes you need to go more often. Not drinking enough fluids can also create excess bacteria growth, which can lead to bladder infections.
The following beverages and foods are known bladder irritantseliminating them from your diet or at least cutting back may help improve your bladder control and function:
Bottom Line: It’s All About Patient Preference
While Dr. Crisp does encourage weight loss for her overweight patients struggling with incontinence, she emphasizes that when she creates a treatment plan, it’s all about patient preference. “We go through all of their options, including pelvic floor, physical therapy and outpatient surgery and medication, and if the patient chooses to move toward physical therapy, weight loss and behavioral training, we go through their program with them to try to not only improve muscle strength, but also improve weight loss,” Dr. Crisp explains.
This also involves having the patient cut out items in their diet that are bad for the bladder, like coffee and soda, and acidic foods, like citrus or fruit juices.
Don’t Miss: Ways To Control Your Bladder
Obesity And Skin Issues
1. Dry Skin skin can become incredibly dry due to poor circulation, poor hygiene, or lack of moisturizing.
2. Excessive Moisture this can be an issue due to sweating.
3. Weight and Pressure due to their weight they may develop pressure ulcers between skinfolds or on extremities, or pressure from tight spaces on skin a lack of movement, or from acid from urine and faeces due to incontinence.
4. Cellulitis a bacterial skin infection can occur due to poor hygiene.
5. Other related Health Issues can cause skin problems:
- diabetes if poorly controlled can cause skin breakdowns or diabetic foot ulcers
- less blood flow in areas with heavy deposits of fat
- venous insufficiency/poor circulation to limbs
- a lack of mobility can put skin at risk
- the PH of their skin is usually higher9
TENA is the first continence products to be endorsed by the Skin Health Alliance.
You May Like: Whatâs The Signs Of A Urinary Tract Infection
Male Urinary Incontinence Home Remedies
There are a number of home remedies and lifestyle adaptations that are known to assist with UI, as well as help to prevent it. They can either be tried on their own, such as for mild cases of UI, or combined with other medical treatments. However, a consultation with a urologist is recommended to evaluate each individual case. With expert medical assistance, these home remedies can be adopted in addition to receiving any other necessary treatments.
Also Check: Can Stress Cause Bladder Leakage
Can Obesity Cause Urinary Incontinence
Obesity is turning from a health condition into a public health crisis worldwide.
The prevalence is higher in industrialized and developed nations. In the United States, statistics show that more than 30% of people older than 20 years are obese. But beyond the aesthetics, the main problem of obesity has to do with its comorbidities.
Comorbidities are health problems that usually coexist. For example, high-fat levels in the blood have fat plaque formation as comorbidity.
Obesity has a very long list of comorbidities in almost every body system. In the cardiovascular system, it predisposes to heart attacks and high blood pressure. In the metabolic system, it coexists with type 2 diabetes.
Moreover, in the gastrointestinal tract, being obese increases the risk of acid reflux. In the genitourinary system, many morbidly obese patients also have incontinence.
Urinary incontinence is then counted among the comorbidities of obesity. It is the uncontrollable and unavoidable sensation of voiding. These patients can have either small urine leakages or a large volume depending on the case. This is not only a physical problem. It also bears consequences in the patients psychological, social, and working environment.
In this article, we will explore the link between obesity and incontinence. Besides, you will learn how obesity affects other aspects of the genitourinary system and how weight loss can help treat or at least prevent urinary incontinence.